

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (2): 336-344.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.02.009
收稿日期:2023-06-17
出版日期:2024-02-20
发布日期:2024-03-19
通信作者:
杨茹薇(1984-),女,宁夏人,正高级农艺师,研究方向为植物保护与高产栽培, (E-mail)617950493@qq.com作者简介:刘易(1983-),男,河北人,副研究员,硕士,研究方向为马铃薯高产栽培及抗逆生理,(E-mail)liuyun_5511@163.com
基金资助:
LIU Yi( ), LI Jiangtao, JIANG Yinghong, YANG Ruwei(
), LI Jiangtao, JIANG Yinghong, YANG Ruwei( ), SUN Hui, WU Yan
), SUN Hui, WU Yan
Received:2023-06-17
Published:2024-02-20
Online:2024-03-19
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究NaCl胁迫下外源亚精胺(Spd)对马铃薯幼苗生理特征的影响,为新疆盐渍化区域马铃薯种植提供技术参考。【方法】以晋薯16号马铃薯幼苗为材料,采用不同浓度NaCl模拟盐胁迫处理,研究外源亚精胺Spd对马铃薯植株生长、叶片抗氧化酶活性、渗透调节物质含量的影响。【结果】盐胁迫抑制了马铃薯植株生长,使得超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)等酶促类抗氧化酶活性表现为低盐胁迫促进,高盐胁迫抑制;抗坏血酸(ASA)、谷胱甘肽(DSH)等非酶促类抗氧化酶含量均降低;脯氨酸、可溶性糖、氨基酸含量升高;外源亚精胺(Spd)通过提高叶绿素含量、根系活力,调节渗透调节物质含量,增强抗氧化酶活性等方式维持植物体的正常生理代谢功能。【结论】外源亚精胺(Spd)可提升马铃薯耐盐性,缓解盐胁迫对马铃薯植株的抑制作用,其中0.9 mmol/L Spd(S3)浓度缓解效果最明显。
中图分类号:
刘易, 李江涛, 江应红, 杨茹薇, 孙慧, 吴燕. NaCl胁迫下外源亚精胺对马铃薯幼苗生理特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 336-344.
LIU Yi, LI Jiangtao, JIANG Yinghong, YANG Ruwei, SUN Hui, WU Yan. Effect of exogenous spermidine on physiological characteristics of potato seedlings under NaCl stress[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(2): 336-344.
| 盐处理 NaCl treatment (mmol/L) | Spd处理 Spd treatment (mmol/L) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (mm) | 鲜重(g/株) Fresh weight (g/plant) | 干重(g/株) Dry weight (g/plant) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | S0 | 8.86±0.36 a | 1.41±0.04 a | 1.02±0.05 a | 0.087±0.002 b |
