

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (8): 1907-1915.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.08.010
• 作物遗传育种·种质资源·分子遗传学·耕作栽培·生理生化 • 上一篇 下一篇
赵敏华1,2( ), 宋秉曦1, 张宇鹏1, 高志红1, 朱勇勇1, 陈晓远1(
), 宋秉曦1, 张宇鹏1, 高志红1, 朱勇勇1, 陈晓远1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-07-03
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-19
通信作者:
陈晓远(1968-),男,广东韶关人,教授,博士,硕士生/博士生导师,研究方向为作物水分与养分高效利用,(E-mail)chenxy2@163.com作者简介:赵敏华(1997-),女,山西人,硕士,研究方向为作物水分与养分高效利用,(E-mail)zmhuayk@163.com
基金资助:
ZHAO Minhua1,2( ), SONG Bingxi1, ZHANG Yupeng1, GAO Zhihong1, ZHU Yongyong1, CHEN Xiaoyuan1(
), SONG Bingxi1, ZHANG Yupeng1, GAO Zhihong1, ZHU Yongyong1, CHEN Xiaoyuan1( )
)
Received:2023-07-03
Published:2024-08-20
Online:2024-09-19
Correspondence author:
CHEN Xiaoyuan(1968-), male, from Shaoguan Guangdong,professor,Ph.D.,master/doctoral supervison,research direction:Crop water and nutrients are highly effcient, (E-mail)chenxy2@163.comSupported by:摘要:
【目的】研究旱作条件下减量施用氮肥对水稻营养元素含量以及氮肥偏生产力的影响。【方法】以美香粘为材料进行大田试验,设置5个处理:常规淹水施氮(216 kg/hm2,CK)、旱作施氮(216 kg/hm2,H0)、旱作减氮10%(194.4 kg/hm2,H10)和旱作减氮20%(172.8 kg/hm2,H20)、旱作减氮40%(129.6 kg/hm2,H40),研究不同水分条件和氮肥减施对稻田土壤基础养分、水稻生物量、含氮量以及产量和氮肥偏生产力的影响。【结果】与传统淹水栽培相比,水稻旱作显著提高了土壤有机质含量,显著降低了土壤pH值和速效磷含量,其它养分含量均无显著变化。旱作降低了水稻根、茎、叶、穗生物量、总氮含量以及氮肥偏生产力,水稻单位面积株数、千粒重、产量在旱作处理下无明显变化。在旱作条件下减施氮肥,土壤养分状况变化各异,与旱作和传统淹水栽培相比变化较小。水稻根、茎、叶、穗生物量和含氮量随着氮肥减施程度的增加下降,穗生物量和氮含量在H40处理下相比H0处理显著升高。氮肥偏生产力随着氮肥减施程度增加而提高,在H40时达到最高。与H0相比,H10、H20的产量降低幅度不显著,H40降低幅度大于H10和H20,但其产量与H0差异不显著。【结论】在旱作条件下氮肥减施40%,可在产量不显著降低的同时却显著提高肥料生产力。
中图分类号:
赵敏华, 宋秉曦, 张宇鹏, 高志红, 朱勇勇, 陈晓远. 旱作条件下氮肥减施对水稻产量及氮肥偏生产力的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1907-1915.
ZHAO Minhua, SONG Bingxi, ZHANG Yupeng, GAO Zhihong, ZHU Yongyong, CHEN Xiaoyuan. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer reduction on rice yield and nitrogen partial factor productivity under dry farming conditions[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1907-1915.
