

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2022, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (10): 2341-2351.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.10.001
• Crop Genetics and Breeding·Cultivation Physiology·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Genetics • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHENG ShaoYu1( ), LIN Tao2,3(
), LIN Tao2,3( ), WU Fengquan1, HOU Peike1, ZHANG Liying1, TANG Qiuxiang1(
), WU Fengquan1, HOU Peike1, ZHANG Liying1, TANG Qiuxiang1( )
)
Received:2021-11-04
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-12-21
Correspondence author:
LIN Tao, TANG Qiuxiang
Supported by:
程少雨1( ), 林涛2,3(
), 林涛2,3( ), 吴凤全1, 侯培珂1, 张丽莹1, 汤秋香1(
), 吴凤全1, 侯培珂1, 张丽莹1, 汤秋香1( )
)
通讯作者:
林涛,汤秋香
作者简介:程少雨(1997-),男,河北邯郸人,硕士研究生,研究方向为农田资源高效利用,(E-mail)786249023@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
CHENG ShaoYu, LIN Tao, WU Fengquan, HOU Peike, ZHANG Liying, TANG Qiuxiang. Effects of Density and Irrigation Quota under Drip Irrigation on Nitrate Distribution and Nitrogen Utilization in Cotton Field with Constant Row Spacing of 76cm[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(10): 2341-2351.
程少雨, 林涛, 吴凤全, 侯培珂, 张丽莹, 汤秋香. 密度和灌溉定额互作对76 cm等行距机采棉田水分分布及利用的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(10): 2341-2351.
| 生育时期 Growth period | 日期 Date (D/M) | 天数 Number of days(d) |
|---|---|---|
| 苗期 Seedling stage | 12/5-5/6 | 25 |
| 蕾期 Bud stage | 6/6-25/6 | 20 |
| 花期 Flowering stage | 26/6-23/7 | 28 |
| 铃期 Boll setting stage | 24/7-23/8 | 31 |
| 吐絮期 Boll opening stage | 24/8-30/9 | 38 |
| 全生育时期 Whole growth period | 12/5-30/9 | 142 |
Table 1 Division of growth period for cotton in 2020
| 生育时期 Growth period | 日期 Date (D/M) | 天数 Number of days(d) |
|---|---|---|
| 苗期 Seedling stage | 12/5-5/6 | 25 |
| 蕾期 Bud stage | 6/6-25/6 | 20 |
| 花期 Flowering stage | 26/6-23/7 | 28 |
| 铃期 Boll setting stage | 24/7-23/8 | 31 |
| 吐絮期 Boll opening stage | 24/8-30/9 | 38 |
| 全生育时期 Whole growth period | 12/5-30/9 | 142 |
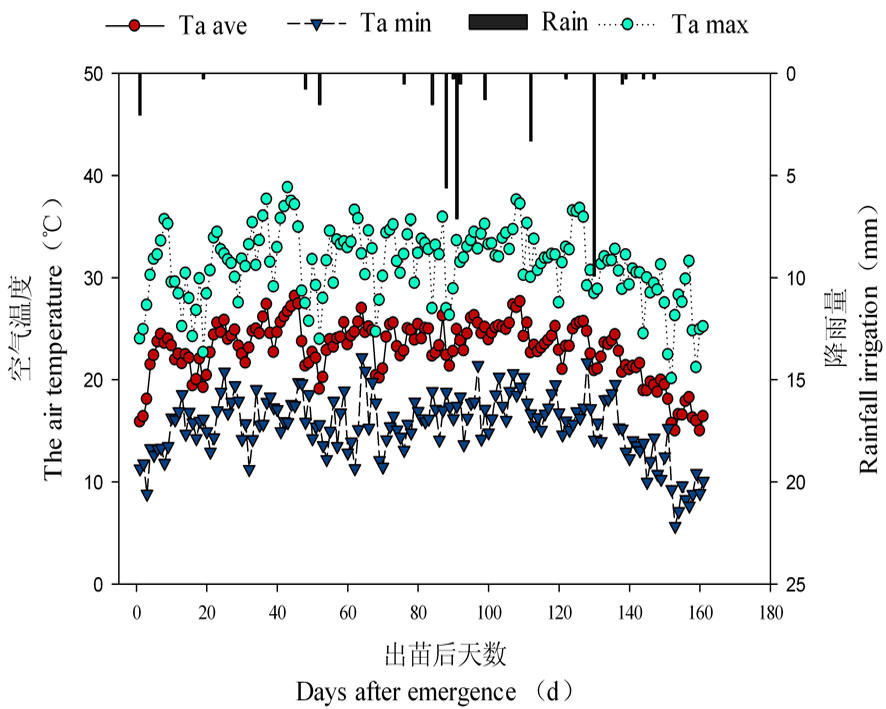
Fig.2 Air temperature and rainfall in cotton fields in 2020 Note:Ta Ave, Ta Max, and Ta min are the average, maximum, and minimum air temperature respectively, and Rian is the irrigation volume of the water
| 土壤 深度 Soil depths (cm) | 处理Treatments | 因素显著性 Factor significance analysis | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | ||||||||||||||
| W1 | W2 | W3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | 密度 Plant density (D) | 灌量 Irriga tion amou nt (I) | 密度 × 灌溉 D×I | |||||
| 0~10 | 17.63 cd | 17.43 de | 18.49 bc | 16.76 de | 18.79 b | 18.86 b | 16.51 e | 22.22 a | 19.30 b | ** | ** | ** | ||||
| 10~20 | 22.43 de | 21.59 e | 24.53 abc | 22.94 cde | 24.89 ab | 23.83 bcd | 22.15 de | 25.82 a | 25.26 ab | * | ** | ** | ||||
| 20~30 | 20.29 d | 20.39 d | 24.89 ab | 20.47 d | 24.17 ab | 23.53 bc | 21.80 cd | 23.08 bc | 25.90 a | * | ** | NS | ||||