| S1 | 8.55±0.39 a | 1.41±0.02 a | 1.00±0.03 a | 0.09±0.002 ab | |
| S2 | 9.09±0.42 a | 1.35±0.07 a | 1.02±0.03 a | 0.088±0.002 b | |
| S3 | 9.32±0.37 a | 1.37±0.04 a | 1.06±0.02 a | 0.09±0.007 a | |
| S4 | 8.59±0.39 a | 1.39±0.02 a | 1.02±0.03 a | 0.088±0.006 ab | |
| T1 | S0 | 7.29±0.26 c | 1.38±0.01 a | 0.89±0.01 bc | 0.075±0.005 ab |
| S1 | 7.15±0.10 c | 1.35±0.03 ab | 0.87±0.02 c | 0.074±0.001 b | |
| S2 | 8.31±0.24 b | 1.30±0.05 b | 0.89±0.03 bc | 0.076±0.003 ab | |
| S3 | 9.14±0.11 a | 1.34±0.02 ab | 0.96±0.03 a | 0.086±0.002 a | |
| S4 | 8.09±0.31 b | 1.30±0.05 b | 0.91±0.01 b | 0.083±0.003 ab | |
| T2 | S0 | 6.86±0.32 b | 1.29±0.01 b | 0.84±0.03 b | 0.065±0.002 b |
| S1 | 6.93±0.21 b | 1.28±0.01 b | 0.86±0.01 b | 0.074±0.002 ab | |
| S2 | 7.82±0.19 a | 1.29±0.01 b | 0.87±0.01 b | 0.081±0.003 ab | |
| S3 | 7.84±0.17 a | 1.33±0.01 a | 0.95±0.01 a | 0.089±0.006 a | |
| S4 | 7.46±0.35 a | 1.26±0.03 b | 0.93±0.01 a | 0.085±0.001 ab | |
| T3 | S0 | 6.01±0.40 b | 1.25±0.00 bc | 0.6±0.01 b | 0.059±0.005 b |
| S1 | 6.24±0.19 ab | 1.24±0.03 bc | 0.66±0.03 ab | 0.077±0.002 a | |
| S2 | 6.55±0.32 ab | 1.21±0.02 c | 0.69±0.03 a | 0.076±0.001 ab | |
| S3 | 6.79±0.26 a | 1.31±0.04 a | 0.69±0.04 a | 0.079±0.003 a | |
| S4 | 6.34±0.19 ab | 1.28±0.01 ab | 0.68±0.01 a | 0.078±0.002 a |
表1 盐胁迫下喷施外源亚精胺马铃薯幼苗生长变化
Tab.1 Effects of exogenous spermidine on potato seedling growth under salt stress
| 盐处理 NaCl treatment (mmol/L) | Spd处理 Spd treatment (mmol/L) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (mm) | 鲜重(g/株) Fresh weight (g/plant) | 干重(g/株) Dry weight (g/plant) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | S0 | 8.86±0.36 a | 1.41±0.04 a | 1.02±0.05 a | 0.087±0.002 b |