| 处理 Treatments | N用量 N dosage (kg/hm2) | P2O5用量 P2O5 dosage (kg/hm2) | K2O 用量 K2O dosage (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 216 | 112.5 | 112.5 |
| H0 | 216 | 112.5 | 112.5 |
| H10 | 194.4 | 112.5 | 112.5 |
| H20 | 172.8 | 112.5 | 112.5 |
| H40 | 129.6 | 112.5 | 112.5 |
表1 试验处理
Tab.1 Experimental treatment
| 处理 Treatments | N用量 N dosage (kg/hm2) | P2O5用量 P2O5 dosage (kg/hm2) | K2O 用量 K2O dosage (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 216 | 112.5 | 112.5 |
| H0 | 216 | 112.5 | 112.5 |
| H10 | 194.4 | 112.5 | 112.5 |
| H20 | 172.8 | 112.5 | 112.5 |
| H40 | 129.6 | 112.5 | 112.5 |
| 处理 Treatments | 第一次 First (kg) | 第二次 Second (kg) | 第三次 Third (kg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尿素 Urea | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superpho- sphate | 氯化钾 Potassium chloride | 尿素 Urea | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superpho- sphate | 氯化钾 Potassium chloride | 尿素 Urea | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superpho- sphate | 氯化钾 Potassium chloride | |
| CK | 0.94 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.83 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 1.39 | 0.58 |
| H0 | 0.94 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.83 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 1.39 | 0.58 |
| H10 | 0.84 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 0.75 | 1.39 | 0.58 |
| H20 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 0.67 | 1.39 | 0.58 |
| H40 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 0.50 | 1.39 | 0.58 |
表2 不同时期氮磷钾施肥量
Tab.2 Fertilization amount in different periods
| 处理 Treatments | 第一次 First (kg) | 第二次 Second (kg) | 第三次 Third (kg) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尿素 Urea | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superpho- sphate | 氯化钾 Potassium chloride | 尿素 Urea | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superpho- sphate | 氯化钾 Potassium chloride | 尿素 Urea | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superpho- sphate | 氯化钾 Potassium chloride | |
| CK | 0.94 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.83 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 1.39 | 0.58 |
| H0 | 0.94 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.83 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 1.39 | 0.58 |
| H10 | 0.84 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 0.75 | 1.39 | 0.58 |
| H20 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 0.67 | 1.39 | 0.58 |
| H40 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 2.36 | 0.99 | 0.50 | 1.39 | 0.58 |
| 处理 Treatments | 土壤养分含量 Soil nutrient content | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH值 pH value | 有机质Organic matter (g/kg) | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen (mg/kg) | 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen (mg/kg) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen (mg/kg) | 速效磷 Olsen-P (mg/kg) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg/kg) | |
| CK | 6.21±0.03a | 2.79±0.82b | 7.21±0.18a | 3.41±0.21c | 100.28±5.77b | 124.77±3.42ab | 133.99±1.27b |
| H0 | 5.83±0.04b | 4.83±0.21a | 7.45±0.96a | 3.84±0.08bc | 98.61±4.01b | 98.74±16.24c | 132.02±4.08bc |
