

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (8): 1872-1882.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.08.006
• 作物遗传育种·种质资源·分子遗传学·耕作栽培·生理生化 • 上一篇 下一篇
袁以琳( ), 颜安(
), 颜安( ), 左筱筱, 侯正清, 张振飞, 肖淑婷, 孙哲, 马梦倩, 赵宇航
), 左筱筱, 侯正清, 张振飞, 肖淑婷, 孙哲, 马梦倩, 赵宇航
收稿日期:2024-01-10
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-19
通信作者:
颜安(1983-),男,四川安岳人,教授,博士,硕士生/博士生导师,研究方向为数字农业技术、农业资源与环境,(E-mail)zryanan@163.com作者简介:袁以琳(1994-),男,河南驻马店人,硕士研究生,研究方向为农业信息化,(E-mail)171043013@qq.com
基金资助:
YUAN Yilin( ), YAN An(
), YAN An( ), ZUO Xiaoxiao, HOU Zhengqing, ZHANG Zhenfei, XIAO Shuting, SUN Zhe, MA Mengqian, ZHAO Yuhang
), ZUO Xiaoxiao, HOU Zhengqing, ZHANG Zhenfei, XIAO Shuting, SUN Zhe, MA Mengqian, ZHAO Yuhang
Received:2024-01-10
Published:2024-08-20
Online:2024-09-19
Correspondence author:
YAN An (1983 - ), male, from Anyue, Sichuan, professor, Ph.D., master/dotoral supervisor, research direction: digital agricultural technology, agricultural resources, and environment, (E-mail) zryanan@163.comSupported by:摘要:
【目的】研究氮肥减量配施生物有机肥对春小麦增产及土壤培肥的影响。【方法】在新疆昌吉回族自治州(简称昌吉州)呼图壁县五工台镇十户村农场进行培肥试验,研究有机肥对土壤有机质和养分的影响。以不施肥(CK)为对照,设置1个常规施肥(CF)处理,2个氮肥减量水平T1D1、T1D2(氮肥减量15%,氮肥减量30%)和2个生物有机肥施肥量T2D1、T2D2(1 125 、2 250 kg/hm2),共6个处理,每个处理4次重复。【结果】与常规施肥CF相比,各氮肥减量配施生物有机肥处理的春小麦LAI和SPAD值均有提高,春小麦理论产量增加了9.03%~28.84%;各氮肥减量处理降低了0~10 cm、10~20 cm土层的土壤pH值和土壤电导率,增加了土壤有机质。氮肥减量相同时,施用2 250 kg/hm2生物有机肥的处理比施用1 125 kg/hm2生物有机肥的处理增加土壤养分含量更高;当生物有机肥施量相同时,各土层氮肥减量15%处理比氮肥减量30%处理的土壤养分含量更高。与不施肥处理CK与常规施肥处理CF相比,各氮肥减量配施生物有机肥处理的土壤细菌数量和放线菌数量呈上升趋势,土壤真菌数量呈下降趋势。【结论】氮肥减量15%时配施生物有机肥是实现肥料资源合理利用和改善土壤环境的良好施肥模式,促进盐碱地春小麦生长发育,降低土壤pH值和电导率,增加土壤养分含量,调节土壤可培养微生物数量结构的效果最佳。
中图分类号:
袁以琳, 颜安, 左筱筱, 侯正清, 张振飞, 肖淑婷, 孙哲, 马梦倩, 赵宇航. 氮肥减量配施生物有机肥对春小麦增产及土壤培肥的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1872-1882.
YUAN Yilin, YAN An, ZUO Xiaoxiao, HOU Zhengqing, ZHANG Zhenfei, XIAO Shuting, SUN Zhe, MA Mengqian, ZHAO Yuhang. Impact of reduced nitrogen fertilization combined with bio-organic fertilizer on spring wheat yield enhancement and soil enrichment[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1872-1882.