| 30~40 | 23.75 ab | 22.79 b | 24.96 ab | 22.13 b | 24.72 ab | 25.37 ab | 25.33 ab | 22.28 b | 27.06 a | NS | * | NS | ||||
| 40~50 | 24.20 ab | 24.67 ab | 25.10 ab | 23.09 b | 25.43 ab | 25.50 ab | 27.25 a | 23.25 b | 26.50 ab | NS | NS | NS | ||||
| 50~60 | 21.97 c | 25.53 abc | 28.11 a | 24.04 bc | 25.02 abc | 25.80 ab | 25.27 abc | 25.40 abc | 26.40 ab | NS | * | NS | ||||
| 60~70 | 20.56 d | 28.93 a | 31.37 a | 27.20 abc | 24.62 bcd | 28.58 ab | 23.88 cd | 27.27 abc | 28.43 ab | NS | ** | * | ||||
| 70~80 | 24.01 d | 32.46 ab | 34.34 a | 30.07 bc | 27.56 cd | 34.73 a | 26.96 cd | 29.12 bc | 30.28 bc | NS | ** | ** | ||||
| 0~80 | 21.86 d | 24.23 bc | 26.47 a | 23.34 cd | 24.40 abc | 25.77 ab | 23.64 cd | 24.80 abc | 26.14 ab | NS | ** | NS | ||||
Table 2 Analysis of variance of soil moisture content of cotton field with 0~80 cm soil layer by density and irrigation quota
| 土壤 深度 Soil depths (cm) | 处理Treatments | 因素显著性 Factor significance analysis | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | ||||||||||||||
| W1 | W2 | W3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | 密度 Plant density (D) | 灌量 Irriga tion amou nt (I) | 密度 × 灌溉 D×I | |||||
| 0~10 | 17.63 cd | 17.43 de | 18.49 bc | 16.76 de | 18.79 b | 18.86 b | 16.51 e | 22.22 a | 19.30 b | ** | ** | ** | ||||
| 10~20 | 22.43 de | 21.59 e | 24.53 abc | 22.94 cde | 24.89 ab | 23.83 bcd | 22.15 de | 25.82 a | 25.26 ab | * | ** | ** | ||||
| 20~30 | 20.29 d | 20.39 d | 24.89 ab | 20.47 d | 24.17 ab | 23.53 bc | 21.80 cd | 23.08 bc | 25.90 a | * | ** | NS | ||||
| 30~40 | 23.75 ab | 22.79 b | 24.96 ab | 22.13 b | 24.72 ab | 25.37 ab | 25.33 ab | 22.28 b | 27.06 a | NS | * | NS | ||||
| 40~50 | 24.20 ab | 24.67 ab | 25.10 ab | 23.09 b | 25.43 ab | 25.50 ab | 27.25 a | 23.25 b | 26.50 ab | NS | NS | NS | ||||
| 50~60 | 21.97 c | 25.53 abc | 28.11 a | 24.04 bc | 25.02 abc | 25.80 ab | 25.27 abc | 25.40 abc | 26.40 ab | NS | * | NS | ||||
| 60~70 | 20.56 d | 28.93 a | 31.37 a | 27.20 abc | 24.62 bcd | 28.58 ab | 23.88 cd | 27.27 abc | 28.43 ab | NS | ** | * | ||||
| 70~80 | 24.01 d | 32.46 ab | 34.34 a | 30.07 bc | 27.56 cd | 34.73 a | 26.96 cd | 29.12 bc | 30.28 bc | NS | ** | ** | ||||
| 0~80 | 21.86 d | 24.23 bc | 26.47 a | 23.34 cd | 24.40 abc | 25.77 ab | 23.64 cd | 24.80 abc | 26.14 ab | NS | ** | NS | ||||
| 土壤 深度 Soil depths (cm) | 处理Treatments | 因素显著性 Factor significance analysis | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | ||||||||||||||
| W1 | W2 | W3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | 密度 Plant density (D) | 灌量 Irriga tion amou nt (I) | 密度 × 灌溉 D×I | |||||
| 0~10 | 0.83 ab | 0.72 cd | 0.72 cd | 0.72 cd | 0.79 bc | 0.72 cd | 0.70 d | 0.89 a | 0.74 cd | NS | * | ** | ||||
| 10~20 | 0.95 abc | 0.88 d | 0.92 bcd | 0.90 d | 0.96 ab | 0.91 cd | 0.92 bcd | 0.98 a | 0.96 ab | * | NS | ** | ||||
| 20~30 | 0.92 bcd | 0.84 e | 0.94 abc | 0.87 de | 0.98 ab | 0.90 cd | 0.92 cd | 0.92 bcd | 0.98 a | * | NS | ** | ||||