| S1 | 8.55±0.39 a | 1.41±0.02 a | 1.00±0.03 a | 0.09±0.002 ab | |
| S2 | 9.09±0.42 a | 1.35±0.07 a | 1.02±0.03 a | 0.088±0.002 b | |
| S3 | 9.32±0.37 a | 1.37±0.04 a | 1.06±0.02 a | 0.09±0.007 a | |
| S4 | 8.59±0.39 a | 1.39±0.02 a | 1.02±0.03 a | 0.088±0.006 ab | |
| T1 | S0 | 7.29±0.26 c | 1.38±0.01 a | 0.89±0.01 bc | 0.075±0.005 ab |
| S1 | 7.15±0.10 c | 1.35±0.03 ab | 0.87±0.02 c | 0.074±0.001 b | |
| S2 | 8.31±0.24 b | 1.30±0.05 b | 0.89±0.03 bc | 0.076±0.003 ab | |
| S3 | 9.14±0.11 a | 1.34±0.02 ab | 0.96±0.03 a | 0.086±0.002 a | |
| S4 | 8.09±0.31 b | 1.30±0.05 b | 0.91±0.01 b | 0.083±0.003 ab | |
| T2 | S0 | 6.86±0.32 b | 1.29±0.01 b | 0.84±0.03 b | 0.065±0.002 b |
| S1 | 6.93±0.21 b | 1.28±0.01 b | 0.86±0.01 b | 0.074±0.002 ab | |
| S2 | 7.82±0.19 a | 1.29±0.01 b | 0.87±0.01 b | 0.081±0.003 ab | |
| S3 | 7.84±0.17 a | 1.33±0.01 a | 0.95±0.01 a | 0.089±0.006 a | |
| S4 | 7.46±0.35 a | 1.26±0.03 b | 0.93±0.01 a | 0.085±0.001 ab | |
| T3 | S0 | 6.01±0.40 b | 1.25±0.00 bc | 0.6±0.01 b | 0.059±0.005 b |
| S1 | 6.24±0.19 ab | 1.24±0.03 bc | 0.66±0.03 ab | 0.077±0.002 a | |
| S2 | 6.55±0.32 ab | 1.21±0.02 c | 0.69±0.03 a | 0.076±0.001 ab | |
| S3 | 6.79±0.26 a | 1.31±0.04 a | 0.69±0.04 a | 0.079±0.003 a | |
| S4 | 6.34±0.19 ab | 1.28±0.01 ab | 0.68±0.01 a | 0.078±0.002 a |
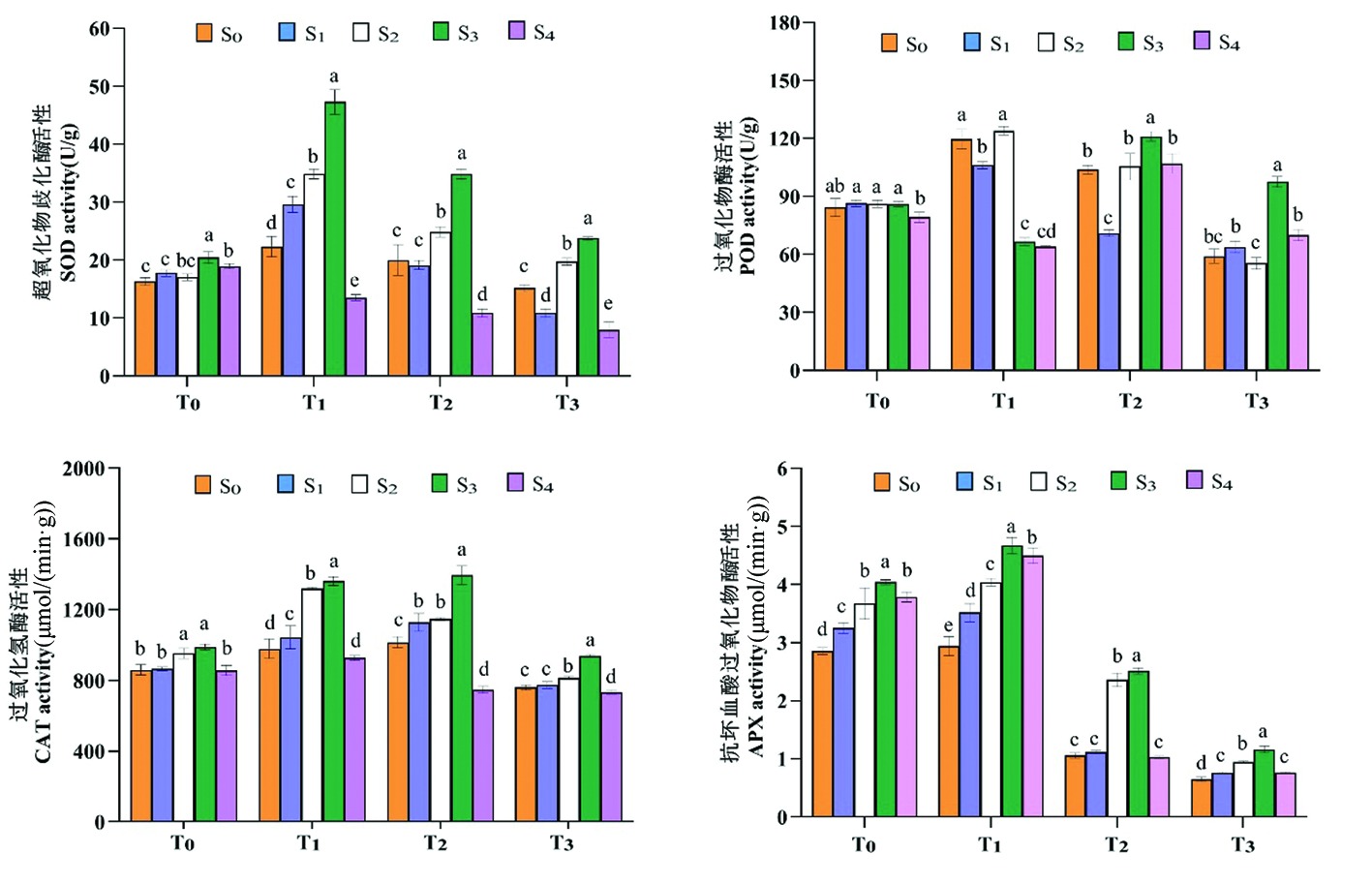
图2 盐胁迫下喷施外源亚精胺马铃薯幼苗酶促类抗氧化物酶活性变化
Fig.2 Effects of exogenous spermidine on enzymatic antioxidant enzyme activities in potato seedlings under salt stress
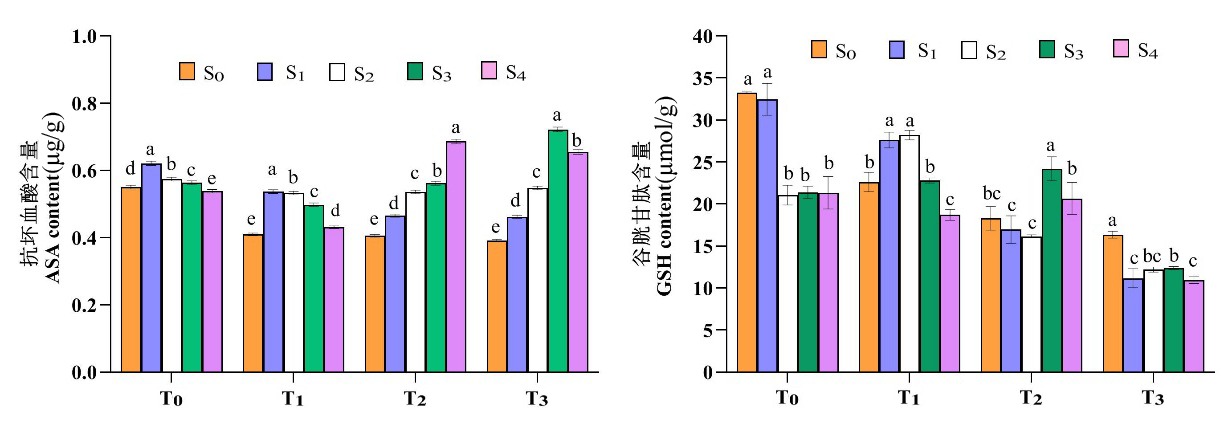
图3 盐胁迫下喷施外源亚精胺马铃薯幼苗非酶促类抗氧化物酶活性变化
