

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (2): 300-309.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.02.005
收稿日期:2023-06-15
出版日期:2024-02-20
发布日期:2024-03-19
通信作者:
林丽(1977-),女,吉林长春人,教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为水利信息化、水资源规划与利用,(E-mail)klmhll@126.com作者简介:惠瑞晗(1998-),女,河南郑州人,硕士,研究方向为智慧农业,(E-mail)hrhdyx1998@163.com
基金资助:
HUI Ruihan( ), LIN Li(
), LIN Li( ), CAO Wei, ZHANG Mengke, LIN Hao, YAO Shuai
), CAO Wei, ZHANG Mengke, LIN Hao, YAO Shuai
Received:2023-06-15
Published:2024-02-20
Online:2024-03-19
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究并分析基于P-M模型棉田智能灌溉系统的试验设计。【方法】基于P-M模型设计一套棉田智能灌溉系统,由数据采集节点、无线通信节点、云平台决策终端、灌溉应用节点四部分组成。数据采集节点的气象设备采集到数据后无线传输至云平台决策终端,终端基于P-M模型计算单次灌溉量,在指定的灌溉时间自动发出灌溉指令,灌溉应用节点接收指令开启阀门精确灌溉,土壤墒情变化由数据采集节点的墒情设备实时监测后无线传输到云平台展现;以当地传统灌溉模式作为对照(CK),灌溉系统设置120%(W1)、100%(W2)和80%(W3)3种灌溉模式,进行田间试验。【结果】3个试验组灌溉工作在无人为干预的条件下实现全智能化,系统有效精准执行灌溉指令;在灌溉水充足的情况下可选用W2模式,总耗水量较传统模式增加16.85%的情况下土壤含盐量下降13.65%,籽棉产量提高20.84%,水分利用效率提高3.41%,能够大幅度提高产量的同时有效改善土壤环境;W3总耗水量较传统灌溉减少6.52%,土壤含盐量上升0.16%,盐渍化速度较传统灌溉模式变缓,籽棉产量提高11.18%,水分利用效率大幅提高,可达到兼顾提高产量与节水的效果。【结论】验证了智能灌溉系统的有效性和可行性,增加了灌溉系统的可选参数范围。
中图分类号:
惠瑞晗, 林丽, 曹伟, 张梦珂, 林豪, 姚帅. 基于P-M模型的棉田智能灌溉系统的设计与试验[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 300-309.
HUI Ruihan, LIN Li, CAO Wei, ZHANG Mengke, LIN Hao, YAO Shuai. Design and experiment of intelligent irrigation system for cotton field based on P-M model[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 300-309.
| 分部 Division | 设备构成 Equipment of composition | 型号规格 Specifications | 性能 Performance | 数量 Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无线通信 Wireless communication | 4G DUT模块 | USR-DR154 | RS485/RS232/TTL转4G Cat1 | 1 |
| DUT模组 | wH-LTE-7S1 | 串口转4G Cat1全网通、移动联通2G | 6 | |
| 数据采集 Data collection | 净辐射仪 | NR-LITE 2 | 量程±2 000 W/m2,灵敏度10 μV/(W/m2) | 1 |
