

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (9): 2112-2121.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.09.005
• 作物遗传育种·种质资源·分子遗传学·耕作栽培·生理生化 • 上一篇 下一篇
收稿日期:2024-02-27
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通信作者:
冶军(1973-),男,新疆人,教授,硕士生导师,研究方向为新型肥料与现代施肥技术,(E-mail)yejun.shz@163.com作者简介:陈瑞杰(1998-)男,河南人,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物营养学,(E-mail)CRJ98028@163.com
基金资助:
CHEN Ruijie( ), LUO Linyi, RUAN Xiangyang, YE Jun(
), LUO Linyi, RUAN Xiangyang, YE Jun( )
)
Received:2024-02-27
Published:2024-09-20
Online:2024-10-09
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究滴灌条件下不同用量腐植酸对新疆棉田土壤养分及棉花生长发育的影响,为新疆棉花生产中腐植酸的应用提供理论依据。【方法】采用田间小区试验,设置CK(0 L/hm2,不施腐植酸),T1(腐植酸225 L/hm2),T2(腐植酸450 L/hm2),T3(腐植酸675 L/hm2)4个处理,分析其对棉田土壤养分、棉花生长发育、产量与品质的影响。【结果】腐植酸显著增加了土壤养分有效性,施用量675 L/hm2时土壤碱解氮含量增加了16.36%~25.66%,有效磷含量增加了23.85%~32.22%,速效钾含量增加了20.15%~29.95%,提高了棉花的光合特性,同一生育期棉花干重和单株叶面积随着腐植酸用量的增加而逐渐增加,在施用量为450 L/hm2时对提升棉花株高和茎粗的效果最佳。棉花产量分别增加了18.60%、27.44%、10.61%。提高了棉花品质,施用量450 L/hm2提高了棉花马克隆值等级。【结论】施用腐植酸提高了土壤养分有效性,增加了土壤速效养分含量,提高了棉花产量和品质,以施用量为450 L/hm2效果最佳。
中图分类号:
陈瑞杰, 罗林毅, 阮向阳, 冶军. 腐植酸对滴灌棉田土壤养分和棉花产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121.
CHEN Ruijie, LUO Linyi, RUAN Xiangyang, YE Jun. Effects of humic acid on soil nutrients, cotton yield and quality in cotton fields under drip irrigation[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121.
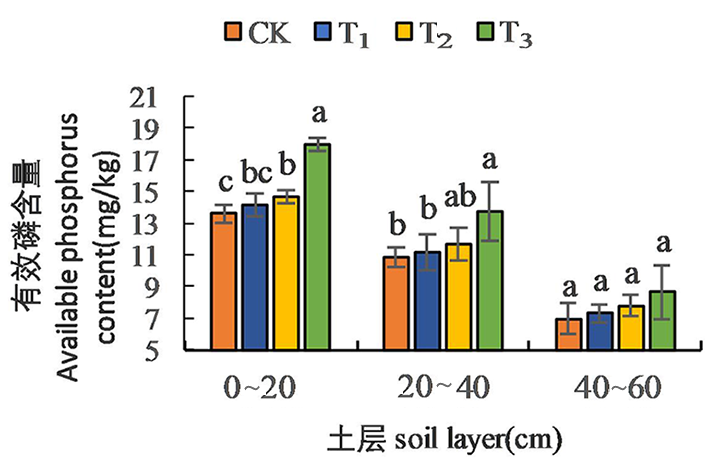
图1 不同处理下土壤有效磷含量的变化 注:不同小写字母表示不同处理间在5%水平差异显著(P<0.05),下同
Fig.1 Changes of soil available phosphorus content under different treatments Notes: Lowercase shows significantly different as 5%(P<0.05),the same as below
| 养分 Nutrient | 处理 Treatments | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | 蕾铃 Squares and bolls | 总积累量 Total accumulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | CK | 9.71±1.93b | 66.44±6.86b | 55.76±3.21b | 131.91±7.38b |
| T1 | 12.08±4.50b | 55.44±5.72b | 56.16±2.72b | 123.68±3.84b | |
| T2 | 17.28±5.32ab | 58.14±4.39b | 58.02±5.65b | 133.45±8.25b | |
| T3 | 22.10±6.56a | 85.13±8.05a | 71.83±8.44a | 179.06±4.51a | |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | CK | 7.18±0.77b | 14.25±3.94a | 24.99±2.26b | 46.41±1.20c |
| T1 | 9.71±1.40ab | 14.61±0.69a | 24.07±3.21b | 48.40±1.31c | |
| T2 | 15.27±3.95a | 13.99±3.71a | 27.25±7.30ab | 56.51±6.04b | |
| T3 | 14.11±4.52a | 19.69±5.79a | 36.71±7.93a | 70.51±6.12a | |
| 全钾 Total potassium | CK | 17.62±1.07d | 59.3±4.15ab | 15.30±1.13c | 92.21±4.78b |
| T1 | 22.28±2.38c | 47.63±7.70b | 31.49±5.14b | 101.40±7.83b | |
| T2 | 26.29±1.04b | 56.26±9.25ab | 30.61±6.72b | 113.17±5.31b | |
| T3 | 31.41±1.94a | 66.56±1.16a | 40.73±1.44a | 138.71±3.79a |
表1 不同处理下棉花地上部养分的积累量
Tab.1 Accumulation of aboveground nutrients in cotton under different treatments(kg/hm2)
| 养分 Nutrient | 处理 Treatments | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | 蕾铃 Squares and bolls | 总积累量 Total accumulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | CK | 9.71±1.93b | 66.44±6.86b | 55.76±3.21b | 131.91±7.38b |