| 30~40 | 0.89 c | 0.94 abc | 0.94 abc | 0.93 abc | 0.99 a | 0.97 ab | 0.92 bc | 0.90 c | 0.97 ab | NS | NS | NS | ||||
| 40~50 | 0.89 bc | 0.98 a | 0.94 ab | 0.93 ab | 0.97 a | 0.98 a | 0.85 c | 0.95 ab | 0.99 a | NS | ** | NS | ||||
| 50~60 | 0.97 ab | 0.95 bc | 0.94 bc | 0.95 bc | 0.93 c | 0.99 a | 0.93 c | 0.97 ab | 0.99 a | NS | ** | ** | ||||
| 60~70 | 0.90 a | 0.80 c | 0.82 c | 0.83 bc | 0.95 a | 0.89 a | 0.89 ab | 0.89 a | 0.91 a | ** | NS | ** | ||||
| 70~80 | 0.86 a | 0.65 b | 0.69 b | 0.70 b | 0.86 a | 0.63 b | 0.81a | 0.82 a | 0.83 a | ** | * | ** | ||||
Table 3 Influence of density and irrigation quota on the uniformity coefficient of soil moisture distribution in cotton fields
| 土壤 深度 Soil depths (cm) | 处理Treatments | 因素显著性 Factor significance analysis | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | ||||||||||||||
| W1 | W2 | W3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | 密度 Plant density (D) | 灌量 Irriga tion amou nt (I) | 密度 × 灌溉 D×I | |||||
| 0~10 | 0.83 ab | 0.72 cd | 0.72 cd | 0.72 cd | 0.79 bc | 0.72 cd | 0.70 d | 0.89 a | 0.74 cd | NS | * | ** | ||||
| 10~20 | 0.95 abc | 0.88 d | 0.92 bcd | 0.90 d | 0.96 ab | 0.91 cd | 0.92 bcd | 0.98 a | 0.96 ab | * | NS | ** | ||||
| 20~30 | 0.92 bcd | 0.84 e | 0.94 abc | 0.87 de | 0.98 ab | 0.90 cd | 0.92 cd | 0.92 bcd | 0.98 a | * | NS | ** | ||||
| 30~40 | 0.89 c | 0.94 abc | 0.94 abc | 0.93 abc | 0.99 a | 0.97 ab | 0.92 bc | 0.90 c | 0.97 ab | NS | NS | NS | ||||
| 40~50 | 0.89 bc | 0.98 a | 0.94 ab | 0.93 ab | 0.97 a | 0.98 a | 0.85 c | 0.95 ab | 0.99 a | NS | ** | NS | ||||
| 50~60 | 0.97 ab | 0.95 bc | 0.94 bc | 0.95 bc | 0.93 c | 0.99 a | 0.93 c | 0.97 ab | 0.99 a | NS | ** | ** | ||||
| 60~70 | 0.90 a | 0.80 c | 0.82 c | 0.83 bc | 0.95 a | 0.89 a | 0.89 ab | 0.89 a | 0.91 a | ** | NS | ** | ||||
| 70~80 | 0.86 a | 0.65 b | 0.69 b | 0.70 b | 0.86 a | 0.63 b | 0.81a | 0.82 a | 0.83 a | ** | * | ** | ||||
| 处理 Treatments | 灌水量 Irrigation amount(mm) | 籽棉产量 Production (kg/hm2) | 水分变化 △W (mm) | 耗水量 ETa (mm) | 日耗水强度 DCC (mm) | 水分利用率 WUE (kg/(hm2·mm)) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | W1 | 315 | 4 481.77 bcd | -12.31 ab | 343.55 c | 2.42 c | 13.09 a |
| W2 | 405 | 4 543.11 abc | -17.86 ab | 428.00 b | 3.01 b | 10.62 c | |
| W3 | 498 | 4 752.62 a | -42.45 b | 496.41 a | 3.50 a | 9.57 de | |
| M2 | W1 | 315 | 4 287.92 de | 13.15 a | 369.01 c | 2.60 c | 11.63 b |
| W2 | 405 | 4 377.48 cde | -12.72 ab | 433.15 b | 3.05 b | 10.12 cde | |
| W3 | 498 | 4 745.95 a | -25.44 b | 513.42 a | 3.62 a | 9.26 ef | |
| M3 | W1 | 315 | 4 629.92 ab | -18.27 ab | 337.59 c | 2.38 c | 13.72 a |
| W2 | 405 | 4 318.60 de | -28.66 b | 417.08 b | 2.94 b | 10.41 cd | |
| W3 | 498 | 4 263.03 e | -37.28 b | 501.58 a | 3.53 a | 8.50 f | |
| 密度 Plant density(D) | * | NS | NS | NS | * | ||
| 灌溉 Irrigation amount (I) | * | * | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 密度×灌溉 D×I | ** | NS | NS | NS | ** | ||