| 聚碳风速变送器 | RS-FSJT-* | 量程0~70 m/s,精度±(0.2+0.03风速)m/s | 1 | |
| 多要素百叶盒 | RS-BYH-M | 湿度量程0~99%RH,温度量程-40~+120℃, 大气压力量程0~120 kPa | 1 | |
| 气象站太阳能板 | DZRC-M-35W-G18 | 最大:功率35 W,电流1.94 A,电压18 V | 1 | |
| 铅蓄电池 | 6-FMD-12.0 | 电压12 V,电流12.0 Ah | 1 | |
| 墒情终端太阳能板 | 290mm×350mm | 最大:功率12 W,电流2 A,电压6 V | 3 | |
| 土壤墒情传感器 | RS-ECTH-N01-TR | 电导率:量程0~20000 μs/cm,分辨率10 μs/cm, 精度±5%;土壤水分:量程0%~100%,分辨率0.1%, 精度±3%;温度:量程-40~80℃,分辨率0.1℃, 精度±0.5℃(25℃) | 9 | |
| 灌溉应用 Irrigation application | 潜水泵 | QY 25-32-4 | 功率:4 kW,扬程:32 m,流量:25 m3/h | 1 |
| PE输水主管软带 | PE材料,内径90 mm | — | 150 m | |
| 滴灌毛管 | PE材料,内径16 mm | — | 若干 | |
| 过滤器 | Y型叠片式过滤器 | 灌溉系统杂质过滤120目 | 3 | |
| 施肥罐 | 压差式 | 容量25 L | 3 | |
| 电磁阀 | 大流量直流脉冲电磁阀 | 90外丝,直流脉冲24 V,ARTHAS电磁头 | 3 | |
| 智能水表 | DN80 | 常用流量63 m3/h,最小流量3.15 m3/h, 读数范围0.01~999 999 m3 | 3 |
表1 智能灌溉系统硬件参数
Tab.1 Hardware parameters of intelligent irrigation system
| 分部 Division | 设备构成 Equipment of composition | 型号规格 Specifications | 性能 Performance | 数量 Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无线通信 Wireless communication | 4G DUT模块 | USR-DR154 | RS485/RS232/TTL转4G Cat1 | 1 |
| DUT模组 | wH-LTE-7S1 | 串口转4G Cat1全网通、移动联通2G | 6 | |
| 数据采集 Data collection | 净辐射仪 | NR-LITE 2 | 量程±2 000 W/m2,灵敏度10 μV/(W/m2) | 1 |
| 聚碳风速变送器 | RS-FSJT-* | 量程0~70 m/s,精度±(0.2+0.03风速)m/s | 1 | |
| 多要素百叶盒 | RS-BYH-M | 湿度量程0~99%RH,温度量程-40~+120℃, 大气压力量程0~120 kPa | 1 | |
| 气象站太阳能板 | DZRC-M-35W-G18 | 最大:功率35 W,电流1.94 A,电压18 V | 1 | |
| 铅蓄电池 | 6-FMD-12.0 | 电压12 V,电流12.0 Ah | 1 | |
| 墒情终端太阳能板 | 290mm×350mm | 最大:功率12 W,电流2 A,电压6 V | 3 | |
| 土壤墒情传感器 | RS-ECTH-N01-TR | 电导率:量程0~20000 μs/cm,分辨率10 μs/cm, 精度±5%;土壤水分:量程0%~100%,分辨率0.1%, 精度±3%;温度:量程-40~80℃,分辨率0.1℃, 精度±0.5℃(25℃) | 9 | |
| 灌溉应用 Irrigation application | 潜水泵 | QY 25-32-4 | 功率:4 kW,扬程:32 m,流量:25 m3/h | 1 |
| PE输水主管软带 | PE材料,内径90 mm | — | 150 m | |
| 滴灌毛管 | PE材料,内径16 mm | — | 若干 | |
| 过滤器 | Y型叠片式过滤器 | 灌溉系统杂质过滤120目 | 3 | |