| T1 | 12.08±4.50b | 55.44±5.72b | 56.16±2.72b | 123.68±3.84b | |
| T2 | 17.28±5.32ab | 58.14±4.39b | 58.02±5.65b | 133.45±8.25b | |
| T3 | 22.10±6.56a | 85.13±8.05a | 71.83±8.44a | 179.06±4.51a | |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | CK | 7.18±0.77b | 14.25±3.94a | 24.99±2.26b | 46.41±1.20c |
| T1 | 9.71±1.40ab | 14.61±0.69a | 24.07±3.21b | 48.40±1.31c | |
| T2 | 15.27±3.95a | 13.99±3.71a | 27.25±7.30ab | 56.51±6.04b | |
| T3 | 14.11±4.52a | 19.69±5.79a | 36.71±7.93a | 70.51±6.12a | |
| 全钾 Total potassium | CK | 17.62±1.07d | 59.3±4.15ab | 15.30±1.13c | 92.21±4.78b |
| T1 | 22.28±2.38c | 47.63±7.70b | 31.49±5.14b | 101.40±7.83b | |
| T2 | 26.29±1.04b | 56.26±9.25ab | 30.61±6.72b | 113.17±5.31b | |
| T3 | 31.41±1.94a | 66.56±1.16a | 40.73±1.44a | 138.71±3.79a |
| 处理 Treat- ments | 净光合速率 Pn (μmol/ (m2·s)) | 蒸腾速率 Tr (mmol/ (m2·h)) | 气孔导度 Gs (mmol/ (m2·s)) | 胞间二氧 化碳浓度 Ci (μmol/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 10.58±1.90c | 2.01±0.22c | 71.86±13.16b | 271.21±8.48a |
| T1 | 13.20±1.41b | 2.02±0.38c | 74.06±7.18b | 262.77±8.88a |
| T2 | 15.83±0.77ab | 2.46±0.15b | 111.39±7.39a | 260.37±7.93a |
| T3 | 16.13±0.21a | 3.42±0.16a | 125.78±9.25a | 240.51±3.09b |
表2 不同处理下棉花光合特性
Tab.2 Cotton yield and constituent factors under different treatments
| 处理 Treat- ments | 净光合速率 Pn (μmol/ (m2·s)) | 蒸腾速率 Tr (mmol/ (m2·h)) | 气孔导度 Gs (mmol/ (m2·s)) | 胞间二氧 化碳浓度 Ci (μmol/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 10.58±1.90c | 2.01±0.22c | 71.86±13.16b | 271.21±8.48a |
| T1 | 13.20±1.41b | 2.02±0.38c | 74.06±7.18b | 262.77±8.88a |
| T2 | 15.83±0.77ab | 2.46±0.15b | 111.39±7.39a | 260.37±7.93a |
| T3 | 16.13±0.21a | 3.42±0.16a | 125.78±9.25a | 240.51±3.09b |
| 处理 Treat- ments | 株数 Number of plants (104/hm2) | 单株铃数 Boll number per plant (个) | 单铃重 Single bell weight (g) | 产量 Yield (Kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.2±4.99a | 5.00±0.52b | 4.74±0.09b | 3748±659b |
| T1 | 16.8±1.56a | 5.56±0.01ab | 4.76±0.08b | 4458±468ab |
| T2 | 16.3±1.76a | 6.14±0.38a | 5.01±0.09a | 5007±565a |
| T3 | 16.9±0.46a | 5.10±0.61b | 4.84±0.15ab | 4160±317ab |
表3 不同处理下棉花产量及构成因素
Tab.3 Cotton yield and constituent factors under different treatments
| 处理 Treat- ments | 株数 Number of plants (104/hm2) | 单株铃数 Boll number per plant (个) | 单铃重 Single bell weight (g) | 产量 Yield (Kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.2±4.99a | 5.00±0.52b | 4.74±0.09b | 3748±659b |
| T1 | 16.8±1.56a | 5.56±0.01ab | 4.76±0.08b | 4458±468ab |
| T2 | 16.3±1.76a | 6.14±0.38a | 5.01±0.09a | 5007±565a |
| T3 | 16.9±0.46a | 5.10±0.61b | 4.84±0.15ab | 4160±317ab |
| 处理 Treatments | 绒长 Fiber length (mm) | 整齐度指数 Maturity Index (%) | 断裂比强度 Strength (cN/tex) | 马克隆值 Micronaire | 伸长率 Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 25.70±0.26c | 80.33±1.37a | 25.10±0.85b | 5.13±0.23a | 5.57±0.12a |
| T1 | 26.57±0.90bc | 80.83±0.55a | 26.33±0.74ab | 5.03±0.21a | 5.77±0.21a |
| T2 | 26.97±0.21b | 81.30±1.91a | 26.67±0.51a | 5.03±0.06a | 5.90±0.20a |