Fig.3 Effects of exogenous spermidine on the activities of non-enzymatic antioxidant enzymes in potato seedlings under salt stress
| [1] |
Ammari T G, Tahhan R, Abubaker S, et al. Soil Salinity Changes in the Jordan Valley Potentially Threaten Sustainable Irrigated Agriculture[J]. Pedosphere:A Quarterly Journal of Soil Science, 2013, 23(3):376-384.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Akhtar Abbas, Shahbaz Khan, Nisar Hussain, et al. Characterizing soil salinity in irrigated agriculture using a remote sensing approach[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2013,55-57:43-52. |
| [3] |
Butcher K, Wick A F, DeSutter T. Soil salinity:a threat to global food security[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2016, 108(6):2189-2200.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 全国土壤普查办公室. 中国土壤[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社,1998. |
| The National Soil Survey Office. Soils of China[M]. Beijmg: China Agriculture Press,1998. | |
| [5] |
Shin D, Moon S J, Han S, et al. Expression of StMYB1R-1,a novel potato single myb-like domain transcription factor,increases drought tolerance[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 155(1):421-432.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Alcázar R, Marco F, Cuevas J C, et al. Involvement of polyamines in plant response to abiotic stress[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2006, 28(23):1867-1876.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Groppa M D, Benavides M P. Polyamines and abiotic stress:recent advances[J]. Amino Acids, 2008, 34(1):35-45.