| 施肥罐 | 压差式 | 容量25 L | 3 | |
| 电磁阀 | 大流量直流脉冲电磁阀 | 90外丝,直流脉冲24 V,ARTHAS电磁头 | 3 | |
| 智能水表 | DN80 | 常用流量63 m3/h,最小流量3.15 m3/h, 读数范围0.01~999 999 m3 | 3 |
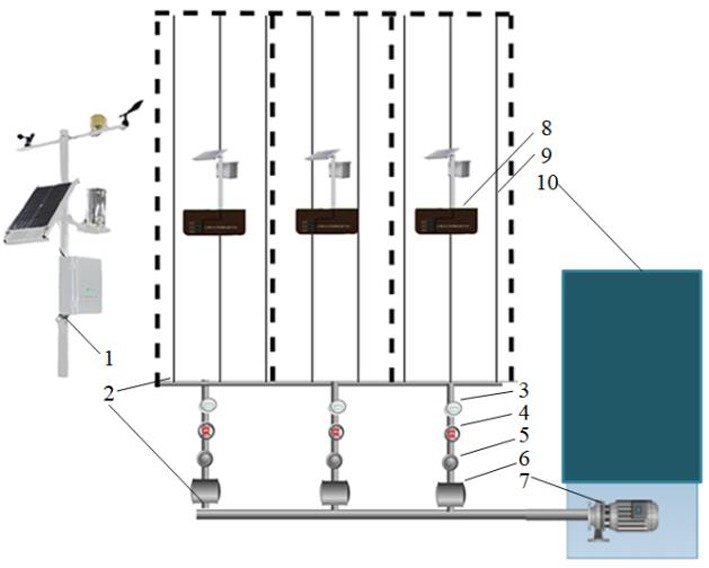
图1 灌溉系统组件布置 注:1.气象站;2.主管;3.水表;4.电磁阀;5.过滤器;6.施肥罐;7.潜水泵;8.墒情传感器终端;9.滴灌毛管;10.沉砂池
Fig.1 Irrigation system component layout Note:1.Weather stations; 2.Main Pipe; 3.Water meter;4.Solenoid valve; 5.The filter; 6.Fertilization can;7.Submersible pump; 8.Moisture sensor terminal; 9.Drip capillary; 10.Sand sink
| 深度 Depth (cm) | 容重 Bulk density (g/cm3) | 质量含水率 Mass moisture content (%) | 田间持水率 Field water holding rate (%) | 含盐量 Salt content (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 1.43 | 19.30 | 28.04 | 0.23 |
| 40 | 1.45 | 31.77 | 32.27 | 0.34 |
| 60 | 1.45 | 39.88 | 30.34 | 0.37 |
表2 试验区土壤基础性质
Tab.2 Soil foundation properties in the experimental area
| 深度 Depth (cm) | 容重 Bulk density (g/cm3) | 质量含水率 Mass moisture content (%) | 田间持水率 Field water holding rate (%) | 含盐量 Salt content (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 1.43 | 19.30 | 28.04 | 0.23 |
| 40 | 1.45 | 31.77 | 32.27 | 0.34 |
| 60 | 1.45 | 39.88 | 30.34 | 0.37 |
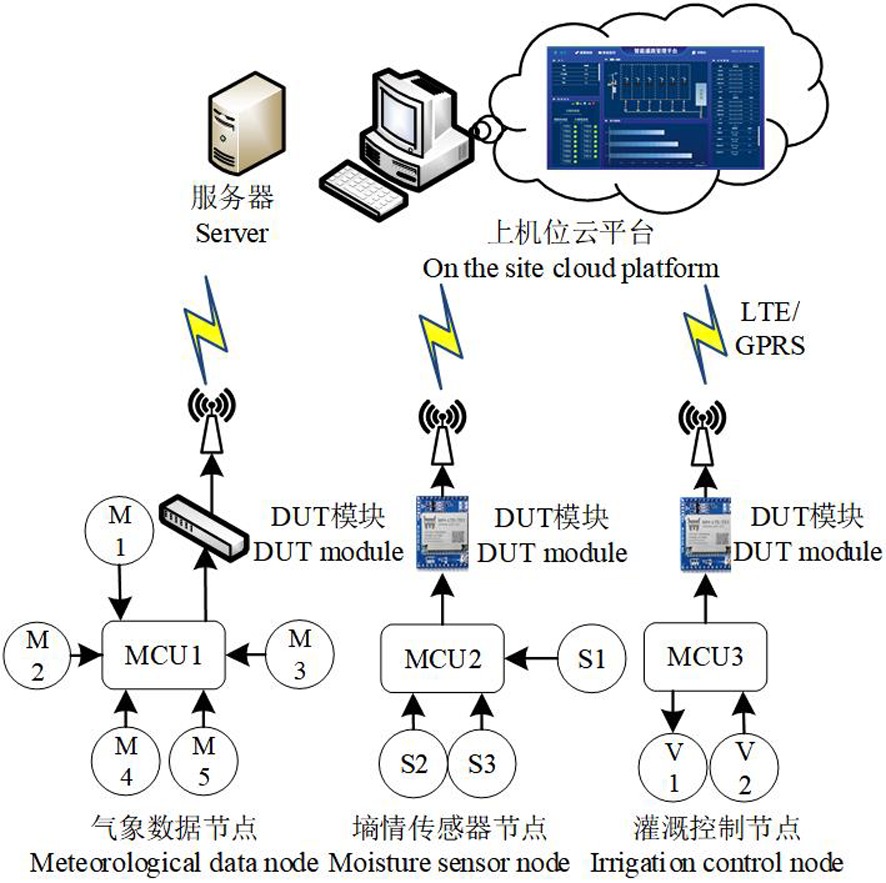
图2 智能灌溉系统架构 注:MCU1:气象监测控制终端;MCU2:墒情监测控制终端;MCU3:灌溉应用控制终端;M1:辐射传感器;M2空气温度传感器;M3:空气湿度传感器;M4:风速传感器;M5:气压传感器;S1:20cm墒情传感器;S2:40cm墒情传感器;S3:60cm墒情传感器;V1:电磁阀;V1:智能远传水表
Fig.2 Intelligent irrigation system architecture Note:MCU1:Meteorological monitoring and control terminal; MCU2:Moisture monitoring and control terminal; MCU3:Irrigation application control terminal; M1:Radiation sensor; M2:Air temperature sensor; M3:Air humidity sensor; M4:Wind speed sensor; M5:Air pressure sensor; S1:20 cm moisture sensor; S2:40 cm moisture sensor; S3:60 cm moisture sensor; V1:Solenoid valve; V1:Intelligent remote water meter
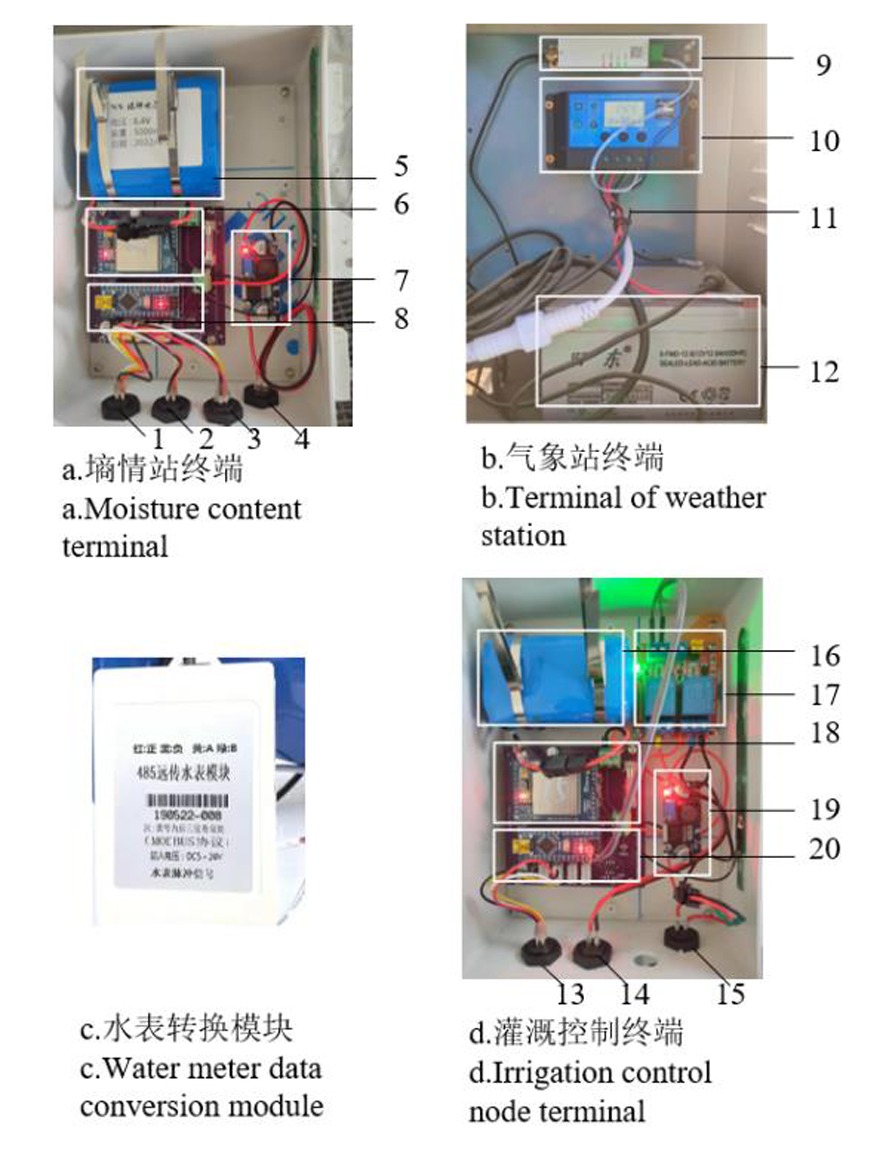