Table 4 Influence of density and irrigation quota on soil water use in cotton fields
| 处理 Treatments | 灌水量 Irrigation amount(mm) | 籽棉产量 Production (kg/hm2) | 水分变化 △W (mm) | 耗水量 ETa (mm) | 日耗水强度 DCC (mm) | 水分利用率 WUE (kg/(hm2·mm)) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | W1 | 315 | 4 481.77 bcd | -12.31 ab | 343.55 c | 2.42 c | 13.09 a |
| W2 | 405 | 4 543.11 abc | -17.86 ab | 428.00 b | 3.01 b | 10.62 c | |
| W3 | 498 | 4 752.62 a | -42.45 b | 496.41 a | 3.50 a | 9.57 de | |
| M2 | W1 | 315 | 4 287.92 de | 13.15 a | 369.01 c | 2.60 c | 11.63 b |
| W2 | 405 | 4 377.48 cde | -12.72 ab | 433.15 b | 3.05 b | 10.12 cde | |
| W3 | 498 | 4 745.95 a | -25.44 b | 513.42 a | 3.62 a | 9.26 ef | |
| M3 | W1 | 315 | 4 629.92 ab | -18.27 ab | 337.59 c | 2.38 c | 13.72 a |
| W2 | 405 | 4 318.60 de | -28.66 b | 417.08 b | 2.94 b | 10.41 cd | |
| W3 | 498 | 4 263.03 e | -37.28 b | 501.58 a | 3.53 a | 8.50 f | |
| 密度 Plant density(D) | * | NS | NS | NS | * | ||
| 灌溉 Irrigation amount (I) | * | * | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 密度×灌溉 D×I | ** | NS | NS | NS | ** | ||
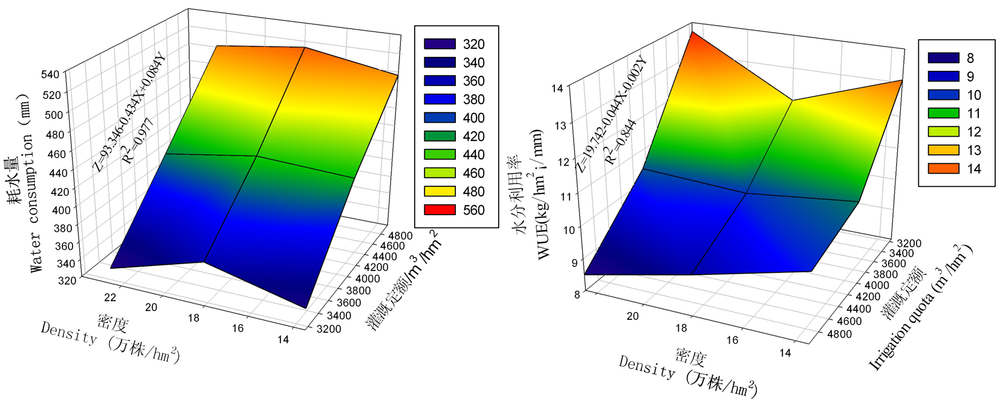
Fig.5 Three-dimensional response surface quantitative regression model of density and irrigation quota on cotton field water consumption and water utilization ratio
| [1] | 尔晨, 林涛, 张昊, 等. 行距对机采棉干物质积累及氮磷利用效率的影响[J]. 棉花学报, 2020, 32(1):77-90. |
| ER Chen, LIN Tao, ZHANG Hao, et al. Effect of row spacing on dry matter accumulation and nitrogen and phosphorus utilization efficiency of machine-picked cotton[J]. Journal of Cotton Science, 2020, 32(1):77-90. | |
| [2] | 邓方宁, 林涛, 何文清, 等. 生物降解地膜覆盖对棉田水-热-盐及产量的影响[J/OL]. 生态学杂志:1-12[2021-02-19]. |
| DENG Fangning, LIN Tao, HE Wenqing, et al. Effects of biodegradable plastic film mulching on water-heat-salt and yield of cotton field[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Ecology :1-12[2021-02-19]. | |
| [3] | 吴凤全, 林涛, 陈兵林, 等. 密度和灌量互作对76 cm等行距机采棉产量形成及水分利用效率的影响[J/OL]. 南京农业大学学报:1-9[2021-02-19]. |
| WANG Fengquan, LIN Tao, CHEN Binglin, et al. Effects of interaction between density and irrigation amount on yield formation and water use efficiency of machine-picked cotton with equal row spacing of 76 cm[J/OL]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University :1-9[2021-02-19]. | |
| [4] | 廖凯, 高振江, 孙巍, 等. 农艺条件对机采棉品质的影响分析[J]. 中国棉花, 2014, 41(11):16-20. |
| LIAO Kai, GAO Zhenjiang, SUN Wei, et al. Analysis of the Influence of Agronomic conditions on the quality of machine-picked cotton[J]. Chinese flower, 2014, 41(11):16-20. | |
| [5] | 缪新龙, 柳延涛, 李军, 等. 北疆棉区棉花高产栽培技术的研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2007,(S2):62-64. |
| MIAO Xinlong, LIU Yantao, LI Jun, et al. Study on high-yield cultivation techniques of cotton in northern Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2007,(S2):62-64. | |
| [6] | 林涛, 汤秋香, 郝卫平, 等. 地膜残留量对棉田土壤水分分布及棉花根系构型的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(19):117-125. |
