

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (10): 2396-2407.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.10.007
• 作物遗传育种·种质资源·分子遗传学·耕作栽培·生理生化 • 上一篇 下一篇
朱夏芬1,2( ), 何伟2, 罗文芳2, 周军辉2, 李克梅1(
), 何伟2, 罗文芳2, 周军辉2, 李克梅1( ), 许建军2(
), 许建军2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-10
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-11-07
通信作者:
李克梅(1972-),女,江苏如皋人,教授,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为蔬菜病害及防治,(E-mail)likemei@xjau.edu.cn;作者简介:朱夏芬(1999-),女,山西晋城人,硕士研究生,研究方向为列当生物防治,(E-mail)1845724579@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHU Xiafen1,2( ), HE Wei2, LUO Wenfang2, ZHOU Junhui2, LI Kemei1(
), HE Wei2, LUO Wenfang2, ZHOU Junhui2, LI Kemei1( ), XU Jianjun2(
), XU Jianjun2( )
)
Received:2024-04-10
Published:2024-10-20
Online:2024-11-07
Correspondence author:
LI Kemei(1972-), femal, from Rugao, Jiangsu, professor, master's supervisor, research direction: vegetable disease and control, (E-mail)likemei@xjau.edu.cn;Supported by:摘要:
【目的】 瓜列当是全寄生恶性杂草,贝莱斯芽孢杆菌JTB8-2能够有效防除瓜列当,探明其作用机制可以为该菌株的田间应用提供理论依据。【方法】 采用盆栽、酶活测定及超高效液相色谱-质谱联合(UHPLC-MRM-MS /MS)技术,分析贝莱斯芽孢杆菌JTB8-2诱导番茄抗瓜列当机制。【结果】 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌JTB8-2发酵液处理在番茄移栽后20、30和40 d时,寄生的瓜列当结节数量分别为0.33、0.17和0.33个/株,较NB培养基处理分别减少了50.75%、79.52%和50.75%,较清水对照分别减少了81.67%、96.96%和95.54%。菌株发酵液浇灌番茄植株3、20和30 d后,番茄根部过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性均高于NB培养基处理和清水对照;番茄根系中28种植物激素类代谢物中 11种代谢物含量具有差异,菌株JTB8-2处理的番茄根系中细胞分裂素类与生长素类化合物含量高于清水对照。【结论】 菌株JTB8-2处理的番茄根系中过氧化氢酶活性、细胞分裂素与生长素相关激素的增加诱导了番茄系统抗性,减少了瓜列当寄生量。
中图分类号:
朱夏芬, 何伟, 罗文芳, 周军辉, 李克梅, 许建军. 基于防御酶与代谢组学分析贝莱斯芽孢杆菌JTB8-2诱导番茄拮抗瓜列当机制[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2396-2407.
ZHU Xiafen, HE Wei, LUO Wenfang, ZHOU Junhui, LI Kemei, XU Jianjun. Metabolomics analysis of Bacillus velezensis JTB8-2 induced tomato antagonism towards Orobanche aegyptiaca based on defense enzyme[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(10): 2396-2407.