图3 智能灌溉系统各节点终端连接 注:1.20 cm墒情传感器接口;2.40 cm墒情传感器接口;3.60 cm墒情传感器接口;4.太阳能板接口;5.蓄电池;6.DUT模块;7.太阳能转换模块;8.墒情数据汇集节点;9.DUT模块;10.气象站控制终端;11.传感器及电源;12.蓄电池;13.水表接口;14.电磁阀接口;15.太阳能板接口;16.蓄电池;17.电磁阀数据转换模;18.DUT模块;19.太阳能转换模块;20.灌溉控制终端数据汇集节点
Fig.3 Terminal connection diagram of each node of the intelligent irrigation system Note:1.20 cm moisture sensor interface; 2.40 cm moisture sensor interface; 3.60 cm moisture sensor; 4.Solar panel connector; 5.Battery; 6.DUT module; 7.Solar panel conversion module; 8.Moisture sensor collection node; 9.DUT module; 10.Weather station control terminal; 11.Sensor and power supply; 12.Battery; 13.Water meter connection; 14.Solenoid valve interface; 15.Solar panel connector; 16.Battery; 17.Solenoid valve data conversion module; 18.DUT Module; 19.Solar panel conversion module; 20.Irrigation control terminal data collection node
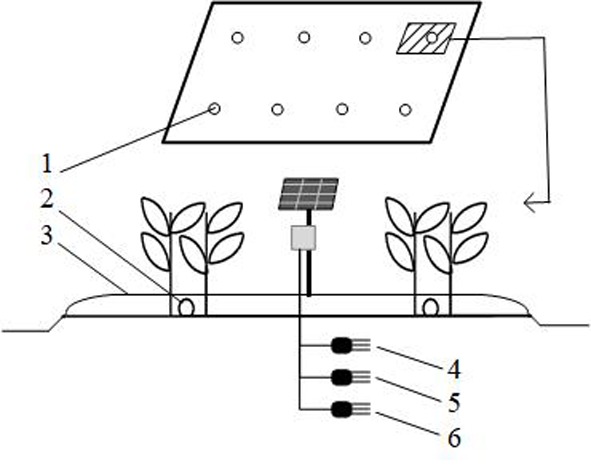
图5 土壤墒情传感器布设位置 注:1.墒情站;2.滴灌带;3.覆膜;4.20 cm墒情传感器;5.40 cm墒情传感器;6.60 cm墒情传感器
Fig.5 Position of the soil moisture sensor Note:1.Moisture content station; 2.Drip irrigation belt; 3.Film coating; 4.20 cm moisture sensor; 5.40 cm moisture sensor; 6.60 cm moisture sensor
| 处理 Treatments | 单铃质量 The quality of single boll (g) | 单株铃数 Boll number per | 收获密度 Harvested density (104株/hm2) | 籽棉产量 Seed cotton yield (kg/hm2) | 总耗水量 The total water consumption (mm) | 水分利用效率 WUE (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 5.60±0.07a | 7.80±0.30d | 15.99±0.55a | 6 291.96±198.42c | 591.09 | 1.065±0.034c |
| W2 | 5.59±0.09a | 9.45±0.13a | 16.32±0.25a | 7 755.27±247.16a | 492.58 | 1.574±0.050b |
| W3 | 5.40±0.05b | 9.16±0.13b | 16.02±0.25a | 7 135.28±159.97b | 394.06 | 1.811±0.041a |
| CK | 5.51±0.05a | 8.14±0.08c | 15.90±0.30a | 6 418.03±121.45c | 421.56 | 1.522±0.029b |
表3 不同灌溉模式下棉花的产量、产量构成和水分利用效率变化
Tab.3 Effects of different irrigation modes on yield, yield composition and water use efficiency of cotton