| LIN Tao, TANG Qiuxiang, HAO Weiping, et al. Effect of mulch residue on soil moisture distribution and cotton root system configuration in cotton fields[J]. Chinese journal of agricultural engineering, 2019, 35(19):117-125. | |
| [7] | 侯英俊. 研究机采种植模式下棉花种植密度[J]. 现代农业研究, 2020, 26(10):95-96. |
| HOU Yingjun. research on cotton planting density under mechanized cropping pattern[J]. Modern agricultural research, 2020, 26(10):95-96. | |
| [8] | 娄善伟, 高云光, 郭仁松, 等. 不同栽培密度对棉花植株养分特征及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(4):953-958. |
| LOU Shanwei, GAO Yunguang, GUO Rensong, et al. Effects of different cultivation densities on plant nutrient Characteristics and Yield of cotton[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2010, 16(4):953-958. | |
| [9] | 朱文美. 灌水量和种植密度互作对冬小麦产量及水分利用效率的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2018. |
| ZHU Wenmei. The interaction between irrigation amount and planting density influences the yield and WUE of winter wheat[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. 2018 | |
| [10] | 田文仲, 温红霞, 高海涛, 等. 不同播期、播种密度及其互作对小麦产量的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2011, 40(2):45-49. |
| TIAN Wenzhong, Wen Hongxia, GAO Haotai, et al. Effects of different sowing dates, planting densities and their interactions on wheat yield[J]. Henan agricultural sciences, 2011, 40(2):45-49. | |
| [11] | 张文斌. 种植密度对全膜双垄沟播玉米生理特性及产量的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2009. |
| ZHANG Wenbin. Effects of planting density on physiological characteristics and yield of corn sown with double furrows on whole film[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University. 2009 | |
| [12] | 姚名泽. 南疆机采棉膜下滴灌土壤水分运移特征、耗水规律及产量品质研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2013. |
| YAO Mingze. Study on soil water transport characteristics, water consumption rule and Yield and quality of drip irrigation under cotton picking film in Southern Xinjiang[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University. 2013 | |
| [13] | 马兴华, 王东, 于振文, 等. 不同施氮量下灌水量对小麦耗水特性和氮素分配的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(8):1955—1965. |
| MA Xinghua, WANG Dong, YU Zhenwen, et al. Effects of different n application rates on water consumption characteristics and Nitrogen distribution of wheat[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2010, 30(8):1955—1965. | |
| [14] | 龚子同, 陈鸿昭, 杨帆, 等. 中亚干旱区土壤地球化学和环境[J]. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(1):1-9. |
| GONG Zitong, CHEN Hongzhao, YANG Fan, et al. Soil geochemistry and Environment in arid Regions of Central Asia[J]. Study on arid Regions, 2017, 34(1):1-9. | |
| [15] | 赵黎明, 李明, 郑殿峰, 等. 灌溉方式与种植密度对寒地水稻产量及光合物质生产特性的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(6):159-169. |
| ZHAO Liming, LI Ming, ZHENG Dianfeng, et al. Effects of irrigation methods and planting density on rice yield and photosynthetic matter production characteristics in cold region[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31 (6):159-169. | |