| H10 | 5.82±0.01b | 4.00±0.30ab | 8.35±0.76a | 3.17±0.53c | 103.98±6.02b | 110.33±0.97bc | 141.22±1.27a |
| H20 | 5.62±0.01c | 4.00±0.59ab | 8.75±0.49a | 28.41±0.25a | 155.21±5.95a | 125.64±0.46ab | 141.83±3.83a |
| H40 | 5.35±0.01d | 3.69±0.11ab | 7.68±0.83a | 4.45±0.51b | 96.96±2.57b | 137.85±11.75a | 126.25±0.76c |
表3 不同处理下土壤养分含量的变化
Tab. 3 Changes of soil nutrient content of different treatments
| 处理 Treatments | 土壤养分含量 Soil nutrient content | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH值 pH value | 有机质Organic matter (g/kg) | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen (mg/kg) | 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen (mg/kg) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen (mg/kg) | 速效磷 Olsen-P (mg/kg) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg/kg) | |
| CK | 6.21±0.03a | 2.79±0.82b | 7.21±0.18a | 3.41±0.21c | 100.28±5.77b | 124.77±3.42ab | 133.99±1.27b |
| H0 | 5.83±0.04b | 4.83±0.21a | 7.45±0.96a | 3.84±0.08bc | 98.61±4.01b | 98.74±16.24c | 132.02±4.08bc |
| H10 | 5.82±0.01b | 4.00±0.30ab | 8.35±0.76a | 3.17±0.53c | 103.98±6.02b | 110.33±0.97bc | 141.22±1.27a |
| H20 | 5.62±0.01c | 4.00±0.59ab | 8.75±0.49a | 28.41±0.25a | 155.21±5.95a | 125.64±0.46ab | 141.83±3.83a |
| H40 | 5.35±0.01d | 3.69±0.11ab | 7.68±0.83a | 4.45±0.51b | 96.96±2.57b | 137.85±11.75a | 126.25±0.76c |
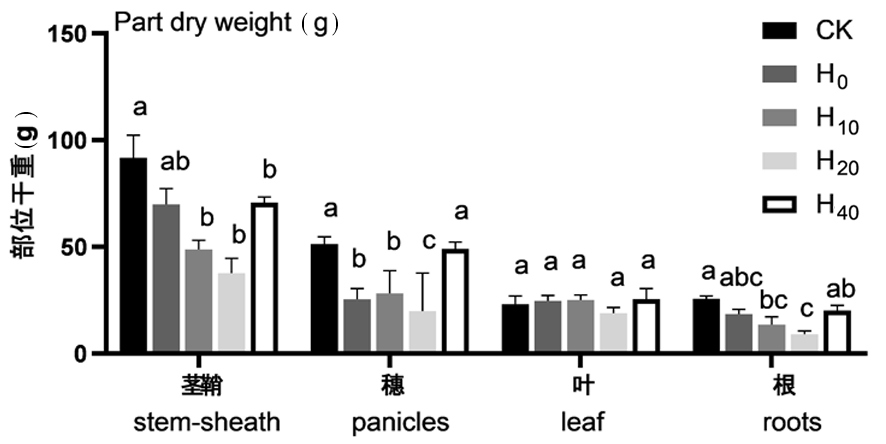
图1 不同处理水稻各器官生物量 注:茎鞘、穗、叶、根分别在CK、H0、H10、H20、H40处理下的生物量含量,图中a、b、c、d字母代表各部位之间的差异性比较,具有相同字母则表示无显著性差异(P>0.05),具有不同字母则表示差异显著(P<0.05),仅进行各部位组间比较
Fig.1 Biomass of different parts of rice under different treatments Notes: The biomass contents of stem-sheath, panicles, leaf and roots under CK, H0, H10, H20 and H40 treatments were compared. The letters a, b, c and d represent the differences between different parts. The same letters indicate no significant difference (P>0.05), and different letters indicate significant difference (P<0.05)
| 处理 Treatments | 植株氮含量 plant nitrogen content (g/株) | 植株总氮量 Total nitrogen content of plant (g/株) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎 Stem | 穗 Cluster | 叶片 Leaf | 根 Root | ||
| CK | 0.67±0.07a | 0.69±0.05a | 0.54±0.07a | 0.35±0.07a | 2.25 |
| H0 | 0.66±0.07a | 0.39±0.01c | 0.54±0.02a | 0.24±0.03b | 1.83 |
| H10 | 0.31±0.05b | 0.36±0.01c | 0.44±0.06b | 0.13±0.02c | 1.24 |
| H20 | 0.41±0.15b | 0.30±0.03d | 0.31±0.11c | 0.11±0.04c | 1.25 |
| H40 | 0.35±0.02b | 0.54±0.05b | 0.38±0.01c | 0.14±0.01c | 1.45 |
表4 水稻成熟期植株各器官氮含量的变化
Tab.4 Changes of nitrogen content in different parts of rice plant after harvest
| 处理 Treatments | 植株氮含量 plant nitrogen content (g/株) | 植株总氮量 Total nitrogen content of plant (g/株) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎 Stem | 穗 Cluster | 叶片 Leaf | 根 Root | ||
| CK | 0.67±0.07a | 0.69±0.05a | 0.54±0.07a | 0.35±0.07a | 2.25 |
| H0 | 0.66±0.07a | 0.39±0.01c | 0.54±0.02a | 0.24±0.03b | 1.83 |
| H10 | 0.31±0.05b | 0.36±0.01c | 0.44±0.06b | 0.13±0.02c | 1.24 |
| H20 | 0.41±0.15b | 0.30±0.03d | 0.31±0.11c | 0.11±0.04c | 1.25 |
| H40 | 0.35±0.02b | 0.54±0.05b | 0.38±0.01c | 0.14±0.01c | 1.45 |
| 处理 Treatments | 产量 Yield (kg/hm2) | 千粒重 thousand-grain weight (g/千粒) | 株数 (株/cm2) | 氮肥偏生产力 nitrogen partial factor productivity (kg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12 894.74±131.58a | 24.17±1.01a | 40.50±2.12a | 53 |
| H0 | 12 587.72±303.87ab | 23.94±0.72a | 39.50±3.54a | 52.44 |
