

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2022, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (3): 691-699.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.03.019
• Plant Protection·Agricultural Product Analysis and Detection • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Xiaofeng1( ), CAI Shulin2, SU Zhuowen2, ZHANG Dianpeng2(
), CAI Shulin2, SU Zhuowen2, ZHANG Dianpeng2( ), SONG Bo1, XU Bingqiang1, Abudukeyoum Kader1, YANG Sen1
), SONG Bo1, XU Bingqiang1, Abudukeyoum Kader1, YANG Sen1
Received:2021-05-17
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-03-28
Correspondence author:
ZHANG Dianpeng
Supported by:
朱晓锋1( ), 蔡淑琳2, 苏卓文2, 张殿朋2(
), 蔡淑琳2, 苏卓文2, 张殿朋2( ), 宋博1, 徐兵强1, 阿布都克尤木·卡德尔1, 杨森1
), 宋博1, 徐兵强1, 阿布都克尤木·卡德尔1, 杨森1
通讯作者:
张殿朋
作者简介:朱晓锋(1979-),男,河南许昌人,研究员,博士,研究方向为特色林果有害生物综合防控,(E-mail) zxf5117@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHU Xiaofeng, CAI Shulin, SU Zhuowen, ZHANG Dianpeng, SONG Bo, XU Bingqiang, Abudukeyoum Kader, YANG Sen. Study on the Community Structure and Function of Fungi Associated (Symbiotic) with Scolytus schevyrewi That Infest Fruit Trees[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(3): 691-699.
朱晓锋, 蔡淑琳, 苏卓文, 张殿朋, 宋博, 徐兵强, 阿布都克尤木·卡德尔, 杨森. 果园脐腹小蠹伴生(共生)真菌群落组成及功能分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(3): 691-699.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.03.019
| 树种 Variety of tree | 采集地点 Place | 地理坐标 Geographical coordinate |
|---|---|---|
| 西梅 Prune | 疏勒县塔仔洪乡 | 76°11'01.61",39°16'44.03 |
| 桃 Peach | 英吉沙县城关镇 | 76°08'16.32",38°55'57.12" |
| 杏 Apricot | 阿克陶县巴仁乡 | 75°37'45.34",39°25'03.14" |
| 扁桃 Almond | 疏附县占敏乡 | 75°49'40.57",39°24'12.08" |
Table 1 Geographic information of sample collection place
| 树种 Variety of tree | 采集地点 Place | 地理坐标 Geographical coordinate |
|---|---|---|
| 西梅 Prune | 疏勒县塔仔洪乡 | 76°11'01.61",39°16'44.03 |
| 桃 Peach | 英吉沙县城关镇 | 76°08'16.32",38°55'57.12" |
| 杏 Apricot | 阿克陶县巴仁乡 | 75°37'45.34",39°25'03.14" |
| 扁桃 Almond | 疏附县占敏乡 | 75°49'40.57",39°24'12.08" |
| 取样部位 Sampling part | Shannon | Simpson | ACE | Chao | OUT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肠道Gut | 1.80±0.69a | 0.46±0.18a | 179.05±122.77a | 177.79±122.65a | 177.00±122.55a |
| 体表 Body surface | 1.71±0.51a | 0.40±0.16a | 88.07±23.47a | 87.20±23.45a | 85.00±23.44a |
Table 2 Alpha diversity index of fungi associated with S.schevyrewi
| 取样部位 Sampling part | Shannon | Simpson | ACE | Chao | OUT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肠道Gut | 1.80±0.69a | 0.46±0.18a | 179.05±122.77a | 177.79±122.65a | 177.00±122.55a |
| 体表 Body surface | 1.71±0.51a | 0.40±0.16a | 88.07±23.47a | 87.20±23.45a | 85.00±23.44a |
| 取样部位Sampling part | 门Phylum | 纲Class | 目Order | 科Family | 属Genus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肠道Gut | 7 | 23 | 62 | 114 | 204 |
| 体表Body surface | 6 | 20 | 43 | 74 | 111 |
| 体表+肠道 Body surface and gut | 7 | 24 | 66 | 124 | 221 |
Table 3 Community structure of fungi associated with S.schevyrewi
| 取样部位Sampling part | 门Phylum | 纲Class | 目Order | 科Family | 属Genus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肠道Gut | 7 | 23 | 62 | 114 | 204 |
| 体表Body surface | 6 | 20 | 43 | 74 | 111 |