| [16] | 关红杰, 李久生, 栗岩峰. 干旱区滴灌均匀系数和灌水量对土壤水氮分布的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(24):121-128. |
| GUAN Hongjie, LI Jiusheng, LI Yanfeng. Effects of drip irrigation uniformity coefficient and irrigation amount on soil water and nitrogen distribution in arid area[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28 (24):121-128. | |
| [17] | 祖米来提·吐尔干, 林涛, 严昌荣, 等. 地膜覆盖时间对新疆棉田水热及棉花耗水和产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(11):113-120. |
| Zumilaiti Turgan, LIN Tao, YAN Changrong, et al. Effect of mulching Time on water Heat of Cotton Field and cotton consumption and Yield in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(11):113-120. | |
| [18] | Persaud N, Khosla R. Khosla. Partitioning soil-water losses in different plant populations of dry-land corn[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 1999, 42(2). |
| [19] | 张冬梅, 张伟, 陈琼, 等. 种植密度对旱地玉米植株性状及耗水特性的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2014, 22(4):102-108. |
| ZHANG Dongmei, ZHANG Wei, CHEN Qiong, et al. Effects of planting density on plant characters and Water consumption characteristics of dryland maize[J]. Maize Science. 2014, 22(4):102-108. | |
| [20] | 陈佰鸿, 曹建东, 王利军, 等. 不同滴灌条件下土壤水分分布与运移规律[J]. 节水灌溉, 2010,(7):6-9,13. |
| CHEN Baihong, CAO Jiandong, MAO Lijun, et al. Distribution and migration of soil water under different drip irrigation conditions[J]. Water-saving Irrigation, 2010,(7):6-9,13. | |
| [21] | 张前兵, 于磊, 艾尼娃尔·艾合买提, 等. 新疆绿洲区不同灌溉方式及灌溉量下苜蓿田间土壤水分运移特征[J]. 中国草地学报, 2015, 37(2):68-74. |
| ZHANG Qianbing, YU Lei, Aevar Aihemaiti, et al. Characteristics of soil water transport in Alfalfa field under different irrigation Methods and irrigation amount in Xinjiang Oasis[J]. Chinese journal of grassland science. 2015, 37(2):68-74. | |
| [22] | Nasrin Azad, Javad B, Vahid R, et al. Developing an optimization model in drip fertigation management to consider environmental issues and supply plant requirements[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2018,208. |
| [23] | 杨林川. 半干旱区垄沟结构和密度对土壤水热及春玉米产量的调控[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. 2019. |
| YANG Linchuan. Regulation of ridge structure and density on soil hydrothermal and spring maize yield in semi-arid region[D]. Yanglin: Northwest A&F University. 2019. | |
| [24] | Hagai Y, Uri Y, Alon B. Consequences of irrigation and fertigation of vegetable crops with variable quality water: Israel as a case study[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2020,242. |
| [25] | GB/T 50485-2009.微灌工程技术规范[S]. |
| GB/T 50485-2009.Technical Specifications for Micro-irrigation Engineering[S]. | |
| [26] |
ZHANG D, Luo Z,LiuS. Effects of deficit irrigation and plant density on the growth, yield and fiber quality of irrigated cotton[J]. Field Crops Res. 2016, 197,1-9.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Ali M H, Talukder M S U. Increasing water productivity in crop production—A synthesis[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2008, 95(11):0-1213. |