| 处理 Treatments | 单铃质量 The quality of single boll (g) | 单株铃数 Boll number per | 收获密度 Harvested density (104株/hm2) | 籽棉产量 Seed cotton yield (kg/hm2) | 总耗水量 The total water consumption (mm) | 水分利用效率 WUE (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 5.60±0.07a | 7.80±0.30d | 15.99±0.55a | 6 291.96±198.42c | 591.09 | 1.065±0.034c |
| W2 | 5.59±0.09a | 9.45±0.13a | 16.32±0.25a | 7 755.27±247.16a | 492.58 | 1.574±0.050b |
| W3 | 5.40±0.05b | 9.16±0.13b | 16.02±0.25a | 7 135.28±159.97b | 394.06 | 1.811±0.041a |
| CK | 5.51±0.05a | 8.14±0.08c | 15.90±0.30a | 6 418.03±121.45c | 421.56 | 1.522±0.029b |
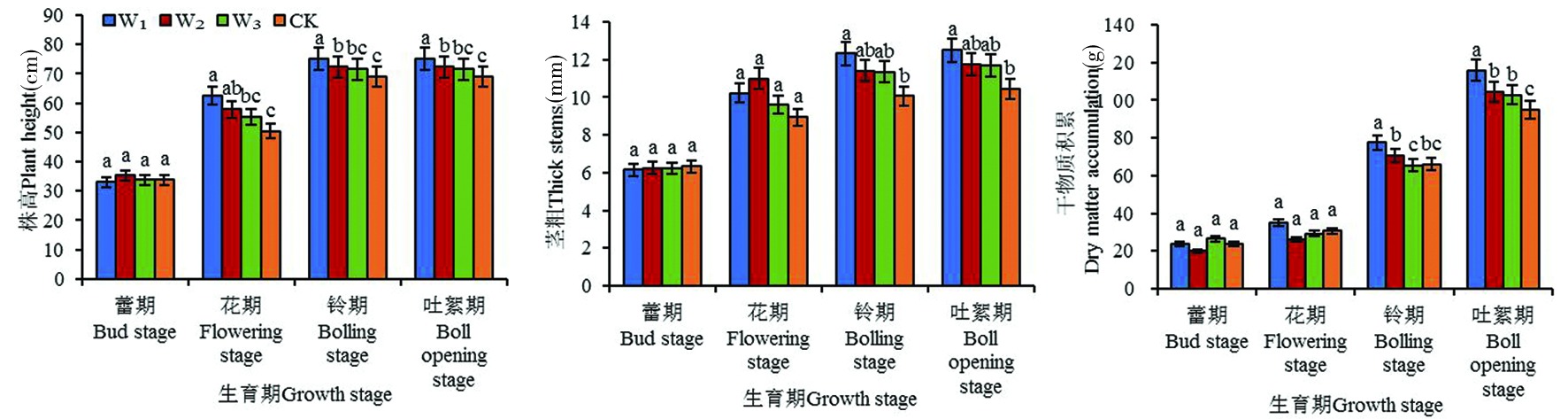
图8 不同灌溉模式下棉花不同生长阶段株高、茎粗和干物质积累的变化 注:不同字母表示不同处理间0.05水平下差异显著,(P<0.05),下同
Fig.8 Changes of plant height, stem diameter and dry matter accumulation in different growth stages of cotton under different irrigation modes Note:Different letters indicate significant differences between treatments at the 0.05 level, (P<0.05),the same as below
| [1] | 李会芳, 朱艳芬, 蔡倒录. 新疆农业用水及主要农作物用水特征问题研究[J]. 农业与技术, 2021, 41(21):40-43. |
| LI Huifang, ZHU Yanfen, CAI Daolu. Study on the characteristics of agricultural water use and main crop water use in Xinjiang[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2021, 41(21):40-43. | |
| [2] | 张振龙. 新疆城镇化与水资源耦合协调发展研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2018. |
| ZHANG Zhenlong. Research on the coupling and coordinated development of urbanization and water resources in Xinjiang[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2018. | |
| [3] |
杨宏伟, 李思恩. 多年膜下滴灌对土壤水盐及棉花产量的影响[J]. 节水灌溉, 2022,(10):79-85.
DOI |
|
YANG Hongwei, LI Sien. Effects of drip irrigation under plastic film for many years on soil water and salt and cotton yield[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2022,(10):79-85.