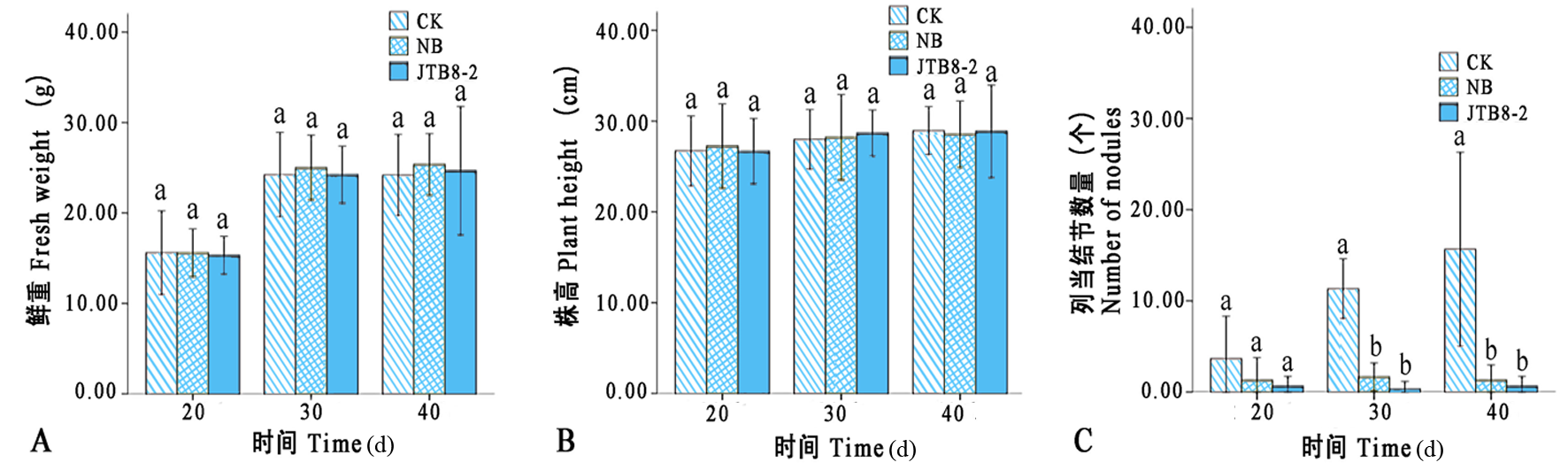
图1 20、30和40 d各处理下番茄鲜重、株高和瓜列当寄生量的变化 注:A:番茄植株鲜重;B:番茄株高;C:寄生的瓜列当结节数量
Fig. 1 Changes of tomato fresh weight, plant height and number of O. aegyptiaca nodules at 20, 30 and 40 d
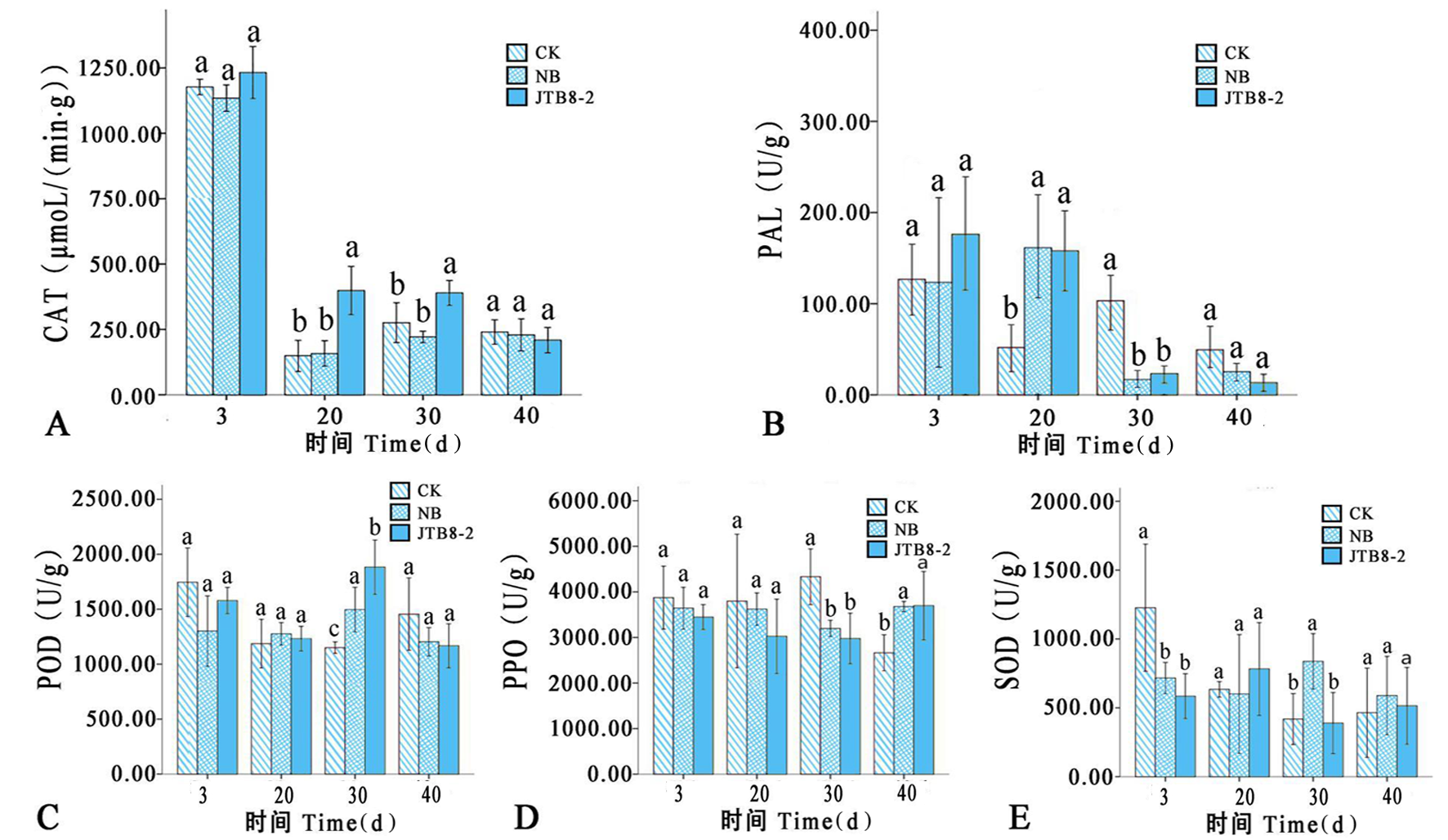
图3 各处理下不同时期防御酶酶活性的变化 注:A:过氧化氢酶(CAT);B:苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL);C:过氧化物酶(POD);D:多酚氧化酶(PPO);E:超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)
Fig.3 Changes of activity of defense enzymes in different periods of each treatment Note: A: Catalase (CAT); B: phenylalanine ammonolyase (PAL); C: Peroxidase (POD); D: Polyphenol oxidase (PPO); E: Superoxide dismutase (SOD)
| 时间 Time (d) | 处理 Treatments | 1-氨基环 丙烷羧酸 1-Aminocyclo propanecar boxylic acid | 吲哚-3-乙酸 Indole-3- acetic acid | 顺式-玉米素 Cis-Zeatin | 异戊烯基腺苷 Isopentenyl adenosine | 反式玉米 素核苷 trans- Zeatin- riboside | 褪黑素 Melatonine | 水杨酸 Salicylic acid | 3-吲哚甲醛 Indole- 3-carboxa ldehyde | 茉莉酸 Jasmonic acid | 二氢茉莉酸 Dihydrojas monic acid | 脱落酸 Abscisic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | CK | 901.32±47.38 b | 179.69±6.73 b | 5.02±1.02 b | 2.9±0.23 a | 201.81±24.05 b | 0.74±0.01 a | 603.92±63.52 b | 18.40±0.83 b | 331.88±124.89 b | 8.52±0.97 b | 338.90±20.61 b |
| NB | 1 727.7±139.06 a | 172.96±4.68 b | 11.51±0.62 a | 4.46±1.15 a | 344.26±55.36 a | 0.76±0.03 a | 1 135.76±102.83 a | 36.71±0.85 b | 608.77±44.14 a | 22.05±3.56 a | 488.11±40.29 a | |
| JTB8-2 | 1 668.43±122.45 a | 212.71±3.42 a | 13.23±1.06 a | 2.97±0.21 a | 183.79±8.29 b | 0.84±0.08 a | 642.91±48.71 b | 73.36±10.18 a | 205.02±13.87 b | 13.71±0.68 b | 417.70±21.58 ab | |
| 20 | CK | 867.28±27.13 b | 165.87±2.79 a | 0 | 3.37±0.41 a | 155.52±38.42 b | 0.81±0.02 a | 1 077.13±150.23 a | 15.32±1.90 a | 211.33±39.76 b | 15.20±2.64 b | 145.3±43.15 b |