| T3 | 28.20±0.20a | 80.70±0.89a | 27.33±0.42a | 4.90±0.10a | 5.53±0.15a |
表4 不同处理下棉花品质的变化
Tab.4 Changes of cotton quality under different treatment
| 处理 Treatments | 绒长 Fiber length (mm) | 整齐度指数 Maturity Index (%) | 断裂比强度 Strength (cN/tex) | 马克隆值 Micronaire | 伸长率 Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 25.70±0.26c | 80.33±1.37a | 25.10±0.85b | 5.13±0.23a | 5.57±0.12a |
| T1 | 26.57±0.90bc | 80.83±0.55a | 26.33±0.74ab | 5.03±0.21a | 5.77±0.21a |
| T2 | 26.97±0.21b | 81.30±1.91a | 26.67±0.51a | 5.03±0.06a | 5.90±0.20a |
| T3 | 28.20±0.20a | 80.70±0.89a | 27.33±0.42a | 4.90±0.10a | 5.53±0.15a |
| [1] | 马革新. 施氮对不同质地滴灌棉花根系生长和氮素利用的影响[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2017. |
| MA Gexin. Effect of the Nitrogen on Growth of Root System and the Nitrogen Utilization of Drip-irrigated Cotton in Different Soil Textures[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2017. | |
| [2] | 马丹, 赵库, 沙木和别克·阿咱别克, 等. 磷肥种类和施用方式对新疆棉田磷素利用及棉花产量的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(2):86-92. |
| MA Dan, ZHAO Ku, ShamuhebiekeAzanbieke, et al. Effects of phosphate fertilizer types and application methods on phosphorus utilization and cotton yield in Xinjiang cotton field[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2020, 38(2):86-92. | |
| [3] | 吕宁, 祝宏辉, 程文明. 农业化肥减量及生物肥料替代可行性研究——来自新疆棉区调查数据的实证[J]. 地理研究, 2022, 41(5): 1459-1480. |
| LYU Ning, ZHU Honghui, CHENG Wenming. Feasibility study on reduction of agricultural chemical fertilizer and substitution of bio-fertilizer: an empirical study of cotton survey data in Xinjiang[J]. Geographical Research, 2022, 41(5): 1459-1480. | |
| [4] | Chemistry; Studies from Northeast Agricultural University Further Understanding of Chemistry (Synthetic Humic Acids Solubilize Otherwise Insoluble Phosphates to Improve Soil Fertility)[J]. Chemicals & Chemistry, 2020, 5494. |
| [5] | 郭书利. 腐植酸相关概念探讨[J]. 腐植酸, 2020, (5): 69-71. |
| GUO Shuli. Discussion on related concepts of humic acid[J]. Humic Acid, 2020, (5): 69-71. | |
| [6] | 刘增兵, 赵秉强, 林治安. 腐植酸尿素氨挥发特性及影响因素研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(1): 208-213. |
| LIU Zengbing, ZHAO Bingqiang, LIN Zhian. Ammonia volatilization characteristics and related affecting factors of humic acid urea[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2010, 16(1): 208-213. | |
| [7] | 李军, 袁亮, 赵秉强, 等. 磷肥中腐植酸添加比例对玉米产量、磷素吸收及土壤速效磷含量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(3):641-648. |
| LI Jun, YUAN Liang, ZHAO Bingqiang, et al. Effect of adding humic acid to phosphorous fertilizer on maize yield and phosphorus uptake and soil available phosphorus content[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2017, 23(3):641-648. | |
| [8] | Abourayya M S, Kaseem N E, Mahmoud T S M, et al. Impact of soil application with humic acid and foliar spray of milagro bio-stimulant on vegetative growth and mineral nutrient uptake of Nonpareil almond young trees under Nubaria conditions[J]. Bulletin of the National Research Centre, 2020, 44(1): 38. |