DOI |
|
| [4] | 郁晓庆, 吴普特, 韩文霆, 等. 基于无线传感器网络的农田灌溉远程监控系统[J]. 排灌机械工程学报, 2013, 31(1):66-69,80. |
| YU Xiaoqing, WU Pute, HAN Wenting, et al. Remote monitoring system for farmland irrigation based on wireless sensor network[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2013, 31(1):66-69,80. | |
| [5] |
Saeed I A, Shi Q L, Wang M J, et al. Development of a Low-Cost Multi-Depth Real-Time Soil Moisture Sensor Using Time Division Multiplexing Approach[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7:19688-19697.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
贾志峰, 朱红艳, 王建莹, 等. 基于介电法原理的传感器技术在土壤水分监测领域应用探究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(32):246-252.
DOI |
|
JIA Zhifeng, ZHU Hongyan, WANG Jianying, et al. Research on the application of sensor technology based on the principle of dielectric method in the field of soil moisture monitoring[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015, 31(32):246-252.
DOI |
|
| [7] | 张迪. 基于PLC与物联网技术的自动节水灌溉系统设计[J]. 电子设计工程, 2020, 28(15):171-175. |
| ZHANG Di. Design of automatic water-saving irrigation system based on PLC and Internet of Things technology[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2020, 28(15):171-175. | |
| [8] | 贺茜. 基于大数据分析的智慧灌溉系统研究与实现[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020. |
| HE Xi. Research and implementation of intelligent irrigation system based on big data analysis[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology, 2020. | |
| [9] | Zhang J, Li A C, Li J L, et al. Research of real-time image acquisition system based on ARM 7 for agricultural environmental monitoring[C]// 2011 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering.IEEE, 2011:6216-6220. |
| [10] | 张博文. 基于物联网的智慧农业监控系统研究[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2017. |
| ZHANG Bowen. Research on intelligent agricultural monitoring system based on the Internet of Things[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University, 2017. | |
| [11] | 赵燕东, 郑焱, 周海洋, 等. 基于海棠茎干含水率的智能灌溉控制策略研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(7):323-331. |
| ZHAO Yandong, ZHENG Yan, ZHOU Haiyang, et al. Research on intelligent irrigation control strategy based on stem moisture content of begonia[J]. Journal of Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(7):323-331. | |
| [12] | 韩文霆, 张立元, 牛亚晓, 等. 无人机遥感技术在精量灌溉中应用的研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(2):1-14. |
| HAN Wenting, ZHANG Liyuan, NIU Yaxiao, et al. Research progress in the application of unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing technology in precision irrigation[J]. Journal of Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(2):1-14. | |
| [13] | 杨永民, 顾涛, 吴迪, 等. 基于光学和雷达遥感信息的灌溉信号分析及灌溉面积提取方法研究—以华北平原灵寿县磁右灌区为例[J]. 水利学报, 2022, 53(9):1039-1048. |
| YANG Yongmin, GU Tao, WU Di, et al. Research on irrigation signal analysis and irrigation area extraction method based on optical and radar remote sensing information taking Ciyou irrigation area in Lingshou County, North China Plain as an example[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2022, 53(9):1039-1048. | |
| [14] | 杨伟志, 孙道宗, 刘建梅, 等. 基于物联网和人工智能的柑橘灌溉专家系统[J]. 节水灌溉, 2019,(9):116-120,124. |
| YANG Weizhi, SUN Daozong, LIU Jianmei, et al. Citrus irrigation expert system based on the Internet of Things and artificial intelligence[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2019,(9):116-120,124. | |
| [15] | Kan Y B, Wang L L, Zhang Y S, et al. Research on Control System of Tropical Intelligent Agriculture in Hainan[J]. Applied Mechanics & Materials, 2013, 385-386:923-926.. |
| [16] | 单立. 试验区作物的气象特征与作物需水量测算方法[J]. 低碳世界, 2021, 11(3):278-280. |
| SHAN Li. Meteorological characteristics of crops in the experimental area and calculation method of crop water demand[J]. Low Carbon World, 2021, 11(3):278-280. | |
| [17] |
Ershadi A, McCabe M F, Evans J P, et al. Impact of model structure and parameterization on Penman- Monteith type evaporation models[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 525:521-535
DOI URL |
| [18] | Sagar A, Singh P K. Evapotranspiration based micro irrigation scheduling of tomato crop under naturally ventilated polyhouse[J]. Current Journal of Applied Science and Technology, 2019, 36(6):1-7. |
| [19] | 赵文利, 熊育久, 邱国玉, 等. 模型结构与参数化差异对蒸散发估算的影响[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(1):162-172. |
| ZHAO Wenli, XIONG Yujiu, QIU Guoyu, et al. Effects of model structure and parameterization differences on evapotranspiration estimation[J]. Journal of Peking University(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 57(1):162-172. | |
| [20] | 杜江涛, 张楠, 龚珂宁, 等. 基于DSSAT模型的南疆膜下滴灌棉花灌溉制度优化[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(11):3760-3768. |
| DU Jiangtao, ZHANG Nan, GONG Kening, et al. Optimization of cotton irrigation system under mulch drip irrigation in southern Xinjiang based on DSSAT model[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(11):3760-3768. | |
| [21] |
Kalashnikov A A. Development of Readings Correction Techniques for Industrial Hydrostatic Level Meters[J]. Automation and Remote Control, 2021, 82(2):333-341.