| NB | 1 230.02±58.74 a | 208.54±15.12 a | 0 | 4.33±0.67 a | 377.79±32.72 a | 0.8±0.06 a | 1 109.04±264.36 a | 20.83±4.13 a | 388.77±53.69b | 9.67±1.21 ab | 125.72±24.16 b | |
| JTB8-2 | 1 318.32±123.47 a | 185.66±15.45 a | 0 | 6.19±1.30 a | 429.49±63.58 a | 0.77±0.01 a | 860.63±80.24 a | 28.43±5.71 a | 584.65±69.52 a | 6.24±1.00 a | 303.16±19.00 a | |
| 30 | CK | 2 061.35±266.97 a | 122.59±10.45 b | 0b | 1.84±0.29 b | 180.08±11.35 a | 0.84±0.05 a | 1 315.59±87.63 a | 20.05±1.70 a | 765.03±46.15 a | 11.54±2.31 a | 1 004.80±219.91 a |
| NB | 1 794.80±141.57 a | 177.72±7.90 a | 0 b | 3.29±0.16 a | 230.88±86.56 a | 0.77±0.05 a | 841.93±145.93 a | 20.85±4.98 a | 368.51±110.82 b | 3.32±0.39 b | 327.14±80.60 b | |
| JTB8-2 | 1 942.68±230.51 a | 169.77±15.11 a | 6.82±1.21a | 3.57±0.16 a | 307.98±63.41 a | 0.83±0.02 a | 1 292.95±432.77 a | 13.56±1.35 a | 235.59±31.28 b | 3.06±0.41 b | 359.94±41.51 b | |
| 40 | CK | 1 685.18±225.68 a | 143.83±15.81 ab | 0 | 4.62±1.91 a | 247±29.36 a | 1.26±0.14 ab | 1 087.71±332.90 a | 75.11±15.16 a | 86.96±14.54 a | 9.21±2.18 a | 102.1±4.94 ab |
| NB | 1 791.51±171.03 a | 181.93±13.16 a | 0 | 5.38±0.63 a | 223.25±39.89 a | 1.53±0.05 a | 535.96±76.85 a | 66.31±19.89 a | 202.2567 a | 15.38±1.79 a | 79.87±12.55 b | |
| JTB8-2 | 1 823.99±172.58 a | 126.34±10.53 b | 0 | 2.51±0.02 a | 157.78±10.06 a | 1.08±0.06 b | 388.13±36.23 a | 29±0.91 a | 1 034.6467 a | 10.92±1.43 a | 129.64±8.29 a |
表1 番茄根部11种植物激素类代谢差异物的变化
Tab.1 Changes of metabolism differences of 11 plant hormones in tomato roots
| 时间 Time (d) | 处理 Treatments | 1-氨基环 丙烷羧酸 1-Aminocyclo propanecar boxylic acid | 吲哚-3-乙酸 Indole-3- acetic acid | 顺式-玉米素 Cis-Zeatin | 异戊烯基腺苷 Isopentenyl adenosine | 反式玉米 素核苷 trans- Zeatin- riboside | 褪黑素 Melatonine | 水杨酸 Salicylic acid | 3-吲哚甲醛 Indole- 3-carboxa ldehyde | 茉莉酸 Jasmonic acid | 二氢茉莉酸 Dihydrojas monic acid | 脱落酸 Abscisic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | CK | 901.32±47.38 b | 179.69±6.73 b | 5.02±1.02 b | 2.9±0.23 a | 201.81±24.05 b | 0.74±0.01 a | 603.92±63.52 b | 18.40±0.83 b | 331.88±124.89 b | 8.52±0.97 b | 338.90±20.61 b |