| 体表+肠道 Body surface and gut | 7 | 24 | 66 | 124 | 221 |
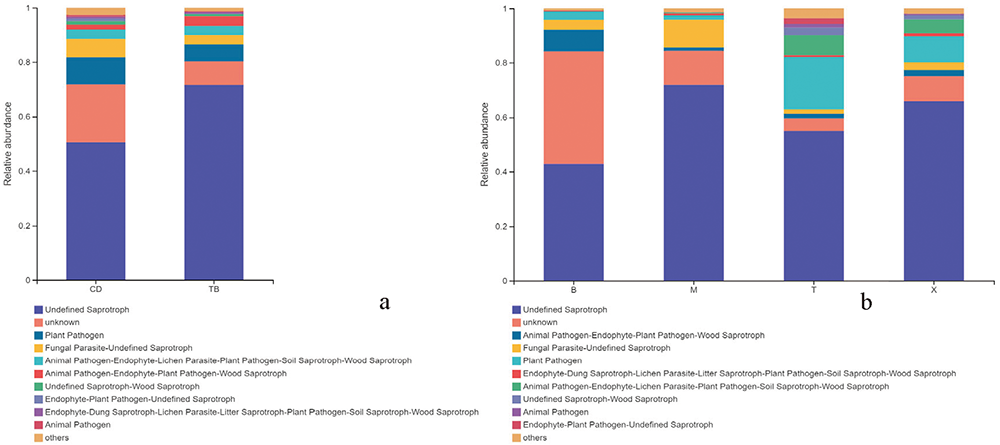
Fig.2 Composition of functional groups inferred of associated fungi with S.schevyrewi Note:CD: Gut, TB: Body surface, B: Almond, M: Prune, T: Peach, X: Apricot
| 取样部位Sampling part | 中文名称Chinese name | 拉丁名Scientific name |
|---|---|---|
| 体表、肠道 Body surface and gut | 出芽短梗霉菌 | Aureobasidium pullulans |
| 新疆假丝酵母 | Candida xinjiangensis | |
| 假丝酵母(疑似新种) | Candida sp. | |
| 汉姆酵母 | Wickerhamomyces silvicola | |
| 未命名 | Yamadazyma Mexicana | |
| 未命名 | Geosmithia pallid | |
| 未命名 | Candida peoriensis | |
| 体表 Body surface | 威克汉姆西弗酵母 | Wickerhamomyces ciferrii |
| 大孢枝孢菌 | Cladosporium macrocarpum | |
| 季也蒙毕赤酵母 | Meyerozyma guilliermondii | |
| 胶红酵母 | Rhodotorula mucilaginosa | |
| 未命名 | Naganishia albida | |
| 肠道Gut | 拟青霉 | Paecilomyces sp. |
Table 4 Isolation and identification of associated fungi with S.schevyrewi
| 取样部位Sampling part | 中文名称Chinese name | 拉丁名Scientific name |
|---|---|---|
| 体表、肠道 Body surface and gut | 出芽短梗霉菌 | Aureobasidium pullulans |
| 新疆假丝酵母 | Candida xinjiangensis | |
| 假丝酵母(疑似新种) | Candida sp. | |
| 汉姆酵母 | Wickerhamomyces silvicola | |
| 未命名 | Yamadazyma Mexicana | |
| 未命名 | Geosmithia pallid | |
| 未命名 | Candida peoriensis | |
| 体表 Body surface | 威克汉姆西弗酵母 | Wickerhamomyces ciferrii |
| 大孢枝孢菌 | Cladosporium macrocarpum | |
| 季也蒙毕赤酵母 | Meyerozyma guilliermondii | |
| 胶红酵母 | Rhodotorula mucilaginosa | |
| 未命名 | Naganishia albida | |
| 肠道Gut | 拟青霉 | Paecilomyces sp. |
| 种名Specific name | 功能Function |
|---|---|
| 新疆假丝酵母 C.xinjiangensis | 为新疆果树脐腹小蠹伴生真菌鉴定之新种[ |
| C.peoriensis | 无相关研究报道。 |
| 汉姆酵母 W.silvicola | 具有杀菌活性,能够分泌mycocin,子囊菌的45属140余种真菌对mycocin敏感[ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母 W.ciferrii | 无相关报道。 |
| 季也蒙毕赤酵母 M.guilliermondii | 为棘胫小蠹Platypus koryoensis伴生菌[ |
| 胶红酵母 R.mucilaginosa | 常作为生防菌防治水果采后病害[ |
| Y.Mexicana | 为多种小蠹虫伴生菌[ |
| N.albida | 无相关报道。 |
| 出芽短梗霉菌 A.pullulans | 对桃褐腐病、多种水果(葡萄、苹果、草莓)灰霉病等采后病害具有显著抑制作用[ |
| G.pallida | 常与小蠹虫伴生[ |
| 大孢枝孢菌 C.macrocarpum | 腐生菌[ |
Table 5 Function analysis of the associated fungi with S.schevyrewi
| 种名Specific name | 功能Function |
|---|---|
| 新疆假丝酵母 C.xinjiangensis | 为新疆果树脐腹小蠹伴生真菌鉴定之新种[ |
| C.peoriensis | 无相关研究报道。 |
| 汉姆酵母 W.silvicola | 具有杀菌活性,能够分泌mycocin,子囊菌的45属140余种真菌对mycocin敏感[ |
| 威克汉姆西弗酵母 W.ciferrii | 无相关报道。 |
| 季也蒙毕赤酵母 M.guilliermondii | 为棘胫小蠹Platypus koryoensis伴生菌[ |
| 胶红酵母 R.mucilaginosa | 常作为生防菌防治水果采后病害[ |
| Y.Mexicana | 为多种小蠹虫伴生菌[ |
| N.albida | 无相关报道。 |
| 出芽短梗霉菌 A.pullulans | 对桃褐腐病、多种水果(葡萄、苹果、草莓)灰霉病等采后病害具有显著抑制作用[ |
| G.pallida | 常与小蠹虫伴生[ |
| 大孢枝孢菌 C.macrocarpum | 腐生菌[ |
| [1] | Langstrom B, Heliovaara K, Moraal L G, et al. Bark and wood boring insects in living trees in Europe, A synbook[M]. Springer Netherlands, 2004. |
| [2] | 唐明, 陈辉. 华山松大小蠹共生真菌对寄主树木的影响[J]. 林业科学, 1999, 35(6): 63-66. |
| TANG Ming, CHENG Hui. Effect of symbiotic fungi of Dendroctonus armandi on host trees[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 1999, 35(6): 63-66. | |
| [3] | 叶辉. 小蠹虫伴生菌研究概况[J]. 世界林业研究, 1997,(1): 31-36. |
| YE Hui. Research status of fungi associated with beetles[J]. World Forestry Research, 1997,(1): 31-36. | |
| [4] | 吕全, 张星耀, 杨忠岐, 等. 红脂大小蠹伴生菌研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 2008, 44(2): 134-142. |