| [9] | Izhar Shafi M, Adnan M, Fahad S, et al. Application of single superphosphate with humic acid improves the growth, yield and phosphorus uptake of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in calcareous soil[J]. Agronomy, 2020, 10(9): 1224. |
| [10] | 王振振, 张超, 史春余, 等. 腐植酸缓释钾肥对土壤钾素含量和甘薯吸收利用的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2012, 18(1): 249-255. |
| WANG Zhenzhen, ZHANG Chao, SHI Chunyu, et al. Effects of Ha-K fertilizer on potassium content of soil and absorption and utilization of potassium in sweet potato[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2012, 18(1): 249-255. | |
| [11] | 顾鑫, 任翠梅, 王丽娜, 等. 施用腐植酸改良大庆苏打盐碱土的效应[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021, (4): 77-82. |
| GU Xin, REN Cuimei, WANG Lina, et al. Effects of humic acid application on soda saline-alkali soil in Daqing[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021, (4): 77-82. | |
| [12] | 刘灿华, 袁天佑, 闫军营, 等. 减氮配施腐植酸对耕层土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020, (5): 77-83. |
| LIU Canhua, YUAN Tianyou, YAN Junying, et al. Effects of combined application of humic acid and reducing N fertilizer on soil physical and chemical properties[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2020, (5): 77-83. | |
| [13] | Karimi E, Shirmardi M, Dehestani Ardakani M, et al. The effect of humic acid and biochar on growth and nutrients uptake of Calendula (Calendula officinalis L.)[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2020, 51(12): 1658-1669. |
| [14] | Raheem S M, Al Jaf H I, Tofiq G K. Influence of foliar and soil application of humic acid on growth and yield of lettuce[J]. Journal of Biology, Agriculture and Healthcare, 2018, 8(8): 1-4. |
| [15] | Martins J D L, Soratto R P, Fernandes A M. The effect of humic substances and phosphate fertilizer on growth and nutrient uptake of the potato[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2020, 51(11): 1525-1544. |
| [16] | Nardi S, Schiavon M, Francioso O. Chemical structure and biological activity of humic substances define their role as plant growth promoters[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(8): 2256. |
| [17] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| BAO Shidan. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. | |
| [18] | 王兴鹏, 辛朗, 杜江涛, 等. 基于DSSAT模型的南疆膜下滴灌棉花生长与产量模拟[J]. 农业机械学报, 2022, 53(9): 314-321. |
| WANG Xingpeng, XIN Lang, DU Jiangtao, et al. Simulation of cotton growth and yield under film drip irrigation condition based on DSSAT model in southern Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(9): 314-321. | |
| [19] | 周爽, 其力莫格, 谭钧, 等. 腐植酸提高土壤氮磷钾养分利用效率的机制[J]. 腐植酸, 2015, (2): 1-8. |
| ZHOU Shuang, QI Limoge, TAN Jun, et al. Strategies in efficient utilization of soil NPK nutrients with humic acid amendments[J]. Humic Acid, 2015, (2): 1-8. | |
| [20] | 宋挚, 郭新送, 范仲卿, 等. 腐植酸等碳替代有机肥对葡萄产量、品质及土壤养分的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2022, 37(3):158-167. |