| [28] | 王亮. 残膜量和灌溉量对棉田水氮利用特征的影响及其生理机制研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2017. |
| WANG Liang. Effects of residual film amount and irrigation amount on water and nitrogen utilization characteristics of cotton fields and its physiological mechanism[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [29] | WEN H Z, LLEI Z L, QIU S, et al. Effects of Water Stress on Photosynthesis, Yield, and Water Use Efficiency in Winter Wheat[J]. Water, 2020, 12(8). |
| [30] | 李燕山, 白建明, 许世坤, 等. 不同灌水量对膜下滴灌冬马铃薯生长及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2015, 33(6):8-13. |
| LI Yanshan, BAI Jianming, XU Shikun, et al. Effects of different irrigation amounts on potato growth and water use efficiency under drip irrigation in winter[J]. Agricultural research in arid areas, 2015, 33(6)8-13. | |
| [31] |
Barbieri P, Echarte L, Maggiora A, et al. Maize evapotrans piration and water-use efficiency in response to row spacing[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2012, 104(4):939.
DOI URL |
| [32] | REN X M, Sun D B, Wang Q S. Modeling the effects of plant density on maize productivity and water balance in the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2016,(171):40-48. |
| [33] | 牛玉萍. 有限滴灌下种植密度对棉花产量形成及水分利用效率的影响[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2016. |
| NIU Yuping. Effect of planting density under limited drip irrigation on cotton yield formation and water use efficiency[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2016. | |
| [34] | Seyed H A, Zahra J. Assessing the physical and empirical reference evapotranspiration (ETO) models and time series analyses of the influencing weather variables on ET0 in a semi-arid area[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020,276. |
| [35] | 陈志君, 孙仕军, 张旭东, 等. 东北雨养区覆膜和种植密度对玉米田间土壤水分和根系生长的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(1):224-229,235. |
| CHEN Zhijun, SUN Shijun, ZHANG Xudong, et al. Effects of film mulching and planting density on soil moisture and root growth of Maize in rain-fed areas of Northeast China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation. 2017, 31(1):224-229,235. |
| [1] | ZHANG Chengjie, HU Haoran, DUAN Songjiang, WU Yifan, ZHANG Jusong. Effects of nitrogen-dense interaction on growth, development, yield and quality of Gossypium barbadense L. [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 1821-1830. |
| [2] | ZHAO Ying-shan;GOU Ling;XUE Jun;SHI Zhi-guo;YAO Min-na;ZHANG Wang-feng. Changes of Radiation Use Efficiency of Spring Maize under Different Plant Densities in Xinjiang [J]. , 2015, 52(12): 2166-2172. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 91
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 233
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||