| H10 | 12 543.86±151.94ab | 23.48±0.49a | 37.00±1.41a | 58.07 |
| H20 | 12 456.14±724.68ab | 22.91±0.36ab | 26.50±2.12b | 64.88 |
| H40 | 12 061.40±200.98b | 22.15±0.63b | 24.50±0.71b | 83.76 |
表5 不同处理对水稻产量及其构成因素及氮肥偏生产力的影响
Tab.5 Effects of different treatments on rice yield and its components
| 处理 Treatments | 产量 Yield (kg/hm2) | 千粒重 thousand-grain weight (g/千粒) | 株数 (株/cm2) | 氮肥偏生产力 nitrogen partial factor productivity (kg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12 894.74±131.58a | 24.17±1.01a | 40.50±2.12a | 53 |
| H0 | 12 587.72±303.87ab | 23.94±0.72a | 39.50±3.54a | 52.44 |
| H10 | 12 543.86±151.94ab | 23.48±0.49a | 37.00±1.41a | 58.07 |
| H20 | 12 456.14±724.68ab | 22.91±0.36ab | 26.50±2.12b | 64.88 |
| H40 | 12 061.40±200.98b | 22.15±0.63b | 24.50±0.71b | 83.76 |
| [1] |
高志红, 陈晓远, 曾越. 局部根系水分胁迫下氮素形态对水稻幼苗生理特性和根系生长的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(2): 154-161.
DOI |
| GAO Zhihong, CHEN Xiaoyuan, ZENG Yue. Effects of N forms on physiological characteristics and root growth of rice seedling in condition of partial root water stress[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2019, 34(2): 154-161. | |
| [2] | Wang W Q, Peng S B, Liu H Y, et al. The possibility of replacing puddled transplanted flooded rice with dry seeded rice in central China: a review[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, (214): 310-320. |
| [3] |
高志红, 林浴霞, 张宇鹏, 等. 不同水分胁迫和氮素形态对水稻生长及木质部液流离子含量的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(2): 146-153.
DOI |
| GAO Zhihong, LIN Yuxia, ZHANG Yupeng, et al. Growth and ion content in rice seedling xylem sap under different water stresses and nitrogen forms[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(2): 146-153. | |
| [4] | Jiang H, Song Z, Su Q W, et al. Transcriptomic and metabolomic reveals silicon enhances adaptation of rice under dry cultivation by improving flavonoid biosynthesis, osmoregulation, and photosynthesis[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, (13): 967537. |
| [5] |
Jiang H, Thobakgale T, Li Y Z, et al. Construction of dominant rice population under dry cultivation by seeding rate and nitrogen rate interaction[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 7189.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Zhan J H, Lu X, Liu H Y, et al. Mesocotyl elongation, an essential trait for dry-seeded rice (Oryza sativa L.): a review of physiological and genetic basis[J]. Planta, 2019, 251(1): 27. |
| [7] | Jiang W J, Huang W C, Liang H, et al. Is rice field a nitrogen source or sink for the environment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, (283): 117122. |
| [8] | Liu X W, Wang H Y, Zhou J M, et al. Effect of N fertilization pattern on rice yield, N use efficiency and fertilizer-N fate in the Yangtze River Basin, China[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(11): e0166002. |
| [9] |
Padukkage D, Geekiyanage S, Reparaz J M, et al. Bradyrhizobium japonicum, B. elkanii and B. diazoefficiens interact with rice (Oryza sativa), promote growth and increase yield[J]. Current Microbiology, 2021, 78(1): 417-428.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
汤国平, 熊强强, 钟蕾, 等. 双季早稻氮素亏缺补偿效应的形成及其生理机制初探[J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(8): 1585-1593.