| 处理 Treatments | 基肥 Base fertilizer | 追施氮肥 Top dressing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化肥 Chemical fertilizer | ||||||
| N | P2O5 | K2O | 生物有机肥 Biological organic fertilizer | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 孕穗期 Booting stage | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CF | 120 | 120 | 75 | 0 | 120 | 60 |
| T1D1 | 102 | 120 | 75 | 1 125 | 102 | 51 |
| T1D2 | 102 | 120 | 75 | 2 250 | 102 | 51 |
| T2D1 | 84 | 120 | 75 | 1 125 | 84 | 42 |
| T2D2 | 84 | 120 | 75 | 2 250 | 84 | 42 |
表1 试验各处理施肥量
Tab.1 Fertilization amount of each treatment(kg/hm2)
| 处理 Treatments | 基肥 Base fertilizer | 追施氮肥 Top dressing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化肥 Chemical fertilizer | ||||||
| N | P2O5 | K2O | 生物有机肥 Biological organic fertilizer | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 孕穗期 Booting stage | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CF | 120 | 120 | 75 | 0 | 120 | 60 |
| T1D1 | 102 | 120 | 75 | 1 125 | 102 | 51 |
| T1D2 | 102 | 120 | 75 | 2 250 | 102 | 51 |
| T2D1 | 84 | 120 | 75 | 1 125 | 84 | 42 |
| T2D2 | 84 | 120 | 75 | 2 250 | 84 | 42 |
| 处理 Treatments | 穗长 Spike length (cm) | 穗数 Panicle number (104 /hm2) | 穗粒数 Grains per panicle (粒) | 千粒重 1 000 grain weight (g) | 理论产量 Grain yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.17±0.09b | 497.35±22.94b | 17.00±0.58d | 31.33±0.58c | 3 202.66±256.33d |
| CF | 9.96±0.08a | 624.75±31.21a | 21.60±0.69c | 34.86±0.45b | 5 363.75±246.03c |
| T1D1 | 10.26±0.23a | 586.25±12.46a | 31.80±1.80a | 35.57±0.41b | 6 592.18±68.15a |
| T1D2 | 10.45±0.39a | 598.51±29.23a | 33.00±0.6a | 40.65±3.03a | 6 910.93±123.82a |
| T2D1 | 10.23±0.22a | 570.96±16.43a | 28.00±1.06b | 36.97±0.86b | 5 848.35±431.75bc |
| T2D2 | 10.27±0.18a | 573.91±9.94a | 30.80±0.40a | 36.76±0.68b | 6 489.454±69.23ab |