DOI |
| [22] | 毛善君, 崔建军, 王世斌, 等. 煤矿智能开采信息共享管理平台构建研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(6):1937-1948. |
| MAO Shanjun, CUI Jianjun, WANG Shibin, et al. Research on the construction of intelligent coal mining information sharing management platform[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(6):1937-1948. | |
| [23] | 徐微, 李睿勋, 陈泽昕, 等. 基于NB-IoT智能点滴监测系统的设计与实现[J]. 自动化与仪表, 2022, 37(9):94-98. |
| XU Wei, LI Ruixun, CHEN Zexin, et al. Design and implementation of intelligent drip monitoring system based on NB-IoT[J]. Automation and Instrumentation, 2022, 37(9):94-98. | |
| [24] | 白俊. 数据挖掘技术在智能灌溉决策系统中的应用[J]. 农机化研究, 2022, 44(9):247-250,259. |
| BAI Jun. Application of data mining technology in intelligent irrigation decision-making system[J]. Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2022, 44(9):247-250,259. | |
| [25] | 耿耘, 刘浩, 李云峰, 等. 麦后移栽棉蒸发蒸腾规律和作物系数[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2022, 41(7):24-34. |
| GENG Yun, LIU Hao, LI Yunfeng, et al. Evapotranspiration and crop coefficient of transplanted cotton after wheat[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2022, 41(7):24-34. | |
| [26] | 莫兴国, 李宏轩, 刘苏峡, 等. 用土壤温度估算表层土壤导温率与热通量的研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2002, 10(1):62-64. |
| MO Xingguo, LI Hongxuan, LIU Suxia, et al. Study on estimating surface soil thermal conductivity and heat flux using soil temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2002, 10(1):62-64. | |
| [27] | 辛玉琛, 张敬东, 常义, 等. 土壤墒情监测仪器拟合公式研究[J]. 水文, 2017, 37(4):68-73. |
| XIN Yuchen, ZHANG Jingdong, CHANG Yi, et al. Study on fitting formula of soil moisture monitoring instrument[J]. Hydrology, 2017, 37(4):68-73. | |
| [28] |
谢芳荻, 阎建忠, 刘林山, 等. 青藏高原高寒荒漠区土壤湿度监测仪器的校正方法探讨[J]. 地理研究, 2017, 36(11):2112-2128.
DOI |
| XIE Fangdi, YAN Jianzhong, LIU Linshan, et al. Discussion on calibration methods of soil moisture monitoring instruments in alpine desert areas of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Geographic Research, 2017, 36(11):2112-2128. | |
| [29] | 金福一. 土壤水分自动监测仪器现场率定技术要点分析[J]. 中国防汛抗旱, 2016, 26(1):63-65. |
| JIN Fuyi. Analysis of key technical points for field calibration of automatic soil moisture monitoring instrument[J]. China Flood Control and Drought Relief, 2016, 26(1):63-65. | |
| [30] | 辛明亮, 何新林, 吕廷波, 等. 土壤可溶性盐含量与电导率的关系实验研究[J]. 节水灌溉, 2014,(5):59-61. |
| XIN Mingliang, HE Xinlin, LYU Tingbo, et al. Experimental study on the relationship between soil soluble salt content and electrical conductivity[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2014,(5):59-61. | |
| [31] | 赵国莲. 电导率温度校正计算方法的改进[J]. 环境卫生工程, 2000, 8(4):153-154. |
| ZHAO Guolian. Improvement of conductivity temperature correction calculation method[J]. Environmental Health Engineering, 2000, 8(4):153-154. | |
| [32] |
林涛, 梅旭荣, 郝卫平, 等. 亏缺灌溉对机采棉水分利用及产量形成的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(3):419-429.
DOI |
|
LIN Tao, MEI Xurong, HAO Weiping, et al. The effect of deficit irrigation on the yield and water utilization of machine picked cotton under condition of drip irrigation[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(3):419-429.
DOI |
|
| [33] | 白蒙, 吕廷波, 徐强, 等. 水分调控对机采棉土壤水盐运移的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(4):842-847. |
| BAI Meng, LYU Tingbo, XU Qiang, et al. Pick up cotton moisture control on machine the effect of soil water and salt migration[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 33(4):842-847. | |
| [34] | 巨龙, 王全九, 王琳芳, 等. 灌水量对半干旱区土壤水盐分布特征及冬小麦产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2007, 23(1):86-90. |
| JU Long, WANG Quanjiu, WANG Linfang, et al. Effects of irrigation amounts on yield of winter wheat and distribution characteristics of soil water-salt in semi-arid region[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2007, 23(1):86-90. | |
| [35] | 程少雨, 林涛, 吴凤全, 等. 种植密度和灌溉定额对机采棉田土壤盐分特征的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(12):3933-3943. |
| CHENG Shaoyu, LIN Tao, WU Fengquan, et al. Effects of planting density and irrigation quota on soil salinity characteristics in machine-picked cotton fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(12):3933-3943. | |
| [36] | 牛玉萍, 陈宗奎, 陈厚川, 等. 不同滴灌模式下种植密度对棉花冠层结构特性的调节[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2016, 53(10):1765-1777. |
| NIU Yuping, CHEN Zongkui, CHEN Houchuan, et al. Effect of planting density on canopy structure characteristics of cotton under different drip irrigation patterns[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 53(10):1765-1777. | |
| [37] |
陈利军, 林涛, 吴凤全, 等. 种植密度和灌溉定额互作对76 cm等行距机采棉生长发育及产量形成影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(12):2899-2908.