DOI |
|
TANG Guoping, XIONG Qiangqiang, ZHONG Lei, et al. Primary research on the formation and its physiological mechanism of nitrogen deficiency compensatory effects in double-season early rice[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(8): 1585-1593.
DOI |
|
| [11] | Jacoby R, Peukert M, Succurro A, et al. The role of soil microorganisms in plant mineral nutrition-current knowledge and future directions[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, (8): 1617. |
| [12] | Liu Q, Wu K, Song W Z, et al. Improving crop nitrogen use efficiency toward sustainable green revolution[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2022, (73): 523-551. |
| [13] | 李姗, 黄允智, 刘学英, 等. 作物氮肥利用效率遗传改良研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2021, 43(7): 629-640. |
| LI Shan, HUANG Yunzhi, LIU Xueying, et al. Genetic improvement of nitrogen use efficiency in crops[J]. Hereditas(Beijing), 2021, 43(7): 629-640. | |
| [14] | Huang L N, Cheng S M, Liu H L, et al. Effects of nitrogen reduction combined with organic fertilizer on growth and nitrogen fate in banana at seedling stage[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, (214): 113826. |
| [15] | Li T L, Wang Z G, Wang C X, et al. Ammonia volatilization mitigation in crop farming: a review of fertilizer amendment technologies and mechanisms[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, (303): 134944. |
| [16] | Sun H J, Zhang H L, Xiao H D, et al. Wheat straw biochar application increases ammonia volatilization from an urban compacted soil giving a short-term reduction in fertilizer nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2019, 19(4): 1624-1631. |
| [17] |
宫亮, 金丹丹, 牛世伟, 等. 长期定位氮肥减施对水稻产量和氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2022, 28(3): 42-46.
DOI |
|
GONG Liang, JIN Dandan, NIU Shiwei, et al. Effects of long-term position nitrogen fertilizer reduction on rice yield and nitrogen absorption and utilizationn[J]. China Rice, 2022, 28(3): 42-46.
DOI |
|
| [18] | 尹彩侠, 刘志全, 孔丽丽, 等. 减氮增密提高寒地水稻产量与氮素吸收利用[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2022, 39(6): 1124-1132. |
| YIN Caixia, LIU Zhiquan, KONG Lili, et al. Reducing nitrogen and increasing rice transplanting density in a cold region of China can improve rice yield, nitrogen absorption, and nitrogen utilization[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2022, 39(6): 1124-1132. | |
| [19] |
张小祥, 邵士梅, 赵步洪, 等. 氮肥减施模式对不同穗型迟熟中粳水稻产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3): 278-294.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Xiaoxiang, SHAO Shimei, ZHAO Buhong, et al. Effects of nitrogen reduction model on yield and nitrogen absorption and utilization of late-maturing mid-japonica rice with different panicle types[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 278-294.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 彭晓宗, 翟丽梅, 王洪媛, 等. 辽河三角洲稻区缓释肥施用下氮肥减施潜力研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022,(5): 51-60. |
| PENG Xiaozong, ZHAI Limei, WANG Hongyuan, et al. Reduction potential of nitrogen fertilizer under slow-release fertilizer application in Liaohe Delta rice area[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022,(5): 51-60. | |
| [21] |
朱勇勇, 宋秉羲, 杨王敏, 等. 旱作条件下氮肥减施对水稻生长、产量与经济收益的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2150-2156.