| NB | 1 727.7±139.06 a | 172.96±4.68 b | 11.51±0.62 a | 4.46±1.15 a | 344.26±55.36 a | 0.76±0.03 a | 1 135.76±102.83 a | 36.71±0.85 b | 608.77±44.14 a | 22.05±3.56 a | 488.11±40.29 a | |
| JTB8-2 | 1 668.43±122.45 a | 212.71±3.42 a | 13.23±1.06 a | 2.97±0.21 a | 183.79±8.29 b | 0.84±0.08 a | 642.91±48.71 b | 73.36±10.18 a | 205.02±13.87 b | 13.71±0.68 b | 417.70±21.58 ab | |
| 20 | CK | 867.28±27.13 b | 165.87±2.79 a | 0 | 3.37±0.41 a | 155.52±38.42 b | 0.81±0.02 a | 1 077.13±150.23 a | 15.32±1.90 a | 211.33±39.76 b | 15.20±2.64 b | 145.3±43.15 b |
| NB | 1 230.02±58.74 a | 208.54±15.12 a | 0 | 4.33±0.67 a | 377.79±32.72 a | 0.8±0.06 a | 1 109.04±264.36 a | 20.83±4.13 a | 388.77±53.69b | 9.67±1.21 ab | 125.72±24.16 b | |
| JTB8-2 | 1 318.32±123.47 a | 185.66±15.45 a | 0 | 6.19±1.30 a | 429.49±63.58 a | 0.77±0.01 a | 860.63±80.24 a | 28.43±5.71 a | 584.65±69.52 a | 6.24±1.00 a | 303.16±19.00 a | |
| 30 | CK | 2 061.35±266.97 a | 122.59±10.45 b | 0b | 1.84±0.29 b | 180.08±11.35 a | 0.84±0.05 a | 1 315.59±87.63 a | 20.05±1.70 a | 765.03±46.15 a | 11.54±2.31 a | 1 004.80±219.91 a |
| NB | 1 794.80±141.57 a | 177.72±7.90 a | 0 b | 3.29±0.16 a | 230.88±86.56 a | 0.77±0.05 a | 841.93±145.93 a | 20.85±4.98 a | 368.51±110.82 b | 3.32±0.39 b | 327.14±80.60 b | |
| JTB8-2 | 1 942.68±230.51 a | 169.77±15.11 a | 6.82±1.21a | 3.57±0.16 a | 307.98±63.41 a | 0.83±0.02 a | 1 292.95±432.77 a | 13.56±1.35 a | 235.59±31.28 b | 3.06±0.41 b | 359.94±41.51 b | |
| 40 | CK | 1 685.18±225.68 a | 143.83±15.81 ab | 0 | 4.62±1.91 a | 247±29.36 a | 1.26±0.14 ab | 1 087.71±332.90 a | 75.11±15.16 a | 86.96±14.54 a | 9.21±2.18 a | 102.1±4.94 ab |