表2 春小麦产量及其构成因素
Tab.2 Yield and its components of spring wheat
| 处理 Treatments | 穗长 Spike length (cm) | 穗数 Panicle number (104 /hm2) | 穗粒数 Grains per panicle (粒) | 千粒重 1 000 grain weight (g) | 理论产量 Grain yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.17±0.09b | 497.35±22.94b | 17.00±0.58d | 31.33±0.58c | 3 202.66±256.33d |
| CF | 9.96±0.08a | 624.75±31.21a | 21.60±0.69c | 34.86±0.45b | 5 363.75±246.03c |
| T1D1 | 10.26±0.23a | 586.25±12.46a | 31.80±1.80a | 35.57±0.41b | 6 592.18±68.15a |
| T1D2 | 10.45±0.39a | 598.51±29.23a | 33.00±0.6a | 40.65±3.03a | 6 910.93±123.82a |
| T2D1 | 10.23±0.22a | 570.96±16.43a | 28.00±1.06b | 36.97±0.86b | 5 848.35±431.75bc |
| T2D2 | 10.27±0.18a | 573.91±9.94a | 30.80±0.40a | 36.76±0.68b | 6 489.454±69.23ab |
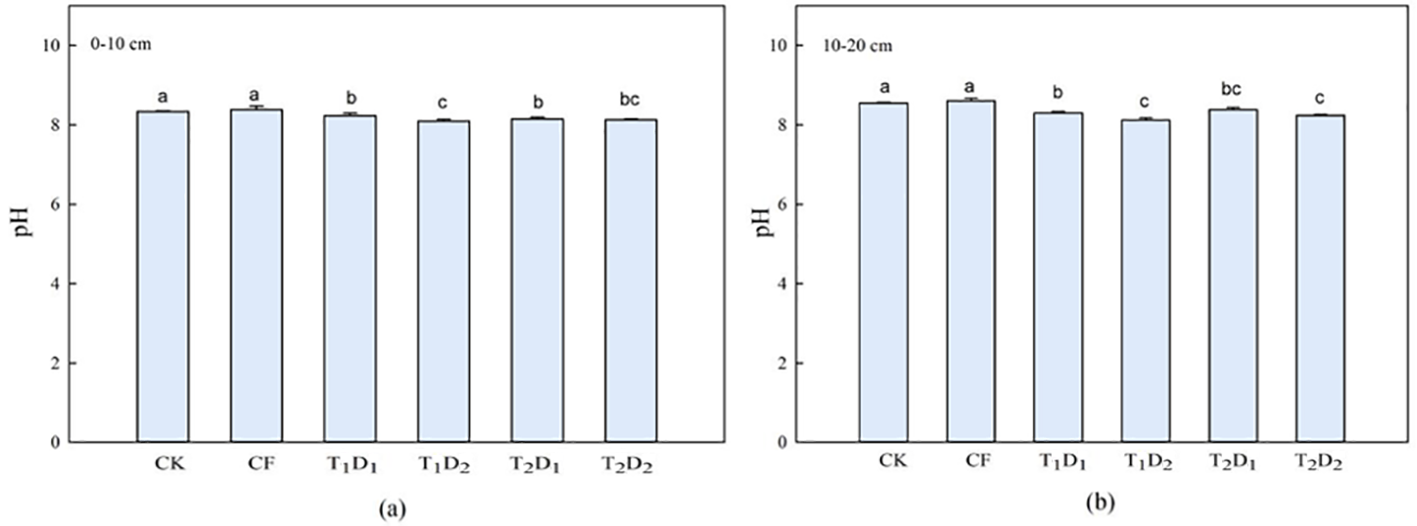
图3 氮肥减量配施生物有机肥下土壤pH值的变化 注:(a)0~10 cm土壤pH;(b)10~20 cm土壤pH值
Fig.3 Changes of nitrogen reduction combined with bio organic fertilizer on soil pH Notes: (a) 0~10 cm soil pH; (b) 10~20 cm soil pH
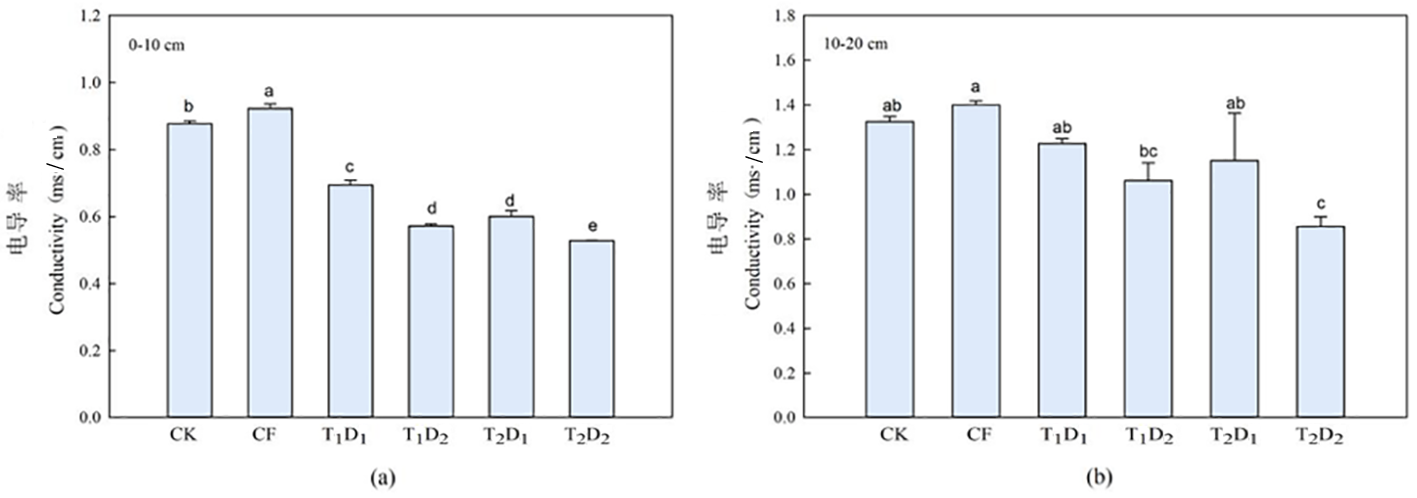
图4 氮肥减量配施生物有机肥下土壤电导率的变化 注:(a)0~10 cm电导率;(b)10~20 cm电导率
Fig.4 Changes of nitrogen reduction combined with bio organic fertilizer on soil electrical conductivity Notes: (a)0-10 cm conductivity; (b)10-20 cm conductivity
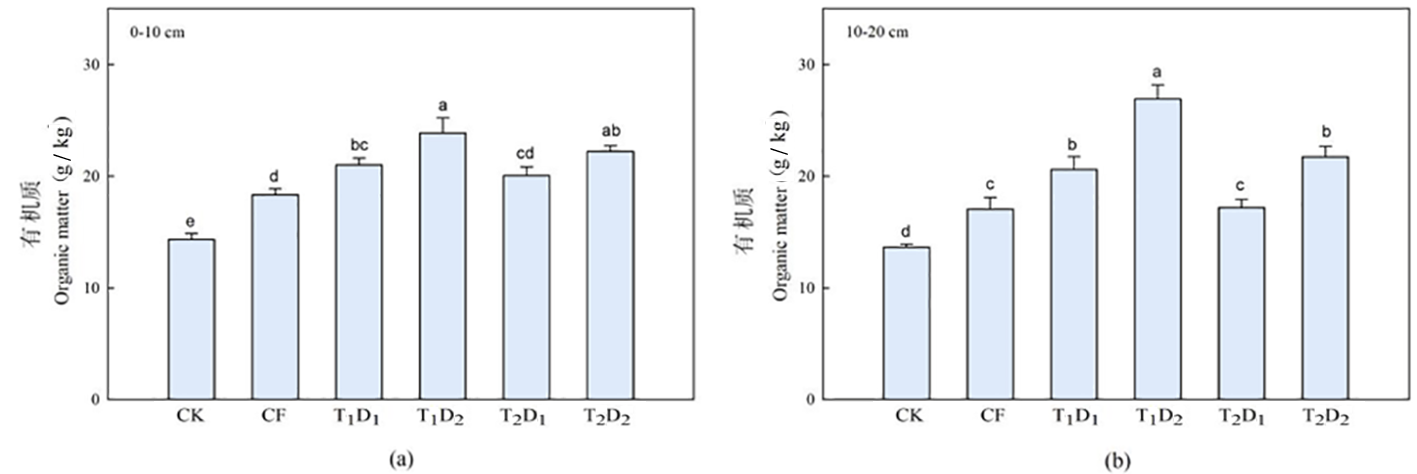
图5 氮肥减量配施生物有机肥下土壤有机质含量的变化 注:(a)0~10 cm有机质;(b)10~20 cm有机质
Fig.5 Changes of nitrogen reduction combined with bio organic fertilizer on soil organic matter content Notes: (a) 0-10 cm organic matter;(b) 10-20 cm organic matter

图6 氮肥减量配施生物有机肥下土壤全氮、全磷、全钾含量的变化 注:(a)0~10 cm全氮;(b)10~20 cm全氮;(c)0~10 cm全磷;(d)10~20 cm全磷;(e)0~10 cm全钾;(f)10~20 cm全钾
Fig.6 Changes of reduced nitrogen fertilizer combined with bio organic fertilizer on the contents of total nitrogen, total phosphorus and total potassium in soil Notes: (a) 0-10 cm total nitrogen; (b) 10-20 cm total nitrogen; (c) 0-10 cm total phosphorus; (d) 10-20 cm total phosphorus; (e) 0-10 cm total potassium; (f) 10-20 cm total potassium