| LÜ Quan, ZHANG Xinyao, YANG Zhongqi, et al. Progress in study on the fungi associated with Dendroctonus valens[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2008, 44(2): 134-142. | |
| [5] | 鲁敏, 孙江华. 危害松树的小蠹虫与其伴生菌的相互关系[J]. 昆虫知识, 2008, 45(4): 518-527. |
| LU Min, SUN Jianghua. Interactions among scolytid bark beetles and the associated fungi during attacking the living conifers[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 2008, 45(4): 518-527. | |
| [6] | Wood, S.L., Bright, D.E. A catalog of Scolytidae and Platypodidae (Coleoptera), Part 2: Taxonomic index[M]. Brigham Young University: Monte L.Bean Life Science Museum, 1992. |
| [7] | 李宏, 朱晓锋, 阿布都克尤木, 等. 喀什地区多毛小蠹发生与为害规律[J]. 植物保护, 2009, 35(6): 135-138. |
| LI Hong, ZHU Xiaofeng, Abudu Keyoumu, et al. Occurrence and damage of Scolytus seulensis in Kashi[J]. Plant Protection, 2009, 35(6): 135-138. | |
| [8] | 张鲁豫, 赵莉, 李军如, 等. 轮台县杏树多毛小蠹生物学特性研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2011, 48(9): 1655-1660. |
| ZHANG Luyu, ZHAO Li, LI Junru, et al. Study on bionomics of almond bark beetle in Luntai county[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 48(9): 1655-1660. | |
| [9] | 李江霖, 张涛, 李新唐, 等. 新疆果树多毛小蠹生物学特性及防治[J]. 植物保护, 1995, 21(1): 8-10. |
| LI Jianglin, ZHANG Tao, LI Xintang, et al. Study on bionomics of Scolytus seulensis Murayama and its control[J]. Plant Protection, 1995, 21(1): 8-10. | |
| [10] | 魏景超. 真菌鉴定手册[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1979. |
| WEI Jingchao. Manual of fungal identification[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1979. | |
| [11] |
ZHU X, Zhang D, Yang S, et al. Candida xinjiangensis sp.nov., a new anamorphic yeast species isolated from Scolytus scheryrewi Semenov in China[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2017, 199(2): 377-383.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Golubv W I. Antifungal Activity of Wickerhamomyces silvicola[J]. Mikrobiologiia, 2015, 84(5): 529. |
| [13] |
Yun Y.H,., Suh D.Y,., Yoo H.D., et al. Yeast Associated with the Ambrosia Beetle, Platypus koryoensis, the Pest of Oak Trees in Korea[J]. Mycobiology, 2015, 43(4): 458-466.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Mokhtarnejad L, Etebarian H R, Fazeli M R, et al. Evaluation of different formulations of potential biocontrol yeast isolates efficacy on apple blue mold at storage condition[J]. Archives of Phytopathology and Plant Protection, 2011, 44(10): 970-980.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Fard F.A, Eteberian H R, Sahebani N. Biological control of gray mold of apple by Candida membranifaciens, Rhodotorula mucilaginosa and Pichia guilliermondii[J]. Iranian Journal of Plant Pathology, 2012, 48(1): 17-26. |
| [16] | 高云慨, 张荣意, 钟利文, 等. 1株新分离拮抗酵母菌株对芒果炭疽病生防效果及其分类鉴定[J]. 热带生物学报, 2015, 6(1): 47-52. |
| GAO Yungai, ZHANG Rongyi, ZHONG Liwen, et al. Classification and identification of a new isolated yeast strain and its biocontrol activity against postharvest anthracnose of mango fruit[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2015, 6(1): 47-52. | |