| NB | 1 791.51±171.03 a | 181.93±13.16 a | 0 | 5.38±0.63 a | 223.25±39.89 a | 1.53±0.05 a | 535.96±76.85 a | 66.31±19.89 a | 202.2567 a | 15.38±1.79 a | 79.87±12.55 b | |
| JTB8-2 | 1 823.99±172.58 a | 126.34±10.53 b | 0 | 2.51±0.02 a | 157.78±10.06 a | 1.08±0.06 b | 388.13±36.23 a | 29±0.91 a | 1 034.6467 a | 10.92±1.43 a | 129.64±8.29 a |
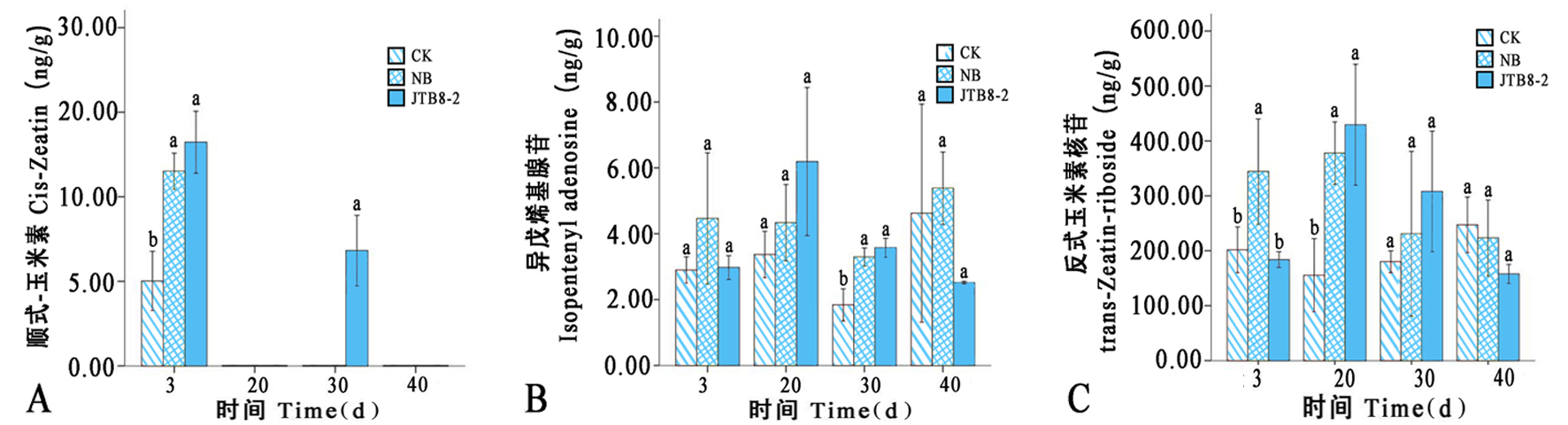
图6 各处理在不同时期番茄根部细胞分裂素类化合物含量的变化 注:A:顺式-玉米素;B:异戊烯基腺苷;C:反式玉米素核苷
Fig.6 Changes of contents of cytokinin compounds in tomato roots under different treatments at different periods Notes: A: Cis-Zeatin; B: Isopentenyl adenosine; C: trans-Zeatin-riboside
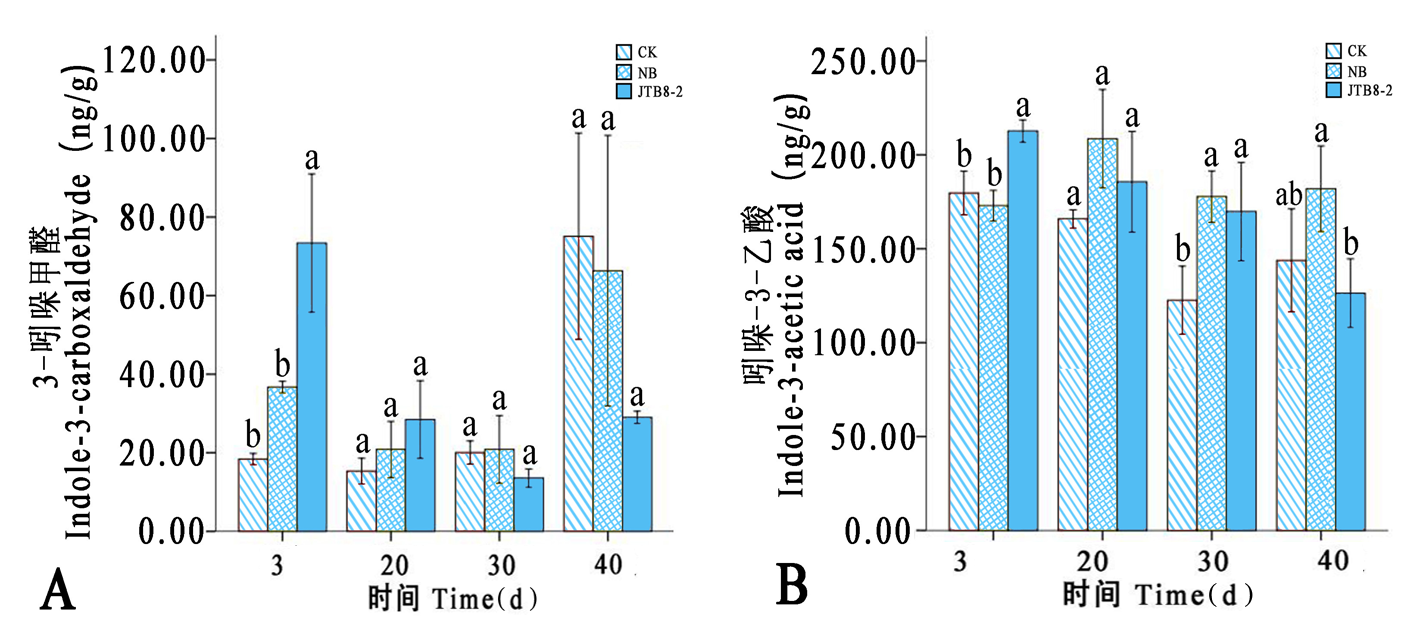
图7 各处理在不同时期番茄根部生长素类化合物含量的变化 注:A:3-吲哚甲醛;B:吲哚-3-乙酸
Fig.7 Changes of contents of auxin compounds in tomato roots under different treatments at different periods Note: A: Indole-3-carboxaldehyde; B: Indole-3-acetic acid

图8 各处理在不同时期番茄根部茉莉酸类化合物含量的变化 注:A:茉莉酸;B:二氢茉莉酸
Fig.8 Content of jasmonic acid compounds in tomato roots at different periods under different treatments Note: A: Jasmonic acid; B: Dihydrojasmonic acid
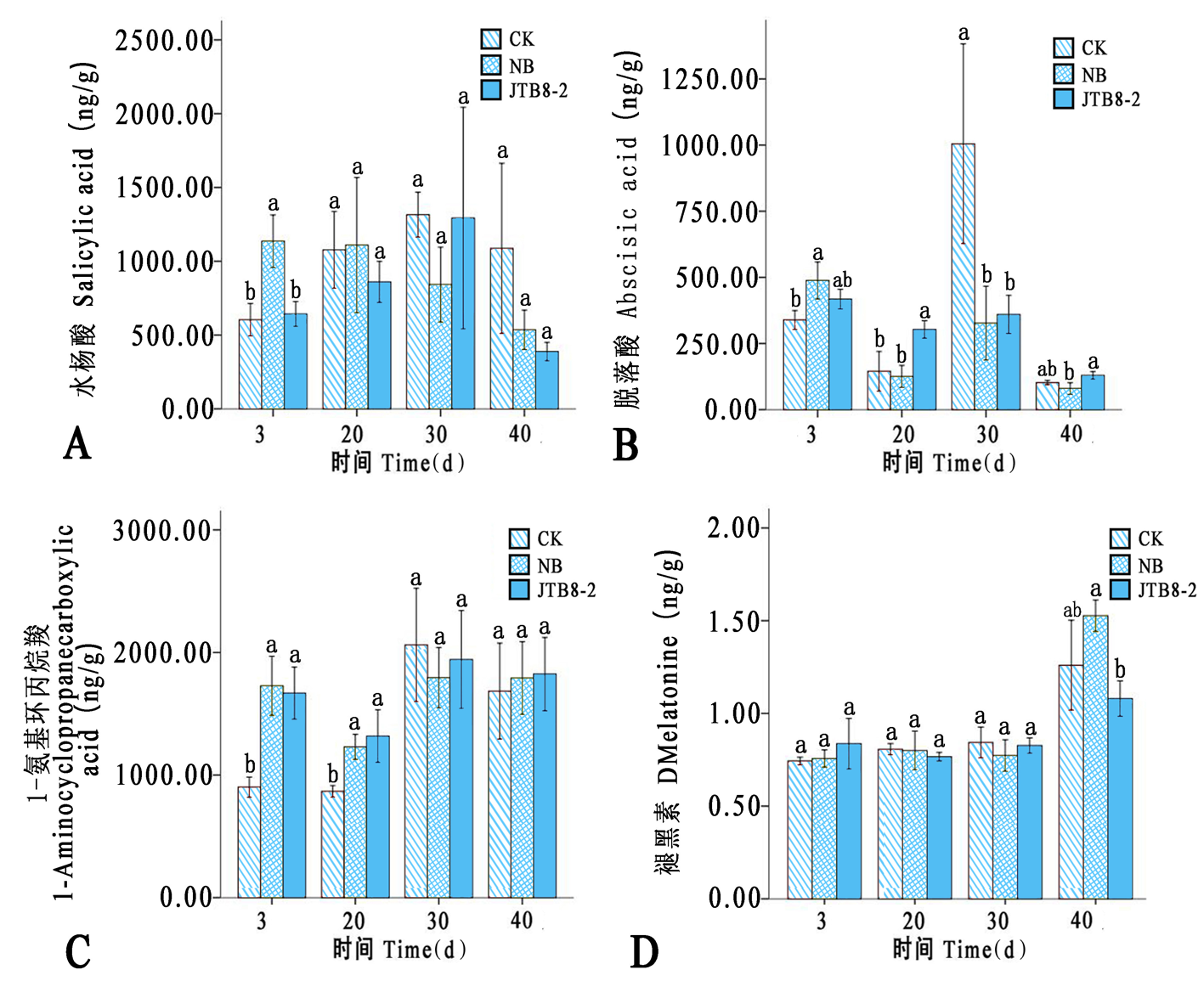
图9 各处理在不同时期番茄根部其他植物激素含量的变化 注:A:水杨酸;B:脱落酸;C:1-氨基环丙烷羧;D:褪黑素
Fig.9 Changes content of other plant hormones in tomato roots under different treatments at different periods Note: A:Salicylic acid; B:Abscisic acid; C:1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid; D:Dmelatonine
| [1] | 阴知勤, 周桂玲. 新疆高等寄生植物(二)——列当科[J]. 八一农学院学报, 1993, 16(1): 48-54. |
| YIN Zhiqin, ZHOU Guiling. A higher parasitic plant in Xinjiang (II)—Orabanchaceae[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 1993, 16(1): 48-54. | |
| [2] | 吴海荣, 强胜. 检疫杂草列当(Orobanche L.)[J]. 杂草科学, 2006, 24(2): 58-60. |
| WU Hairong, QIANG Sheng. The quarantine weed Orobanche L[J]. Weed Science, 2006, 24(2): 58-60. | |
| [3] | 姚兆群, 曹小蕾, 付超, 等. 新疆列当的种类、分布及其防治技术研究进展[J]. 生物安全学报, 2017, 26(1): 23-29. |