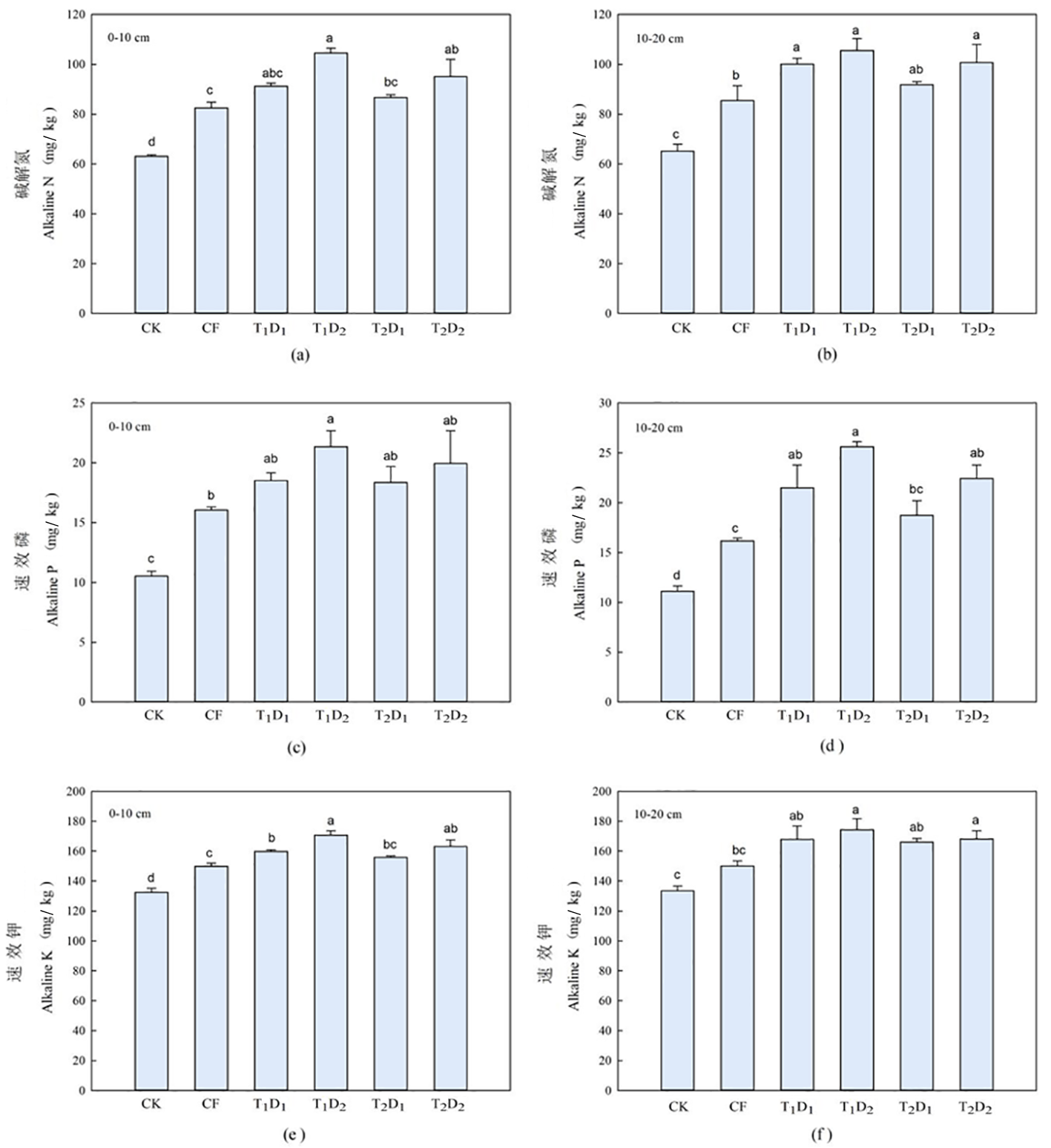
图7 氮肥减量配施生物有机肥下土壤碱解氮、速效磷、速效钾含量的变化 注:(a)0~10 cm碱解氮,(b)10~20 cm碱解氮,(c)0~10 cm速效磷,(d)10~20 cm速效磷,(e)0~10 cm速效钾,(f)10~20 cm速效钾
Fig.7 Effects of nitrogen reduction combined with bio organic fertilizer on the contents of alkali hydrolyzable nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium in soil Notes: (a) 0-10 cm alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen,(b) 10-20 cm alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen,(c) 0-10 cm available phosphorus,(d) 10-20 cm available phosphorus, (e) 0-10 cm available potassium, (f) 10-20 cm available potassium
| 处理 Treatments | 细菌 Bacteria (106 cfu/g) | 真菌 Fungus (104 cfu/g) | 放线菌 Actinomycetes (105 cfu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.30±0.14d | 5.65±0.49ab | 2.77±0.18c |
| CF | 1.19±0.29d | 6.90±0.85a | 3.30±0.28c |
| T1D1 | 6.15±0.78c | 4.35±0.63bc | 4.15±0.21b |
| T1D2 | 9.50±0.02b | 3.07±0.79c | 4.78±0.31ab |
| T2D1 | 8.00±0.01bc | 3.90±0.57c | 4.35±0.35b |
| T2D2 | 12.50±0.71a | 3.01±0.13c | 5.20±0.42a |
表3 氮肥减量配施生物有机肥下土壤微生物数量的变化
Tab.3 Changes of nitrogen reduction combined with bio organic fertilizer on the number of soilmicroorganisms
| 处理 Treatments | 细菌 Bacteria (106 cfu/g) | 真菌 Fungus (104 cfu/g) | 放线菌 Actinomycetes (105 cfu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.30±0.14d | 5.65±0.49ab | 2.77±0.18c |
| CF | 1.19±0.29d | 6.90±0.85a | 3.30±0.28c |
| T1D1 | 6.15±0.78c | 4.35±0.63bc | 4.15±0.21b |
| T1D2 | 9.50±0.02b | 3.07±0.79c | 4.78±0.31ab |
| T2D1 | 8.00±0.01bc | 3.90±0.57c | 4.35±0.35b |
| T2D2 | 12.50±0.71a | 3.01±0.13c | 5.20±0.42a |
| [1] | 杨利, 颜安, 宁松瑞, 等. 生物有机肥对盐胁迫小麦幼苗生长和土壤培肥的影响[J]. 新疆农业大学学报, 2021, 44(4): 291-299. |