| [17] | Nakatani M. Suppression of rice blast, cabbage black leaf spot, and tomato bacterial wilt diseases by TA-2 and the nature of protection[J]. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B - Soil & Plant Science, 2015, 65(7): 1-8. |
| [18] | 程哲. 热激处理增强生防酵母菌(Rhodotorula mucilaginosa)抗逆性及生防效力的研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学, 2016. |
| CHENG Zhe. Effect of heat on stress tolerance and biocontrol efficacy of the antagostic yeast Rhodotorula mucilaginosa[D]. Hefi: Hefi University of Technology, 2016. | |
| [19] | 束兆林, 杨红福, 陈红州, 等. 胶红酵母(Rhodotorula mucilaginosa)对梨果采后青霉病、灰霉病的控制效果[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(8): 110-112. |
| SHU Zhaolin, YANG Hongfu, CHEN Hongzhou, et al. Control effect of Rhodotorula mucilaginosa on Postharvest penicilliosis and Botrytis cinerea of pear[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(8): 110-112. | |
| [20] | 徐占利. 梨果采后病害新型拮抗菌分离、筛选及安全性研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学, 2010. |
| XU Zhanli. Solation, screening and security study of new antagonists against the postharvest diseases of pear[D]. Zhengjiang:Jiangsu University, 2010. | |
| [21] |
Rivera F.N, Gonzaiea E, Gomea Z. et al. Gut-associated yeast in bark beetles of the genus Dendroctonus erichson (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae)[J]. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 2009, 98(2): 325-342.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Miranda M, Phaff H, Starmer W. Pichia mexicana, a new heterothallic yeast from cereoid cacti in the north American sonoran desert[J]. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 1982, 32(1): 101-107.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 王红. 苹果和梨果表面酵母多样性及其食用安全性研究[D]. 济南:齐鲁工业大学, 2013. |
| WANG Hong. The diversity and edible safety of yeasts on the surface of apple and pear[D]. Jinan:Qilu University of Technology, 2013. | |
| [24] | 王晨, 卢彩鸽, 刘德文, 等. 桃采后褐腐病生防酵母菌的筛选及鉴定[J]. 河南农业科学, 2017, 46(5): 90-94. |
| WANG Chen, LU Caige, LIU Dewen, et al. Screening and Identification of Yeast Strains to control brown rot of postharvest peaches[J]. Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 46(5): 90-94. | |
| [25] |
Mari M, Martini C, Guidarelli M, et al. Postharvest biocontrol of monilinia laxa, Monilinia fructicola and Monilinia fructigena on stone fruit by two Aureobasidium pullulans strains[J]. Biological Control, 2012, 60(2): 132-140.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 巩文峰, 李月飞, 上官妮妮, 等. 出芽短梗霉对苹果采后灰霉病的防治[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2016, 32(2): 251-257. |
| GONG Wenfeng, LI Yuefei, SHANGGUAN Nini, et al. Control of Apple Postharvest Gray Mold by Aureobasidium pullulans[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2016, 32(2): 251-257. | |
| [27] | Naik B S, Krishnappa M, Krishnamurthy Y L. Endophytic assemblage in L.and antagonistic activities[J]. Archives of Phytopathology & Plant Protection, 2015, 48(1): 28-33. |
| [28] | 黄蓉, 杨龙, 张静, 等. 出芽短梗霉菌株YW1防治储藏期草莓灰霉病的研究[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2013, 29(4): 531-537. |
| HUANG Rong, YANG Long, ZHANG Jing, et al. Efficacy of Aureobasidium pullulans YW1 in suppression of gray mold on post-harvest strawberry fruits[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2013, 29(4): 531-537. | |