| YAO Zhaoqun, CAO Xiaolei, FU Chao, et al. Review of the distribution and management technology of various Orobanche L. species in Xinjiang, China[J]. Journal of Biosafety, 2017, 26(1): 23-29. | |
| [4] |
何伟, 罗文芳, 许建军, 等. 贝莱斯芽胞杆菌JTB8-2的筛选、鉴定及其对瓜列当拮抗作用研究[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2020, 36(5): 786-794.
DOI |
|
HE Wei, LUO Wenfang, XU Jianjun, et al. Screening, identification and antagonistic effect of Bacillus velezensis JTB8-2 on orobanch eaegyptaica[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2020, 36(5): 786-794.
DOI |
|
| [5] |
何伟, 罗文芳, 周军辉, 等. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌JTB8-2对加工番茄促生作用及其安全性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1260-1269.
DOI |
|
HE Wei, LUO Wenfang, ZHOU Junhui, et al. Growth promoting effect and safety evaluation of Bacillus velezensis JTB8-2 on processed tomato[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(5): 1260-1269.
DOI |
|
| [6] | Iasur Kruh L, Bari V K, Abu-Nassar J, et al. Characterization of an endophytic bacterium (Pseudomonas aeruginosa), originating from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.), and its ability to inhabit the parasitic weed Phelipanche aegyptiaca[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2020, 15(7): 1766292. |
| [7] | Iasur Kruh L, Lahav T, Abu-Nassar J, et al. Host-Parasite-Bacteria triangle: the microbiome of the parasitic weed Phelipanche aegyptiaca and tomato- Solanum lycopersicum (mill.) as a host[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 269. |
| [8] | 王亚娇, 纪莉景, 栗秋生, 等. 生物除草菌剂Br-2对番茄列当的防治效果[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2017,(4): 65-68. |
| WANG Yajiao, JI Lijing, LI Qiusheng, et al. Control efficacy of microbial herbicide Br-2 against Orobanche aegyptiaca[J]. China Vegetables, 2017,(4): 65-68. | |
| [9] |
王亚娇, 纪莉景, 栗秋生, 等. 多功能列当生防镰刀菌的筛选及种类鉴定[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2016, 32(6): 788-793.