DOI |
| ZHU Yongyong, SONG Bingxi, YANG Wangmin, et al. Effects of reduced nitrogen application on rice growth, yield and economy profits under dry farming conditions[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(11): 2150-2156. | |
| [22] | Jin X X, Zuo Q, Ma W W, et al. Water consumption and water-saving characteristics of a ground cover rice production system[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, (540): 220-231. |
| [23] | 何进宇, 刘飞杨, 马波, 等. 不同旱作节水灌溉条件对土壤理化性质及水稻产量的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2023, 41(1): 121-127. |
| HE Jinyu, LIU Feiyang, MA Bo, et al. Effects of different irrigation conditions on soilphysicochemical properties and rice yield[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2023, 41(1): 121-127. | |
| [24] | Li Y S, Wu L H, Zhao L M, et al. Influence of continuous plastic film mulching on yield, water use efficiency and soil properties of rice fields under non-flooding condition[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2007, 93(2): 370-378. |
| [25] | 柳燕兰, 马明生, 张绪成, 等. 施肥对旱作区新修梯田土壤理化性质及马铃薯产量的影响[J]. 寒旱农业科学, 2022, 1(11): 115-118. |
| LIU Yanlan, MA Mingsheng, ZHANG Xucheng, et al. Effects of fertilization on soil physical and chemical properties and potato yield of new terraced farmland in raid-fed region[J]. Journal of Cold-Arid Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 1(11): 115-118. | |
| [26] | 孙红, 孙明明, 吕世翔, 等. 水旱轮作对土壤和水稻的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2019,(10): 141-143. |
| SUN Hong, SUN Mingming, LYU Shixiang, et al. Effects of paddy-upland rotations on soil and rice[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019,(10): 141-143. | |
| [27] | 赵龙, 张友良, 王娟, 等. 水稻覆膜旱作对土壤环境及水稻生长的影响研究进展[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2020, 31(5): 255-260. |
| ZHAO Long, ZHANG Youliang, WANG Juan, et al. Research progress of effects of ground cover rice production system with plastic film mulch on soil environment and rice growth[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2020, 31(5): 255-260. | |
| [28] | 李艾芬, 麻万诸, 章明奎. 水稻土的酸化特征及其起因[J]. 江西农业学报, 2014, 26(1): 72-76. |
| LI Aifen, MA Wanzhu, ZHANG Mingkui. Characteristics and causes of acidification of paddy soil[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2014, 26(1): 72-76. | |
| [29] | 樊红柱, 曾祥忠, 张冀, 等. 覆盖旱作水稻的生长及水分利用效率研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2010, 23(2): 349-353. |
| FAN Hongzhu, ZENG Xiangzhong, ZHANG Ji, et al. Effects of different mulch modes on rice production and water utilization efficiency[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 23(2): 349-353. | |
| [30] | 赵成全, 姜洪涛, 任朝明, 等. 水稻旱直播高产高效栽培关键技术的研究[J]. 吉林农业科学, 2007, 32(4): 9-11. |
| ZHAO Chengquan, JIANG Hongtao, REN Chaoming, et al. Studies on key techniques of sowing rice directly on dry land for high yield and high efficiency[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 32(4): 9-11. | |
| [31] | 朱伦. 早稻旱直播栽培试验初报[J]. 广西农学报, 2008, 23(3): 10-11, 15. |
| ZHU Lun. A report on dry direct seeding cultivation technique of early rice[J]. Journal of Guangxi Agriculture, 2008, 23(3): 10-11, 15. | |
| [32] | 庞喆, 王启龙. 不同灌溉量对土壤理化性质及水稻生长发育的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2019, 38(S2): 37-41. |
| PANG Zhe, WANG Qilong. Effects of different irrigation amounts on soil physical and chemical properties and rice growth and development[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2019, 38(S2): 37-41. | |
| [33] | 李金才, 黄义德, 魏凤珍, 等. 旱作对水稻干物质积累、分配及产量的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2001, 29(1): 56-57. |
| LI Jincai, HUANG Yide, WEI Fengzhen, et al. Effects of dry farming on dry matter accumulation, distribution and yield of rice[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2001, 29(1): 56-57. | |
| [34] | 魏永霞, 侯景翔, 吴昱, 等. 不同水分管理旱直播水稻生长生理与节水效应[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(8): 253-264. |