PMID |
| [8] | 张毅, 石玉, 胡晓辉, 等. 外源Spd对盐碱胁迫下番茄幼苗氮代谢及主要矿质元素含量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(5):1401-1408. |
| ZHANG Yi, SHI Yu, HU Xiaohui, et al. Effects of exogenous spermidine on the nitrogen metabolism and main mineral elements contents of tomato seedlings under saline-alkali stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(5):1401-1408. | |
| [9] |
ElSayed A I, Rafudeen M S, El-hamahmy M A M, et al. Enhancing antioxidant systems by exogenous spermine and spermidine in wheat(Triticum aestivum)seedlings exposed to salt stress[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2018, 45(7):745-759.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Tang S, Zhang H X, Ling L, et al. Exogenous spermidine enhances the photosynthetic and antioxidant capacity of rice under heat stress during early grain-filling period[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2018, 45(9):911-921.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | 张志良, 瞿伟菁, 李小方. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009. |
| ZHANG Zhiliang, QU Weijing, LI Xiaofang. Beneficial Role of different Spermidine on Nitrogen plant physiology Experiment guidance[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2009. | |
| [12] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].高等教育出版社, 2000. |
| LI Hesheng. Principle and Technology of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry Experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000. | |
| [13] | 张宪政. 超氧化物歧化酶活性的测定[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1992. |
| ZHANG Xianzheng. Determination of superoxide dismutase activity[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press,1992. | |
| [14] | Nakano Y, Asada K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascor-bate specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts[J]. Plant Cell Physiology, 1981, 22(5):867-880. |
| [15] | 陈建勋, 王晓峰. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 广州: 华南理工大学出版社, 2002. |
| CHEN Jianxuin, WANG Xiaofeng. Experimental Guidance of Plant Physiology[M]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology Press, 2002. | |
| [16] | 陈洁, 林栖凤. 植物耐盐生理及耐盐机理研究进展[J]. 海南大学学报, 2003, 21(2):177-182. |
| CHEN Jie, LIN Qifeng. Progress on Salt Tolerance Physiology and Mechanism of Plants[J]. Journal of Hainan University, 2003, 21(2):177-182. | |
| [17] | 胡立盼. 盐碱胁迫下外源亚精胺对番茄叶片光抑制保护机理[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. |
| HU Lipan. Photoprotective Mechanism of Exogenous Spd in Tomato Leaves under Salinity-Alkalinity stress[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2016. | |
| [18] | 陈雄伟, 马艳萍, 徐呈祥, 等. 多胺及其代谢抑制剂对盐胁迫下枣树叶绿体离子稳态和类囊体膜H+-ATP酶活性的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2012, 32(10):1-8. |
| CHEN Xiongwei, MA Yanping, XU Chengxiang, et al. Effects of exogenous polyamines and polyamine metabolism inhibitors on and chloroplastsionic homeostasisand thylakoid membrane conjugated H+-ATPase activity of Ziziphus jujuba Mill.under salt stress[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2012, 32(10):1-8. | |
| [19] | 隋昌成. 外源亚精胺对葡萄幼苗盐碱胁迫的缓解效应[D]. 山东: 山东农业大学, 2021. |
| SUI Changcheng. The Relieving Effect of Exogenous Spermidine on Saline-alkali Stress in Grape Seedlings[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| [20] |
Zhang R H, Li J, Guo S R, et al. Effects of exogenous putrescine on gas-exchange characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence of NaCl-stressed cucumber seedlings[J]. Photosynthesis Research:An International Journal, 2009, 100(3):155-162.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | 杜红阳, 胡春红, 刘怀攀. 外源亚精胺对盐胁迫下大豆幼苗叶片光合性能和抗氧化代谢的调控效应[J]. 大豆科学, 2016, 35(1):80-85. |