DOI |
|
WANG Yajiao, JI Lijing, LI Qiusheng, et al. Isolation and identification of multifunction Bio-control agent Fusarium against Orobanche cernua[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2016, 32(6): 788-793.
DOI |
|
| [10] | 陈杰, 马永清, 郭振国, 等. 灰黄青霉对瓜列当的防效及对番茄根区土壤微生物的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2019, 27(5): 766-773. |
| CHEN Jie, MA Yongqing, GUO Zhenguo, et al. Effect of Penicillium griseofulvum on control of Orobanche aegyptiaca and microorganisms in rhizosphere soils of tomato[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(5): 766-773. | |
| [11] | 申云鑫, 施竹凤, 李铭刚, 等. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SH-1471发酵条件优化及其番茄枯萎病的防治效果[J]. 微生物学报, 2024, 64(1): 220-237. |
| SHEN Yunxin, SHI Zhufeng, LI Minggang, et al. Bacillus velezensis SH-1471: optimization of fermentation conditions and evaluation of the biocontrol effect on tomato Fusarium wilt[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2024, 64(1): 220-237. | |
| [12] | 马爽. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌K-9的筛选及其对马铃薯疮痂病生防机制的研究[D]. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2023. |
| MA Shuang. Screening of Bacillus Velezensis K-9 and Its Biocontrol Mechanism against Potato Scab Disease[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2023. | |
| [13] | 兰成忠. 黄瓜枯萎病菌LAMP检测及贝莱斯芽孢杆菌FJ17-4生防机制研究[D]. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2021. |
| LAN Chengzhong. LAMP Detection of Fusarium Oxysporum f.sp. cucumerinum Causing Cucumber Fusarium Wilt and Biological Control Mechanism of the Bacillus Velezensis FJ17-4[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| [14] | He W, Li Y, Luo W F, et al. Herbicidal secondary metabolites from Bacillus velezensis JTB8-2 against Orobanche aegyptiaca[J]. AMB Express, 2022, 12(1): 52. |
| [15] | Chen J, Wei J, Gao J M, et al. Allelopathic inhibitory effects of Penicillium griseofulvum produced patulin on the seed germination of Orobanche cumana Wallr. and Phelipanche aegyptiaca Pers[J]. Allelopathy Journal, 2017, 41(1): 65-80. |
| [16] | Aybeke M. Fusarium infection causes genotoxic disorders and antioxidant-based damages in Orobanche spp[J]. Microbiological Research, 2017, 201: 46-51. |
| [17] | 孙正祥, 曹帅, 王蓝琴, 等. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌D61-A对水稻根际土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 20(2): 113-120. |
| SUN Zhengxiang, CAO Shuai, WANG Lanqin, et al. Effects on bacterial community structure of the rhizosphere soil of rice plant treated by Bacillus velezensis D61-A[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 20(2): 113-120. | |
| [18] |
尉婧, 王碧香, 李诗瑶, 等. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)的研究进展[J]. 天津农学院学报, 2022, 29(4): 86-91.
DOI |
| WEI Jing, WANG Bixiang, LI Shiyao, et al. Advances in the study of Bacillus velezensis[J]. Journal of Tianjin Agricultural University, 2022, 29(4): 86-91. | |
| [19] | Chen J, Xue Q H, McErlean C S P, et al. Biocontrol potential of the antagonistic microorganism Streptomyces enissocaesilis against Orobanche cumana[J]. BioControl, 2016, 61(6): 781-791. |
| [20] | Mabrouk Y, Zourgui L, Sifi B, et al. Some compatible Rhizobium leguminosarum strains in peas decrease infections when parasitised by Orobanche crenata[J]. Weed Research, 2007, 47(1): 44-53. |
| [21] | 刘聪, 邓宇宏, 刘选明, 等. 过氧化氢酶在植物生长发育和胁迫响应中的功能研究进展[J]. 生命科学研究, 2023, 27(2): 128-138. |
| LIU Cong, DENG Yuhong, LIU Xuanming, et al. Research advances in the function of catalase in plant growth, development and stress response[J]. Life Science Research, 2023, 27(2): 128-138. | |
| [22] | 赵龙飞, 徐亚军, 邵璇, 等. 两株内生芽孢杆菌对盐胁迫下大豆幼苗超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化物酶活性影响[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49(5): 1664-1677. |
| ZHAO Longfei, XU Yajun, SHAO Xuan, et al. Two endophytic Bacillus strains from soybean nodules affect superoxide dismutase and peroxidase activities in soybean seedlings under salt stress[J]. Microbiology China, 2022, 49(5): 1664-1677. | |
| [23] |
王军, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽, 等. BYDV侵染对燕麦抗氧化防御酶、苯丙氨酸解氨酶及多酚类氧化酶的影响[J]. 草地学报, 2020, 28(1): 56-63.
DOI |
|
WANG Jun, ZHAO Guiqin, CHAI Jikuan, et al. Effects of BYDV infection on antioxidant enzymes, phenylalanine ammonia lyase and polyphenol oxidase in oat[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(1): 56-63.
DOI |
|
| [24] |
祁静静, 秦秀娟, 谢宇, 等. 过氧化氢酶基因CsKat01与柑橘溃疡病相关性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(1): 26-36.
DOI |
|
QI Jingjing, QIN Xiujuan, XIE Yu, et al. Correlation analysis of Citrus catalase gene CsKat01 and Citrus canker disease[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(1): 26-36.