| WEI Yongxia, HOU Jingxiang, WU Yu, et al. Effects of different water management on growth physiology and water-saving of dry direct seeding rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(8): 253-264. | |
| [35] | 徐令旗, 郭晓红, 吕艳东, 等. 旱直播对水稻穗部性状、产量和经济效益的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2021, 39(5): 186-192. |
| XU Lingqi, GUO Xiaohong, LV Yandong, et al. Effects of dry direct seeding on panicle characters, yield and economic benefits of rice[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2021, 39(5): 186-192. | |
| [36] | 武姣娜, 魏晓东, 李霞, 等. 植物氮素利用效率的研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2018, 54(9): 1401-1408. |
| WU Jiaona, WEI Xiaodong, LI Xia, et al. Research progress in nitrogen use efficiency in plants[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2018, 54(9): 1401-1408. | |
| [37] | 程爽, 车阳, 田晋钰, 等. 水稻缓控释氮肥应用研究现状与展望[J]. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2020, 41(2): 1-8. |
| CHENG Shuang, CHE Yang, TIAN Jinyu, et al. Research advances and prospects of slow-controlled release nitrogen fertilizer in rice[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agricultural and Life Science Edition), 2020, 41(2): 1-8. | |
| [38] | 段里成, 吕伟生, 方加海, 等. 施氮量和每穴苗数对双季杂交早稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(10): 2959-2967. |
| DUAN Licheng, LV Weisheng, FANG Jiahai, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rate and seedlings per hole on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of double-season early hybrid rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(10): 2959-2967. | |
| [39] | 郭腾飞, 梁国庆, 周卫, 等. 施肥对稻田温室气体排放及土壤养分的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(2): 337-345. |
| GUO Tengfei, LIANG Guoqing, ZHOU Wei, et al. Effect of fertilizer management on greenhouse gas emission and nutrient status in paddy soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2016, 22(2): 337-345. | |
| [40] | 兰艳, 黄鹏, 江谷驰弘, 等. 施氮量和栽插密度对粳稻D46产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2016, 37(1): 20-28. |
| LAN Yan, HUANG Peng, JIANG Guchihong, et al. Effect of planting density and nitrogen application on yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization of japonica rice cultivar D46[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2016, 37(1): 20-28. | |
| [41] | 董瑜皎, 袁江, 吕世华. 2个氮水平下不同施锌方式对覆膜水稻产量及锌吸收的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2018, 31(8): 1655-1661. |
| DONG Yujiao, YUAN Jiang, LU Shihua. Effects of different Zn application methods on yield and Zn uptake of plastic mulching rice under two nitrogen levels[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 31(8): 1655-1661. | |
| [42] | 邓小强, 范贵国, 王懿. 施氮量对覆膜栽培水稻经济性状、产量与氮肥利用的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2016, 55(16): 4103-4106. |
| DENG Xiaoqiang, FAN Guiguo, WANG Yi. Effects of nitrogen application level on economic characters, yield and nitrogen use of rice cultivated with film mulching[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55(16): 4103-4106. | |
| [43] | 周江明, 赵琳, 董越勇, 等. 氮肥和栽植密度对水稻产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(2): 274-281. |
| ZHOU Jiangming, ZHAO Lin, DONG Yueyong, et al. Nitrogen and transplanting density interactions on the rice yield and N use rate[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(2): 274-281. | |
| [44] | 郝玉波, 李梁, 于洋, 等. 增施秸秆有机肥及减施化肥对玉米产量形成和肥料偏生产力的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2021,(7): 15-18. |
| HAO Yubo, LI Liang, YU Yang, et al. Effects of increasing straw organic fertilizer and decreasing chemical fertilizer on maize yield formation and feitilizer partial factor productivity in black soil area[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021,(7): 15-18. | |
| [45] |
陈晓萍, 曹雪仙, 陈文伟, 等. 氮肥减施对水稻产量、氮吸收和利用的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2021, 62(12): 2367-2370.