| YANG Li, YAN An, NING Songrui, et al. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on wheat seedling growth and soil fertility improvement under salt stress[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2021, 44(4): 291-299. | |
| [2] | 田长彦, 买文选, 赵振勇. 新疆干旱区盐碱地生态治理关键技术研究[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(22): 7064-7068. |
| TIAN Changyan, MAI Wenxuan, ZHAO Zhenyong. Study on key technologies of ecological management of saline alkali land in arid area of Xinjiang[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(22): 7064-7068. | |
| [3] | 蔡宜响. 轮作休耕模式及氮肥减量运筹对土壤理化性质、氮素利用及水稻产量的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2021. |
| CAI Yixiang. Effects of Crop Rotation and Nitrogen Reduction on Soil Quality, Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2021. | |
| [4] | 金丁坤, 侯红燕, 周红, 等. 一种盐碱地水稻氮肥减量施肥方法[J]. 农村经济与科技, 2021, 32(12): 33-35. |
| JIN Dingkun, HOU Hongyan, ZHOU Hong, et al. Nitrogen fertilizer reduction fertilization method for rice in saline-alkali land[J]. Rural Economy and Science-Technology, 2021, 32(12): 33-35. | |
| [5] | 张迎春, 颉建明, 李静, 等. 生物有机肥部分替代化肥对莴笋及土壤理化性质和微生物的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(4): 196-205. |
| ZHANG Yingchun, XIE Jianming, LI Jing, et al. Effects of partial substitution of chemical fertilizer by Bio-organic fertilizer on Asparagus lettuce and soil physical-chemical properties and microorganisms[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(4): 196-205. | |
| [6] | 张金柱. 生物有机肥对盐碱土理化性质及苜蓿生理反应影响的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2007. |
| ZHANG Jinzhu. Effect of Microbial Organic Fertilizer on Physicochemical Property of Saline Alkali Soil and Physiologic Reaction of Alfalfa[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2007. | |