| SONG Zhi, GUO Xinsong, FAN Zhongqing, et al. Effect of Carbon Replacement Organic Fertiliz ers Such as Humic Acid on Grape Yield,Quality and Soil Nutrients[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2022, 37(3):158-167. | |
| [21] | 袁川舟. 胜利褐煤腐植酸的氧化提取、组成结构及吸附K+性能研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019. |
| YUAN Chuanzhou. Oxidative Extraction, Composition Structure and Adsorption K+ Performance of Shengli Brown Coal Humic Acid[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019. | |
| [22] | Zhu J, Li M, Whelan M. Phosphorus activators contribute to legacy phosphorus availability in agricultural soils: a review[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2018, (612): 522-537. |
| [23] | Li Y, Fang F, Wei J L, et al. Humic acid fertilizer improved soil properties and soil microbial diversity of continuous cropping peanut: a three-year experiment[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 12014. |
| [24] | 杨苏, 叶雪峰, 章欢, 等. 褐煤腐殖酸用量对玉米生长及黄河故道潮土养分含量的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2020, 36(4):905-910. |
| YANG Su, YE Xuefeng, ZHANG Huan, et al. Effects of lignite humic acid on corn growth and nutrient content in fluvo-aquic soil along the Yellow River[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 36(4):905-910. | |
| [25] | Trevisan S, Botton A, Vaccaro S, et al. Humic substances affect Arabidopsis physiology by altering the expression of genes involved in primary metabolism, growth and development[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2011, (74): 45-55. |
| [26] | 王云赫, 范仲卿, 郭新送, 等. 腐植酸对不同筋度小麦品种生长特性、产量和品质的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2022, 42(10):1240-1246. |
| WANG Yunhe, FAN Zhongqing, GUO Xinsong, et al. Effect of Humic Acid on Growth Characteris tics,Yield and Quality of Wheat Varieties with Different Gluten[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2022, 42(10):1240-1246. | |
| [27] | Trevisan S, Pizzeghello D, Ruperti B, et al. Humic substances induce lateral root formation and expression of the early auxin-responsive IAA19 gene and DR5 synthetic element in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Biology, 2010, 12(4): 604-614. |
| [28] | Olaetxea M, Mora V, Bacaicoa E, et al. Root ABA and H+-ATPase are key players in the root and shoot growth-promoting action of humic acids[J]. Plant Direct, 2019, 3(10): e00175. |
| [29] | Huertas Tavares O C, Santos L A, Lima de Araújo O J, et al. Humic acid as a biotechnological alternative to increase N-NO3- or N-NH4+ uptake in rice plants[J]. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2019, (20): 101226. |
| [30] | 顾鑫, 任翠梅, 杨丽, 等. 煤炭腐植酸对土壤物理性质及玉米生长发育的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2019, 38(1):26-30. |
| GU Xin, REN Cuimei, YANG Li, et al. The Effects of Amending Soil with Coal Humic Acid on Soil Physical Property and Physiological Growth of Maize[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2019, 38(1):26-30. | |
| [31] | Shen J, Guo M J, Wang Y G, et al. An investigation into the beneficial effects and molecular mechanisms of humic acid on foxtail millet under drought conditions[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(6): e0234029. |