DOI |
| CHEN Xiaoping, CAO Xue-Xian, CHEN Wen-Wei, et al. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer reduction on rice yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 62(12): 2367-2370. | |
| [46] |
鲁伟林, 段仁周, 余新春, 等. 氮肥施用量对杂交粳稻氮素吸收和利用的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(30): 1-6.
DOI |
|
LU Weilin, DUAN Renzhou, YU Xinchun, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen absorption and utilization of japonica hybrid rice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2016, 32(30): 1-6.
DOI |
|
| [47] | 王道中, 张成军, 郭熙盛. 减量施肥对水稻生长及氮素利用率的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2012, 43(1): 161-165. |
| WANG Daozhong, ZHANG Chengjun, GUO Xisheng. Effects of lower fertilizer on rice growth and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2012, 43(1): 161-165. | |
| [48] | 王瑜, 赵庆雷, 信彩云, 等. 氮肥减施对麦茬机插水稻产量及氮肥利用的影响[J]. 农业与技术, 2023, 43(1): 6-8. |
| WANG Yu, ZHAO Qinglei, XIN Caiyun, et al. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer reduction on rice yield and nitrogen utilization by mechanical transplanting after wheat stubble[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2023, 43(1): 6-8. |
| [1] | 张泽华, 叶含春, 王振华, 李文昊, 李海强, 刘健. 等氮配施脲酶抑制剂对滴灌棉花生长发育和产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [2] | 陈瑞杰, 罗林毅, 阮向阳, 冶军. 腐植酸对滴灌棉田土壤养分和棉花产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [3] | 黄铂轩, 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 邵晶晶, 冯卫娜, 庞朝友, 徐文修, 董合林. 不同氮素抑制剂对棉花生长发育、氮素利用与产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [4] | 张鸟, 王卉, 冯国郡, 再吐尼古丽·库尔班. 不同粒用高粱品种产量和农艺性状及品质的差异性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2160-2167. |
| [5] | 陈芳, 李字辉, 孙孝贵, 张庭军. 不同剂量的微生物菌剂对加工番茄产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2285-2289. |
| [6] | 张承洁, 胡浩然, 段松江, 吴一帆, 张巨松. 氮肥与密度互作对海岛棉生长发育及产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1821-1830. |
| [7] | 候丽丽, 王伟, 崔新菊, 周大伟. 有机无机肥配施对冬小麦产量和土壤养分及酶活性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1845-1852. |
| [8] | 陈芳, 李字辉, 王兵跃, 孙孝贵, 张庭军. 微生物菌剂对冬小麦生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1853-1860. |
| [9] | 袁莹莹, 赵经华, 迪力穆拉提·司马义, 杨庭瑞. 基于apriori算法对盆栽春小麦生理指标及产量的分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1861-1871. |
| [10] | 牛婷婷, 马明生, 张军高. 秸秆还田和覆膜对旱作雨养农田土壤理化性质及春玉米产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1896-1906. |
| [11] | 李锁丞, 柳延涛, 董红业, 孙振博, 李紫薇, 张春媛, 王开勇, 李强, 杨明凤. 不同施钾量对滴灌花生光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1926-1936. |
| [12] | 张彩虹, 王国强, 姜鲁艳, 刘涛, 德贤明. 低能耗组装式深冬生产型日光温室环境因子变化及番茄性状分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 2043-2053. |
| [13] | 杨梅, 赵红梅, 迪丽热巴·夏米西丁, 杨卫君, 张金汕, 惠超. 氮肥减量配施生物质炭对春小麦群体结构、光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1582-1589. |
| [14] | 鲁伟丹, 周远航, 马小龙, 高江龙, 樊晓琴, 郭建富, 李健强, 林明. 不同比例有机肥替代化肥对甜菜植株养分及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1631-1639. |
| [15] | 高君, 侯献飞, 苗昊翠, 贾东海, 顾元国, 汪天玲, 黄奕, 陈晓露, 李强. 棉花-花生轮作模式对花生干物质积累量分配及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1648-1656. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 34
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 134
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||