| [7] | 李晓爽, 党红凯, 宋妮, 等. 肥-沙混施对盐碱地冬小麦群体库源关系的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(11): 1695-1705. |
| LI Xiaoshuang, DANG Hongkai, SONG Ni, et al. Effects of mixed application of biological organic fertilizer and Yellow River sediment on the sink-source relationship of winter wheat in saline-alkaline soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(11): 1695-1705. | |
| [8] | 刘艳, 李波, 隽英华, 等. 生物有机肥对盐碱地玉米渗透调节物质及土壤微生物的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2018, 31(5): 1013-1018. |
| LIU Yan, LI Bo, JUN Yinghua, et al. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on osmotic adjustment and soil microorganisms of maize in saline-alkali soil[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 31(5): 1013-1018. | |
| [9] | 朱利霞, 曹萌萌, 桑成琛, 等. 生物有机肥替代化肥对玉米土壤肥力及酶活性的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 2022, 40(1): 67-72. |
| ZHU Lixia, CAO Mengmeng, SANG Chengchen, et al. Effects of bio-fertilizer partially substituting chemical fertilizer on soil fertility and enzyme activity in maize field[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2022, 40(1): 67-72. | |
| [10] | 史可. 重铬酸钾外加热法在施用生物炭土壤有机质含量测定中的应用改进[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022. |
| SHI Ke. Application Improvement of Potassium Dichromate External Heating Method in the Determination of Soil Organic Matter Content with Biochar Applicationn[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| [11] | 孙瑞莲, 朱鲁生, 赵秉强, 等. 长期施肥对土壤微生物的影响及其在养分调控中的作用[J]. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(10): 1907-1910. |
|
SUN Ruilian, ZHU Lusheng, ZHAO Bingqiang, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil microorganism and its role in adjusting and controlling soil fertility[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 15(10): 1907-1910.