DOI |
|
| [25] | 黄建中, 李扬汉. 外源细胞分裂素诱导日本菟丝子形成吸器与钙调素的关系[J]. 西北植物学报, 1991, 11(2): 116-121, 182. |
| HUANG Jianzhong, LI Yanghan. Relationship between haustorial formation of cuscuta japonica induced by exogenous cytokinin and calmodulin[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-occidentalia Sinica, 1991, 11(2): 116-121, 182. | |
| [26] | 姚东瑞, 郑晓明, 黄建中, 等. 寄生植物无根藤吸器发育过程中酸性磷酸酯酶与细胞分裂素变化的研究[J]. 植物学报, 1994, 36(3): 170-174. |
| YAO Dongrui, ZHENG Xiaoming, HUANG Jianzhong, et al. Changes of acid phosphatase and cytokininsduring haustorial development of theparasitic plant cassytha filiformis L[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 1994, 36(3): 170-174. | |
| [27] | Billard E, Goyet V, Delavault P, et al. Cytokinin treated microcalli of Phelipanche ramosa: an efficient model for studying haustorium formation in holoparasitic plants[J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC), 2020, 141(3): 543-553. |
| [28] | 田芳. 分枝列当吸器形成过程显微观察及影响其形成相关基因的筛选分析[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2022. |
| TIAN Fang. Microscopic Observate to Haustorium Formation Process of Phelipanche Aegyptiaca and Screen for Genes That Affects Its Formation[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2022. | |
| [29] | de Wit M, Lorrain S, Fankhauser C. Auxin-mediated plant architectural changes in response to shade and high temperature[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2014, 151(1): 13-24. |
| [30] | Bielach A, Podlesáková K, Marhavy P, et al. Spatiotemporal regulation of lateral root organogenesis in Arabidopsis by cytokinin[J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(10): 3967-3981. |
| [31] |
Glanz-Idan N, Tarkowski P, Tureĉková V, et al. Root-shoot communication in tomato plants: cytokinin as a signal molecule modulating leaf photosynthetic activity[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2020, 71(1): 247-257.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | 陈兆玉, 王永, 丁静, 等. 细胞分裂素受体基因SlHK4突变对番茄抗旱性的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2022, 45(2): 235-243. |
| CHEN Zhaoyu, WANG Yong, DING Jing, et al. Effects of cytokinin receptor gene SlHK4 mutation on drought resistance of tomato[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2022, 45(2): 235-243. | |
| [33] | Liu C F, Yang N, Teng R M, et al. Exogenous methyl jasmonate and cytokinin antagonistically regulate lignin biosynthesis by mediating CsHCT expression in Camellia sinensis[J]. Protoplasma, 2023, 260(3): 869-884. |
| [1] | 史应武, 牛新湘, 杨红梅, 楚敏, 包慧芳, 王宁, 詹发强, 林青, 杨蓉, 龙宣杞, 娄恺. 4种药剂对梨火疫病防病效果及库尔勒香梨产量与品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1432-1440. |
| [2] | 林青, 时红玲, 秦新政, 李月, 王子涵, 高雁, 曾军, 王浩中, 娄恺, 霍向东. 基于非靶向代谢组学分析两种酵母培养物的成分差异[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1218-1226. |
| [3] | 何伟, 罗文芳, 周军辉, 甘中祥, 陈晓刚, 叶仙涛, 许建军. 瓜列当在3种寄主作物上的寄生规律及抗性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 413-420. |
| [4] | 张仕琦, 李晓斌, 张文杰, 韩明, 王世昌, 郑文祥, 欧阳文, 祁居中, 杨开伦. 基于LC/MS的伊犁马3 600 m速度赛赛前、赛后血浆代谢组学差异变化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(2): 501-510. |
| [5] | 王威, 徐乐, 樊艳星, 王帆, 马艳明, 唐中华. 鹰嘴豆种子代谢产物的GC-MS分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(12): 2962-2972. |
| [6] | 何伟, 罗文芳, 周军辉, 许建军, 孙晓军. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌JTB8-2对加工番茄促生作用及其安全性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1260-1269. |
| [7] | 罗文芳, 何伟, 孙晓军, 许建军. 5种植物免疫诱导剂在黄瓜上应用效果[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(1): 107-114. |
| [8] | 张玉栋, 吴娜, 蔡晓虎, 史亚辉, 王俊刚. 棉长管蚜危害对棉花生理生化及其相关防御酶的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(11): 2065-2074. |
| [9] | 沙洁;陈连芳;支金虎;王兰;王德胜;艾尼瓦尔·吾买尔. 水分胁迫对瓜列当、加工番茄发芽和寄生关系的影响[J]. , 2017, 54(4): 707-714. |
| [10] | 陈丽慧;帕提玛·乌木尔汗;崔燕华;李勇;冯宏祖. 棉蚜取食对不同品种棉花防御酶活性的影响[J]. , 2015, 52(10): 1866-1871. |
| [11] | 阿依乃再·孜亚克;吾甫尔·米吉提;阿布都卡地尔·阿布力孜;赵国玉. 基于防御酶活性分析准噶尔乌头拮抗内生菌对玉米斑点病菌的抑制作用[J]. , 2012, 49(6): 1035-1042. |
| [12] | 艾力·吐热克;唐文华;赵震宇. 草酸青霉菌(P-o- 41)发酵液对小麦病害的诱导抗性作用[J]. , 2006, 43(5): 386-390. |
| [13] | 高峰;李国英;王钦英. 水杨酸诱导棉花耐黄萎病的效应[J]. , 2004, 41(5): 333-336. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 46
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 106
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||