DOI |
|
CHEN Lijun, LIN Tao, WU Fengquan, et al. Effects of planting density and irrigation quota on cotton growth and yield formation by 76 cm equal row spacing machine[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(12):2899-2908.
DOI |
|
| [38] |
王亮, 吾买尔江·库尔班, 郭仁松, 等. 深松耕作下灌溉定额对棉田水分利用效率及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(10):2374-2383.
DOI |
|
WANG Liang, Wumaierjiang kuerban, GUO Rensong, et al. Effect of irrigation quota under subsoiling on water use efficiency and yield of cotton field[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(10):2374-2383.
DOI |
|
| [39] | 卡力比尔·买买提, 巴特尔·巴克, 祁嘉郁. 北疆地区棉花生育期需水量变化特征及成因分析[J]. 节水灌溉, 2021,(1):81-85. |
| Kalibier Maimaiti, Bateer Bake, QI Jiayu. Analysis on variation characteristics and causes of water requirement in cotton growing period in Northern Xinjiang[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2021,(1):81-85. | |
| [40] | 刘庆贺, 康小兵. 地下水位下降对干旱区膜下滴灌棉花需水量的影响[J]. 人民长江, 2020, 51(2):138-141,165. |
| LIU Qinghe, KANG Xiaobing. Drawdown influence on film with drip irrigation of cotton water demand in arid areas[J]. Yangtze River, 2020, 51(2):138-141, 165. | |
| [41] | 张慧, 张凯, 陈冰, 等. 不同灌溉量对新疆棉花生长发育及产量形成的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(6):1976-1985. |
| ZHANG Hui, ZHANG Kai, CHEN Bing, et al. Effects of different irrigation amounts on cotton growth and yield formation in Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(6):1976-1985. |
| [1] | 苗红萍, 王晓伟, 田聪华, 李志, 张玉新, 戴俊生. 塔里木河流域棉花生产与布局演变特征及驱动因素分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 217-226. |
| [2] | 王俊铎, 崔豫疆, 梁亚军, 龚照龙, 郑巨云, 李雪源. 新疆棉花生产优势区域分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 60-69. |
| [3] | 郑巨云, 龚照龙, 梁亚军, 耿世伟, 孙丰磊, 阳妮, 李雪源, 王俊铎. 新疆机采棉花生产关键技术模式[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 70-74. |
| [4] | 李杰, 刘佳, 王亮, 张娜, 杨延龙, 郑子漂, 魏鑫, 王萌, 周子馨, 阳妮, 龚照龙, 侯献飞, 黄启秀, 阿不都卡地尔·库尔班, 张济鹏, 张鹏忠. “棉、油、糖”科技成果转化现状及应用分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 89-94. |
| [5] | 扁青永, 付彦博, 祁通, 黄建, 蒲胜海, 孟阿静, 哈丽哈什·依巴提. 新疆南疆盐碱地棉花出苗影响因素及保苗措施分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 95-100. |
| [6] | 李永泰, 高阿香, 李艳军, 张新宇. 脱叶剂对不同敏感性棉花品种生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2094-2102. |
| [7] | 张泽华, 叶含春, 王振华, 李文昊, 李海强, 刘健. 等氮配施脲酶抑制剂对滴灌棉花生长发育和产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [8] | 陈瑞杰, 罗林毅, 阮向阳, 冶军. 腐植酸对滴灌棉田土壤养分和棉花产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [9] | 黄铂轩, 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 邵晶晶, 冯卫娜, 庞朝友, 徐文修, 董合林. 不同氮素抑制剂对棉花生长发育、氮素利用与产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [10] | 王超, 徐文修, 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 冯卫娜, 邵晶晶, 董合林. 棉花苗期生长发育对土壤速效钾水平的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2132-2139. |
| [11] | 张鸟, 王卉, 冯国郡, 再吐尼古丽·库尔班. 不同粒用高粱品种产量和农艺性状及品质的差异性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2160-2167. |
| [12] | 张庭军, 李字辉, 崔豫疆, 孙孝贵, 陈芳. 微生物菌剂对棉花生长及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2269-2276. |
| [13] | 陈芳, 李字辉, 孙孝贵, 张庭军. 不同剂量的微生物菌剂对加工番茄产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2285-2289. |
| [14] | 张承洁, 胡浩然, 段松江, 吴一帆, 张巨松. 氮肥与密度互作对海岛棉生长发育及产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1821-1830. |
| [15] | 董志多, 徐菲, 付秋萍, 黄建, 祁通, 孟阿静, 付彦博, 开赛尔·库尔班. 不同类型盐碱胁迫对棉花种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 38
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 318
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||