| DU Hongyang, HU Chunhong, LIU Huaipan. Effects of Exogenous Spermidine on Photosynthetic Character and Antioxidant Metabolism of Soybean Seedling Leaves under Salt Stress[J]. Soybean Science, 2016, 35(1):80-85. | |
| [22] | 于伟. 水杨酸和亚精胺缓解茄子幼苗盐胁迫的生理机制[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015. |
| YU Wei. Physiological Mechanism of SA and Spd Alleviating Salt Stress in Eggplant Seedling[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| [23] | 邹芳, 王志恒, 杨秀柳, 等. 外源亚精胺对盐胁迫下甜高粱(Sorghum bicolor)幼苗的影响[J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(8):2721-2727. |
| ZOU Fang, WANG Zhiheng, YANG Xiuliu, et al. Effects of Exogenous Spermidine on Sorghum bicolor Seedlings under Salt Stress[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(8):2721-2727. | |
| [24] | 赵东晓, 董亚茹, 孙景诗, 等. 外源亚精胺对桑树盐胁迫的缓解效应[J]. 蚕业科学, 2019, 45(4):484-493. |
| ZHAO Dongxia, DONG Yaru, SUN Jingshi, et al. Alleviation Effect of Exogenous Spermidine on Mulberry Under Salt Stress[J]. Science of Sericulture, 2019, 45(4):484-493. | |
| [25] | 海霞, 米俊珍, 赵宝平, 等. 外源亚精胺对盐胁迫下燕麦幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(6):1003-1011. |
| HAI Xia, MI Junzhen, ZHAO Baoping, et al. Effects of Exogenous Spermidine on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics in Oat Seedlings under Salt Stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2021, 41(6):1003-1011. | |
| [26] |
Kramer G F, Norman H A, Krizek D T. Influence of UV-B radiation on polyamines, lipid peroxidation and membrane lipids in cucumber[J]. Phytochemistry, 1991, 30(7):2101-2108.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Zhu J K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants[J]. Cell, 2016, 167(2):313-324.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 夏关雪莹, 王冰, 屈琳俐, 等. 亚精胺浸种缓解盐碱胁迫对苜蓿生长抑制的研究[J]. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(5):17-23. |
| XIA Guanxueying, WANG Bing, QU Linli, et al. Alfalfa Seed Soaking with Spermidine to Alleviates the Inhibition of Alfalfa Growth under Soil Saline-alkaline Stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(5):17-23. | |
| [29] | 赵勇, 马雅琴, 翁跃进. 盐胁迫下小麦甜菜碱和脯氨酸含量变化[J]. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2005, 31(1):103-106. |
|
ZHAO Yong, MA Yaqin, WENG Yuejin. Variation of Betaine and Proline Contents in Wheat Seedlings Under Salt Stress[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 2005, 31(1):103-106.
PMID |
|
| [30] | 段九菊, 郭世荣, 樊怀福, 等. 盐胁迫对黄瓜幼苗根系脯氨酸和多胺代谢的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2006, 26(12):2486-2492. |
| DUAN Jiuju, GUO Shirong, FAN Huaifu, et al. Effects of Salt Stress on Proline and Polyamine Metabolis ms in the Roots of Cucumber Seedlings[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2006, 26(12):2486-2492. | |
| [31] |
Grzesiak M, Filek M, Barbasz A, et al. Relationships between polyamines,ethylene,osmoprotectants and antioxidant enzymes activities in wheat seedlings agter short-term PEG-and NaCl-induced stresses[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 2013, 69(2):177-189.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
李州, 彭燕. 亚精胺对水分胁迫下白三叶脯氨酸代谢、抗氧化酶活性及其基因表达的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(4):148-156.
DOI |
|
LI Zhou, PENG Yan. Effects of spermidine on proline metabolism,antioxidant enzyme activity and gene expression in white clover leaves under water stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(4):148-156.