| [32] | de Azevedo I G, Olivares F L, Ramos A C, et al. Humic acids and Herbaspirillum seropedicae change the extracellular H+ flux and gene expression in maize roots seedlings[J]. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture, 2019, 6(1): 8. |
| [33] | Olaetxea M, De Hita D, Garcia C A, et al. Hypothetical framework integrating the main mechanisms involved in the promoting action of rhizospheric humic substances on plant root- and shoot- growth[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2018, (123): 521-537. |
| [34] | Jing J Y, Zhang S Q, Yuan L, et al. Humic acid modified by being incorporated into phosphate fertilizer increases its potency in stimulating maize growth and nutrient absorption[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, (13): 885156. |
| [35] | Olaetxea M, Mora V, Bacaicoa E, et al. Root ABA and H+-ATPase are key players in the root and shoot growth-promoting action of humic acids[J]. Plant Direct, 2019, 3(10): e00175. |
| [36] | 陈年来. 作物库源关系研究进展[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2019, 54(1): 1-10. |
| CHEN Nianlai. Research advances on source-sink interaction of the crops[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2019, 54(1): 1-10. | |
| [37] | 朱珊珊, 米俊珍, 赵宝平, 等. 干旱胁迫下喷施黄腐酸对燕麦光合及其抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2022, 42(11): 1902-1909. |
| ZHU Shanshan, MI Junzhen, ZHAO Baoping, et al. Effect of fulvic acid on photosynthesis and antioxidant enzyme activities of Avena sativa under drought stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2022, 42(11): 1902-1909. | |
| [38] | 朱珊珊, 米俊珍, 赵宝平, 等. 干旱胁迫下腐植酸对燕麦光合特性和内源激素的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(1): 24-30, 39. |
| ZHU Shanshan, MI Junzhen, ZHAO Baoping, et al. Effects of humic acid on photosynthesis and endogenous hormones of oat under drought stress[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(1): 24-30, 39. | |
| [39] | 杨晓伟. 矿源腐殖质对土壤特征及菠菜生长的影响研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2022. |
| YANG Xiaowei. Effect of Mineral Humus on Soil Characteristics and Spinach Growth[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2022. | |
| [40] | 孟阿静, 齐莹莹, 吕彩霞, 等. 不同量黄腐酸配施微生物菌肥对玉米生长、养分积累及苗期光合特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(12):2312-2319. |
| MENG Ajing, QI Yingying, LYU Caixia, et al. Effects of Different Quantities of Fulvic Acid Combined Application with Microbial Fertilizer on Corn Growth,Nutrient Accumulation a nd Photosynthetic Characteristics at Seedling Stage[J]. Xinjiang Science, 2021, 58(12):2312-2319. | |
| [41] | Çavuşolu K, Ergin H G. Effects of humic acid pretreatment on some physiological and anatomical parameters of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) exposed to salt stress[J]. Bangladesh Journal of Botany, 2018, 44(4): 591-598. |
| [42] | 王平, 田长彦, 张小勇, 等. 黑液腐植酸肥料对棉花生长及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2012, 30(4): 70-75. |