| [29] |
Zhang D, Davide S, Angelo G, et al. Efficacy of the antagonist Aureobasidium pullulans PL5 against postharvest pathogens of peach, apple and plum and its modes of action[J]. Biological Control, 2010, 54(3): 172-180.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Skrimi B, Bajji M, Massart S, et al. Biocontrol of blue mold on apple fruits by Aureobasidium pullulans (strain Ach 1-1): in vitro and in situ evidence for the possible involvement of competition for nutrients[J]. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci, 2006, 71(3 Pt B): 1151-1157. |
| [31] |
Adikaram N K.B, Joyce D C, Terryc L A. Biocontrol activity and induced resistance as a possible mode of action for Aureobasidium pullulans against grey mould of strawberry fruit[J]. Australasian Plant Pathology, 2002, 31(3): 223-229.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Wachowska U, Glowacka K. Antagonistic interactions between Aureobasidium pullulans and Fusarium culmorum, a fungal pathogen of winter wheat[J]. Biocontrol, 2014, 59(5): 635-645.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Flood J, Rees J. Host produced toxins associated with antagonism by Aureobasidium pullulans against Alternaria solani on wounded tomato leaves[J]. Physiological & Molecular Plant Pathology, 1986, 28(1): 79-88. |
| [34] |
Huang Y T, Kolarik M, Kasson M T, et al. Two new Geosmithia species in G.pallida species complex from bark beetles in eastern USA[J]. Mycologia, 2017, 109(5): 1.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Kolarik M, Hulcr J, Tisserat N, et al. Geosmithia associated with bark beetles and woodborers in the western USA: taxonomic diversity and vector specificity[J]. Mycologia, 2017, 109(10): 1.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Kolarik, M, Kostovcik M, Pazoutova S. Host range and diversity of the genus Geosmithia (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) living in association with bark beetles in the Mediterranean area[J]. Mycological Research, 2007, 111(11): 1298-1310.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Kolarik M, Kubatova, A, Pazoutova S, et al. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Geosmithia putterillii, G.pallida comb.nov.and G.flava sp.nov., associated with subcorticolous insects[J]. Mycological Research, 2004, 108(9): 1053-1069.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Vannini A, Contarini M, Faccoli M, et al. First report of the ambrosia beetle Xylosandrus compactus and associated fungi in the Mediterranean maquis in Italy, and new host-pest associations[J]. Eppo Bulletin, 2017, 47(1): 100-103.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Cizkova D, Srutka P, Kolarik M, et al. Assessing the pathogenic effect of Fusarium, Geosmithia and Ophiostoma fungi from broad-leaved trees.[J]. Folia Microbiologica, 2005, 50(1): 59-62.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Bertelsen J R, De Neergaard E, Smedegaard P V. Fungicidal effects of azoxystrobin and epoxiconazole on phyllosphere fungi, senescence and yield of winter wheat[J]. Plant Pathology, 2001, 50(2): 190-205.