DOI |
|
| [33] | 闫刚, 张春梅, 邹志荣. 外源亚精胺对干旱胁迫下番茄幼苗碳水化合物代谢及相关酶活性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2012, 30(1):143-148. |
| YAN Gang, ZHANG Chunmmei, ZOU Zhirong. Effects of exogenous spermidine on metabolism of nonstructural carbonhydrate and involved activity of enzymes of tomato seedlings under drought stress[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2012, 30(1):143-148. | |
| [34] | 汪志伟. 外源亚精胺(Spd)对盐胁迫下辣椒种子萌发和幼苗生理生化的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2009. |
| WANG Zhiwei. Effects of Exogenous spermidine(Spd)on Seed Germination and Physiological and biochemical Characteristics of Pepper Seedling Under Salt Stress[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2009. | |
| [35] | 潘媛媛, 张毅, 石玉, 等. 外源亚精胺对等渗盐胁迫下番茄幼苗抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(3):57-66. |
| PAN Yuanyuan, ZHANG Yi, SHI Yu, et al. Effects of exogenous spermidine on antioxidant system of tomato seedling under isotonic salt stress[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University(Nat.Sci.Ed), 2019, 47(3):57-66. | |
| [36] | 吴旭红, 冯晶旻. 外源亚精胺对渗透胁迫下南瓜幼苗抗氧化酶活性等生理特性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2017, 35(4):255-262. |
| WU Xuhong, FENG Jingwen. Effects of extraneous spermidine on antioxiclant enzyme activities and other physiological characteristics of pumpkin seedlings under osmotic stress[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2017, 35(4):255-262. | |
| [37] | 段辉国, 赵俊茗, 张轩波, 等. 亚精胺预处理对NaCl胁迫下青稞幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2009, 29(6):1220-1225. |
| DUAN Huiguo, ZHAO Junming, ZHANG Xuanbo, et al. The Effects of Spermidine Pretreatment on Physiological Characteristics of Hulless Barley Seedlings under NaCl Stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2009, 29(6):1220-1225. |
| [1] | 张帆, 陈晓露, 王洁, 侯献飞, 贾东海, 顾元国, 苗昊翠, 李强. 混合盐碱胁迫对花生种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2168-2182. |
| [2] | 洪飞, 贾丰莲, 刘易, 吴燕, 杨茹薇, 孙慧, 李广悦. 新疆马铃薯黑痣病病原菌的分离及定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1766-1771. |
| [3] | 闫文静, 秦丽欢, 阿丽娅·阿力木, 张大海, 李嘉乐, 李欢, 谢辉. 不同处理对‘吊干’杏种子发芽及幼苗生长特性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 2976-2986. |
| [4] | 杨茹薇, 刘易, 古丽米拉·热合木土拉, 孙慧, 江应红. 马铃薯病毒病实时荧光定量PCR检测技术[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2484-2490. |
| [5] | 周小云, 雷斌, 张军高, 梁晶, 龚静云, 周广威, 张少民, 李进. 7.2%萎锈灵和40%拌种灵包衣对棉花幼苗冷胁迫生理生化特征的功效比较[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 176-183. |
| [6] | 徐李娟, 陈勇, 王则玉, 王博, 艾尼江·尔斯满, 郭瑞, 李克梅, 宋素琴. 新疆拜城县马铃薯疮痂病病原菌的分离鉴定及生物学特性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2258-2265. |
| [7] | 肖菁, 刘宁, 许明海, 张金波, 马艳明, 王莉, 徐麟. NaCl胁迫对糜子种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1623-1629. |
| [8] | 陈丽靓, 鲁倩君, 马媛媛, 刘迎, 赵宝龙, 孙军利. 不同葡萄品种的耐盐性比较分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 880-888. |
| [9] | 陈英花, 白如霄, 王娟, 范守杰, 张新疆, 危常州. 叶面喷施油菜素内酯和亚精胺对甜菜生长及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(3): 698-705. |
| [10] | 冯彩军, 宋瑞娇, 宋凌宇, 张松, 齐军仓. 2,4-表芸苔素内酯浸种对干旱胁迫下大麦种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(2): 309-316. |
| [11] | 朱普生, 刘慧英, 曹泽, 刘凯歌, 李雪珍. 外源GSNO对NaCl胁迫下番茄幼苗生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(2): 351-358. |
| [12] | 杨茹薇, 刘易, 李江涛, 古丽米拉·热合木土拉, 罗正乾, 徐琳黎, 沈洪飞. 马铃薯病毒病病原RT-PCR分子鉴定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(12): 3032-3040. |
| [13] | 曾军, 武磊, 高雁, 杨红梅, 林青, 霍向东. 嗜酸光合细菌耦合萎缩芽孢杆菌降解马铃薯加工淀粉废水条件优化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2798-2805. |
| [14] | 姚庆, 施俊杰, 侯献飞, 贾东海, 顾元国, 阿里别里根·哈孜太, 苗昊翠, 李强. 42份匍匐型花生幼苗对盐胁迫的生理响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(10): 2442-2452. |
| [15] | 马媛媛, 李刚, 何旺, 赵宝龙, 鲁倩君, 陈丽靓, 刘迎. 外源褪黑素对NaCl胁迫下草莓幼苗生理特性的缓解效应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(10): 2486-2495. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 41
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 143
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||