PMID |
|
| [12] | 龚兰新, 康新平, 王海娟. 六道湾煤矿塌陷区土壤中总磷及有效磷的测定[J]. 新疆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 26(2): 89-92. |
| GONG Lanxin, KANG Xinping, WANG Haijuan. Determination on the total and effective phosphorus in soil of Urumqi liudaowan coal mines[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2007, 26(2): 89-92. | |
| [13] | 王维进, 李仁岗. 河北平原土壤有效氮测定方法的评价[J]. 土壤通报, 1991, 22(6): 263-266. |
| WANG Weijin, LI Rengang. Evaluation of determination methods of soil available nitrogen in Hebei Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1991, 22(6): 263-266. | |
| [14] | 刘占锋, 傅伯杰, 刘国华, 等. 土壤质量与土壤质量指标及其评价[J]. 生态学报, 2006, 26(3): 901-913. |
| LIU Zhanfeng, FU Bojie, LIU Guohua, et al. Soil quality: concept, indicators and its assessment[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(3): 901-913. | |
| [15] | 李秀英, 赵秉强, 李絮花, 等. 不同施肥制度对土壤微生物的影响及其与土壤肥力的关系[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(8): 1591-1599. |
| LI Xiuying, ZHAO Bingqiang, LI Xuhua, et al. Effects of different fertilization systems on soil microbe and its relation to soil fertility[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, 38(8): 1591-1599. | |
| [16] | 陶梦慧. 生物有机肥施用的土壤和作物效应[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2017. |
| TAO Menghui. Effects of Bio-Organic Fertilizers on Soil and Crops[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [17] |
黄媛媛, 马慧媛, 黄亚丽, 等. 生物有机肥和化肥配施对冬小麦产量及土壤生物指标的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(6): 160-169.
DOI |
| HUANG Yuanyuan, MA Huiyuan, HUANG Yali, et al. Effects of applying bio-organic fertilizer and reducing chemical fertilizer on production and soil biological indexes of winter wheat[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2019, 34(6): 160-169. | |
| [18] | 宋以玲, 于建, 陈士更, 等. 化肥减量配施生物有机肥对油菜生长及土壤微生物和酶活性影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(1): 352-360. |
| SONG Yiling, YU Jian, CHEN Shigeng, et al. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer with application of bio-organic fertilizer on rape growth, microorganism and enzymes activities in soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(1): 352-360. | |
| [19] |
王家宝, 孙义祥, 李虹颖, 等. 生物有机肥用量及部分替代化肥对小麦产量效应的研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(36): 6-11.
DOI |
|
WANG Jiabao, SUN Yixiang, LI Hongying, et al. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer and partial substitution of chemical fertilizer on wheat yield[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(36): 6-11.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 张敏, 陈佳佳, 杨正, 等. 化肥减施配施生物有机肥对花生生长、保护酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(21): 86-93. |
| ZHANG Min, CHEN Jiajia, YANG Zheng, et al. Influences of reduced chemical fertilizer combined with bio-organic fertilizer on growth, protective enzyme activities and yield of peanuts[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(21): 86-93. | |
| [21] | 李北齐, 王倡宪, 孟瑶, 等. 生物有机肥对盐碱土壤养分及玉米产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(21): 182-186. |
|
LI Beiqi, WANG Changxian, MENG Yao, et al. Effects of microbial organic fertilizer on saline-alkali soil nutrient and maize production[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2011, 27(21): 182-186.