DOI URL |
| [41] | 张绍升, 肖荣凤, 林乃铨, 等. 福建橄榄真菌性病害鉴定[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 31(2): 168-173. |
| ZHANG Shaosheng, XIAO Rongfeng, LIN Naiquan, et al. Diagnosis of Chinese olive fungal diseases in Fujian[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Ed.), 2002, 31(2): 168-173. | |
| [42] | 郭书普. 叶类蔬菜病虫害防治原色图鉴[M]. 合肥: 安徽科学技术出版社, 2004. |
| GUO Shupu. Primary color map of pest control of leafy vegetables [M]. Hefi: Anhui Science and Technology Press, 2004. | |
| [43] | 王四宝, 曲爽. 昆虫共生菌及其在病虫害防控中的应用前景[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2017, 32(8): 863-872. |
| WANG Sibao, QU Shuang. Insect symbionts and their potential application in pest and vector-borne disease control[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017, 32(8): 863-872. | |
| [44] |
Davis T S. The ecology of yeasts in the bark beetle holobiont, A century of research revisited. Microbial Ecology, 2015, 69(4): 723-732.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Davis T S, Hofstetter R W. Reciprocal interactions between the bark beetle-associated yeast Ogataea pini and host plant phytochemistry[J]. Mycologia, 2011, 103(6): 1201-1207.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Davis T S, Hofstetter R W, Foster J T, et al. Interactions between the yeast Ogataea pini and filamentous fungi associated with the western pine beetle. Microbial Ecology, 2011, 61(3): 626-634.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WEN Xia, TIAN Lichao, GAO Guizhen. Functional response of Chilomenes quadriplagiata to Tinocallis kahawaluokalani [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2266-2272. |
| [2] | LI Kailiang, ZHANG Zhenyu, HU Hongying. Structure and diversity analysis of insect community in jujube orchard of Hami Area in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 2028-2037. |
| [3] | LI Zhiqiang, CHEN Yudong, LYU Guanghui, WANG Jinlong, JIANG Lamei, WANG Hengfang, LI Hanpeng, ZHANG Lei. Soil water-salt response characteristics and ecological strategies for functional traits of desert herbaceous plants [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 2038-2045. |
| [4] | BAI Ling, FENG Guojun, HU Xiangwei, ZHAO Yun, SHI Shubing. Drought resistance identification and physiological changes of different millet varieties during germination [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(7): 1630-1640. |
| [5] | TIAN Jingyu, GAO Yan, GAO Xingwang, ZENG Jun, ZHAO Pengan, Subinuer Julaiti. Analysis of rhizospheric bacterial community structure and diversity of Hami melon under field cultivation [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1253-1262. |
| [6] | TANG Xixi, Mubarek Ayup, XU Panyun, YU Qiuhong, GUO Chunmiao, ZHANG Ping, GONG Peng. Response of root anatomical structure of different rootstock resources of almond to drought stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 897-907. |
| [7] | LIU Min, JIN Juan, Abudoukayoumu Ayimaiti, FAN Dingyu, HAO Qing, YANG Lei, ZHAO Xiaomei, GENG Wenjuan. Evaluation of cold resistance of three fresh edible jujube cultivars in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 916-924. |
| [8] | FENG Fan, XIE Kaiyun, Aibibula Yimamu, WAN Jiangchun. Effects of intercrop forages on weed control, soil and tree nutrients in orchards [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 982-991. |
| [9] | HU Wencong, PAN Cunde, ZHAO Shanchao, SONG Mengzhen, TONG Haimai, TIAN Chenyang. Microhabitat Interpretation of Survival Quantity and Functional Traits of One-year-old Natural Regeneration Seedlings of Picea schrenkiana var. tianschanica in the Central Part of the Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(2): 454-463. |
| [10] | WANG Wei, XU Le, FAN Yanxing, WANG Fan, MA Yanming, TANG Zhonghua. Multivariable comparative analysis of chickpea seed metabolites based on GC-MS [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(12): 2962-2972. |
| [11] | YAN Pan, WANG Jiuzhao, JIANG Jiyuan, CHEN Qiling. Effects of different ground cover materials on soil environment of apple orchard in oasis of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(7): 1690-1696. |
| [12] | XIN Huinan, LAI Ning, GENG Qinglong, CHEN Shuhuang, LI Na, LI Yongfu, ZHAO Haiyan. Spatial Variability of Farmland Soil Nutrients in Ta'er Basin Based on GIS [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(7): 1776-1785. |
| [13] | LI Haiqiang, WANG Dongmei, LIU Jian. Effects of Walnut-Cotton Intercropping on Arthropod Community Structure and the Population of Natural Enemies in Cotton Fields [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(4): 934-941. |
| [14] | FU Dongqing, WANG Yanchao, MAO Jiaxiang, YANG Fan, SONG Lei, ZHANG Fanfan, MA Chunhui. Comprehensive Quality Analysis and Evaluation Oat Varieties under Dry Farming Conditions in Balluk Mountain [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(2): 344-352. |
| [15] | WANG Weixia, Aliya Alimu, YANG Guang, WANG Zhenxi. Effects of Land Use Patterns on Soil Liable Organic Carbon and Dissolved Organic Carbon in Typical Arid Desert Oasis Area [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(2): 441-450. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||