| WANG Ping, TIAN Changyan, ZHANG Xiaoyong, et al. Effect of different humic acid liquid fertilizer on cotton growth and soil fertility[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2012, 30(4): 70-75. | |
| [43] | Ullah A, Ali M, Shahzad K, et al. Impact of seed dressing and soil application of potassium humate on cotton plants productivity and fiber quality[J]. Plants, 2020, 9(11): 1444. |
| [44] | 张海鹏, 马健, 文俊, 等. 施钾对不同转基因棉花品种光合特性及产量和品质的影响[J]. 棉花学报, 2012, 24(6): 548-553. |
| ZHANG Haipeng, MA Jian, WEN Jun, et al. Effects of potassium application on the photosynthetic characteristics, yield, and fiber properties of different transgenic cotton varieties[J]. Cotton Science, 2012, 24(6): 548-553. | |
| [45] | Basbag S. Effects of Humic Acid Application on Yield and Quality of Cotton(Gossypium hirsutum L.)[J]. Asian Journal of Chemistry: An International Quarterly Research Journal of Chemistry, 2008, 20(3), 1961-1966. |
| [1] | 靳娟, 李丽莉, 杨磊, 樊丁宇, 郝庆. 新疆红枣产业发展现状分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 106-110. |
| [2] | 苗红萍, 王晓伟, 田聪华, 李志, 张玉新, 戴俊生. 塔里木河流域棉花生产与布局演变特征及驱动因素分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 217-226. |
| [3] | 王俊铎, 崔豫疆, 梁亚军, 龚照龙, 郑巨云, 李雪源. 新疆棉花生产优势区域分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 60-69. |
| [4] | 郑巨云, 龚照龙, 梁亚军, 耿世伟, 孙丰磊, 阳妮, 李雪源, 王俊铎. 新疆机采棉花生产关键技术模式[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 70-74. |
| [5] | 方辉, 丁银灯, 范贵强, 高永红, 黄天荣. 新疆南疆小麦产业发展的现状及品质特性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 75-80. |
| [6] | 李杰, 刘佳, 王亮, 张娜, 杨延龙, 郑子漂, 魏鑫, 王萌, 周子馨, 阳妮, 龚照龙, 侯献飞, 黄启秀, 阿不都卡地尔·库尔班, 张济鹏, 张鹏忠. “棉、油、糖”科技成果转化现状及应用分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 89-94. |
| [7] | 扁青永, 付彦博, 祁通, 黄建, 蒲胜海, 孟阿静, 哈丽哈什·依巴提. 新疆南疆盐碱地棉花出苗影响因素及保苗措施分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 95-100. |
| [8] | 杨明花, 廖必勇, 刘强, 彭云承, 达吾来·杰克山, 冯国瑞, 唐式敏. 鲜食糯玉米籽粒营养品质的差异变化分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2087-2093. |
| [9] | 李永泰, 高阿香, 李艳军, 张新宇. 脱叶剂对不同敏感性棉花品种生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2094-2102. |
| [10] | 张泽华, 叶含春, 王振华, 李文昊, 李海强, 刘健. 等氮配施脲酶抑制剂对滴灌棉花生长发育和产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [11] | 黄铂轩, 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 邵晶晶, 冯卫娜, 庞朝友, 徐文修, 董合林. 不同氮素抑制剂对棉花生长发育、氮素利用与产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [12] | 王超, 徐文修, 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 冯卫娜, 邵晶晶, 董合林. 棉花苗期生长发育对土壤速效钾水平的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2132-2139. |
| [13] | 张鸟, 王卉, 冯国郡, 再吐尼古丽·库尔班. 不同粒用高粱品种产量和农艺性状及品质的差异性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2160-2167. |
| [14] | 刘晶, 杜明川, 张文婷, 鲍海娟, 景美玲, 杜文华. 青海不同地区小黑麦种质的筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2183-2190. |
| [15] | 田海燕, 张占琴, 颉建辉, 王建江, 杨相昆. 加工番茄果实番茄红素与主要品质性状的关系[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2197-2202. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 60
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 118
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||