DOI |
|
| [22] | Ahmed M A, El-Agyzy F H A, Shaban K A. Influence of nitrogen sources and bio-fertilizer on soil nutrients, yield and quality of cowpea under saline soil conditions[J]. Asian Soil Research Journal, 2019: 1-14. |
| [23] | 尹志荣, 黄建成, 桂林国, 等. 微生物肥对原生盐碱土理化性质及枸杞生长的影响[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2018, 59(12): 48-51, 75. |
| YIN Zhirong, HUANG Jiancheng, GUI Linguo, et al. Effect of microbial fertilizer on physico chemical property of native saline-alkali soil and growth of wolfberry[J]. Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2018, 59(12): 48-51, 75. | |
| [24] | 柳影, 丁文娟, 曹群, 等. 套种韭菜配施生物有机肥对香蕉枯萎病及土壤微生物的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(2): 303-309. |
| LIU Ying, DING Wenjuan, CAO Qun, et al. Effects of Allium tuberosum interplanting and Bio-organic fertilizer application on banana wilt disease and soil microorganisms[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(2): 303-309. | |
| [25] | Zhao J, Liu J, Liang H, et al. Manipulation of the rhizosphere microbial community through application of a new bio-organic fertilizer improves watermelon quality and health[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(2): e0192967. |
| [1] | 扁青永, 付彦博, 祁通, 黄建, 蒲胜海, 孟阿静, 哈丽哈什·依巴提. 新疆南疆盐碱地棉花出苗影响因素及保苗措施分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 95-100. |
| [2] | 王春生, 李剑峰, 张跃强, 樊哲儒, 王重, 高新, 时佳, 张宏芝, 王立红, 夏建强, 王芳平, 赵奇. 新疆主栽春小麦品种花药培养力基因型差异分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2081-2086. |
| [3] | 袁莹莹, 赵经华, 迪力穆拉提·司马义, 杨庭瑞. 基于apriori算法对盆栽春小麦生理指标及产量的分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1861-1871. |
| [4] | 刘旭欢, 于姗, 刘跃, 石书兵. 不同粒级春小麦种子活力差异比较[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1883-1887. |
| [5] | 杨梅, 赵红梅, 迪丽热巴·夏米西丁, 杨卫君, 张金汕, 惠超. 氮肥减量配施生物质炭对春小麦群体结构、光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1582-1589. |
| [6] | 王一钊, 杨其志, 刘玉秀, 阿拉依·努尔卡马力, Vladimir Shvidchenko, 张正茂. PEG胁迫下评价哈萨克斯坦不同春小麦种质苗期的抗旱性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1352-1360. |
| [7] | 张宏芝, 王立红, 时佳, 孔德鹏, 王重, 高新, 李剑峰, 王春生, 夏建强, 樊哲儒, 张跃强. 土壤水分对不同抗旱性春小麦品种叶片保护性酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1041-1047. |
| [8] | 古力尼尕尔·吐尔洪, 张金汕, 李丹丹, 张路路, 王润琪, 石书兵. 不同引发剂处理对春小麦种子活力及生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 869-877. |
| [9] | 董艳雪, 贾永红, 张金汕, 李丹丹, 王凯, 罗四维, 王润琪, 石书兵. 不同生态区环境下春小麦干物质积累及产量形成分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1848-1857. |
| [10] | 李怀胜, 艾洪玉, 孟玲, 王贺亚, 张磊, 艾海峰. 减氮下运筹养分吸收高峰期追施比例对春小麦的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1866-1872. |
| [11] | 王兴州, 时晓磊, 张恒, 曲可佳, 耿洪伟, 丁孙磊, 张金波, 严勇亮. 引进春小麦品种萌发期耐盐性鉴定及评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1353-1362. |
| [12] | 曲可佳, 时晓磊, 张恒, 王兴州, 耿洪伟, 丁孙磊, 张金波, 严勇亮. PEG处理下引进春小麦品种苗期抗旱性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1363-1371. |
| [13] | 刘兴宇, 袁建钰, 李广, 张娟, 徐万恒, 张霞霞. 陇中黄土高原春小麦品种和优化施肥[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1398-1405. |
| [14] | 朱宝国, 匡恩俊, 滕占林, 孟庆英, 王囡囡, 冯浩原, 邱磊, 高雪冬, 张春峰. 不同生物有机肥配施化肥对大豆植株生长、抗病及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1127-1133. |
| [15] | 贾永红, 魏海鹏, 侯殿亮, 曾潮武, 纳斯如拉·克热木, 梁晓东. 新疆自育春小麦品种抗旱性及农艺性状相关性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(12): 2940-2948. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 33
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 203
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||